Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
14 May 2025
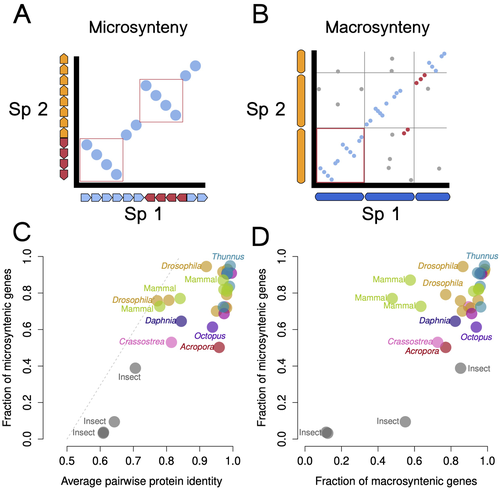
Genomic changes are varied across congeneric species pairs of animalsWarren R. Francis, Sergio Vargas, Gert Wörheide https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.05.611358Exploring the correlation between speciation and genome rearrangementsRecommended by Javier del Campo based on reviews by Jean-Baptiste Ledoux and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Jean-Baptiste Ledoux and 3 anonymous reviewers
Francis et al. (2025) investigate the relationship between genomic rearrangement, specifically macro- and micro-synteny, and speciation across a broad range of animal phyla. Using chromosome-level genome assemblies, they generated 1:1 ortholog pairs and analyzed synteny conservation using custom bioinformatics pipelines to quantify microsynteny. The study is well written, methodologically sound, and offers valuable insights beyond comparative genomics. The authors show that while most congeneric species pairs exhibit disruptions in micro-synteny, they retain high levels of protein sequence identity. They also find that macro- and micro-synteny decay with speciation but are often decoupled, indicating no universal genomic trajectory during divergence. Their conclusion, that synteny patterns alone are insufficient to define species boundaries (Steenwyk and King 2024), is well supported by their data. The discussion effectively situates the work within the broader context of speciation research. It thoughtfully addresses study limitations, such as challenges in synteny block quantification, chromosomal rearrangement rates, and the scarcity of high-quality genome assemblies. The manuscript also outlines clear directions for future research, including the need for more accurate divergence time estimates and expanded taxonomic sampling (Formenti et al. 2022). Formenti G, Theissinger K, Fernandes C, Bista I, Bombarely A, Bleidorn C, et al. (2022) The era of reference genomes in conservation genomics. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 37, 197–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2021.11.008 Francis WR, Vargas S, Wörheide G (2025) Genomic changes are varied across congeneric species pairs of animals. bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.05.611358 Steenwyk JL, King N (2024) The promise and pitfalls of synteny in phylogenomics. PLOS Biology, 22, e3002632. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002632
| Genomic changes are varied across congeneric species pairs of animals | Warren R. Francis, Sergio Vargas, Gert Wörheide | <p>Synteny, the shared arrangement of genes on chromosomes between related species, is a marker of shared ancestry, and synteny-breaking events can result in genomic incompatibilities between populations and ultimately lead to speciation events. D... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Javier del Campo | Anonymous, Nicolas Shogo Locatelli, Jean-Baptiste Ledoux, Anonymous | 2024-09-06 17:57:07 | View |
06 May 2025

Comparison of whole-genome assemblies of European river lamprey (Lampetra fluviatilis) and brook lamprey (Lampetra planeri)Ole K. Tørresen, Benedicte Garmann-Aarhus, Siv Nam Khang Hoff, Sissel Jentoft, Mikael Svensson, Eivind Schartum, Ave Tooming-Klunderud, Morten Skage, Anders Krabberød, Leif Asbjørn Vøllestad, Kjetill S. Jakobsen https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.06.627158Phased genomes suggest that L. fluviatilis and L. planeri are two ecotypes of the same speciesRecommended by Samuel Abalde based on reviews by Ricardo C. Rodríguez de la Vega, Quentin Rougemont and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Ricardo C. Rodríguez de la Vega, Quentin Rougemont and 1 anonymous reviewer
Lampreys are the focus of intense research. Together with hagfishes, they form the Cyclostomata, the sister group of jawed vertebrates, and hence they are a key group for disentangling the early evolution of many vertebrate features (Shimel and Donoghue 2012; McCauley et al. 2015). Ecologically, lamprey species show a diverse array of life modes, including parasitic and non-feeding species, and inhabit freshwater and marine habitats or both (i.e. anadromous species; Docker and Potter 2019). One of these anadromous species, the sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus), took advantage of man-made canals to invade the North American Great Lakes in the early 20th century, decimating many fish populations. Today, the control of these invasive populations is paramount for the survival of the region’s fishing industry (Ferreira-Martins et al. 2021). All these research avenues will benefit from the generation of new genomic data, an invaluable resource in evolutionary and conservation biology. In this manuscript, Tørresen et al. (2025) present phased, chromosome-level assemblies from two lamprey species: the European river lamprey (Lampetra fluviatilis) and the brook lamprey (Lampetra planeri). These two genome assemblies are of high quality and will undoubtedly become a key resource in lamprey research. In particular, the authors showcase the potential of such genomes from two perspectives. First, comparing their assemblies to the already published genomes from P. marinus and another specimen of L. fluviatilis, they propose that lamprey genomes are highly conserved and display large syntenic blocks shared among species. Second, phylogenetic analyses and the annotation of SNPs suggest that L. fluviatilis and L. planeri should be considered two ecotypes of the same species complex, instead of two separate species. This might not be new for anyone knowledgeable in lamprey biology (Rougemont et al. 2017), but it is surprising given the distinct ecology of the two lampreys: L. fluviatilis is a parasitic, anadromous species, whereas L. planeri is a non-feeding, freshwater species. In addition to the biological significance of this manuscript, I would like to acknowledge the robustness of the analytical approaches. These genomes were assembled and annotated following two pipelines recently developed at EBP-Nor, the Norwegian initiative of the Earth BioGenome Project (EBP). These pipelines are designed to be an easy-to-use, end-to-end solution for genomic analyses and are likely to become a standard for the EBP and European Reference Genome Atlas initiatives. There can be no better evidence of their effectiveness than these two phased, chromosome-level, highly complete genome assemblies.
References Docker MF, Potter IC (2019) Life history evolution in lampreys: Alternative migratory and feeding types. In: Docker M (ed) Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control. Fish & Fisheries Series, vol 38. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1684-8_4 Ferreira-Martins D, Champer J, McCauley DW, Zhang Z, Docker MF (2021) Genetic control of invasive sea lamprey in the Great Lakes. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 47, S764-S775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2021.10.018 McCauley DW, Docker MF, Whyard S, Li W (2015) Lampreys as diverse model organisms in the genomics era. BioScience, 65(11), 1046-1056. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biv139 Rougemont Q, Gagnaire PA, Perrier C, Genthon C, Besnard AL, Launey S, Evanno G (2017) Inferring the demographic history underlying parallel genomic divergence among pairs of parasitic and nonparasitic lamprey ecotypes. Molecular Ecology, 26(1), 142-162. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.13664 Shimeld SM, Donoghue PC (2012) Evolutionary crossroads in developmental biology: cyclostomes (lamprey and hagfish). Development, 139(12), 2091-2099. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.074716 Tørresen OK, Garmann-Aarhus B, Hoff SNK, Jentoft S, Svensson M, Schartum E, Tooming-Klunderud A, Skage M, Krabberød A, Vøllestad LA, Jakobsen KS (2025) Comparison of whole-genome assemblies of European river lamprey (Lampetra fluviatilis) and brook lamprey (Lampetra planeri). bioRxiv, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.06.627158 | Comparison of whole-genome assemblies of European river lamprey (*Lampetra fluviatilis*) and brook lamprey (*Lampetra planeri*) | Ole K. Tørresen, Benedicte Garmann-Aarhus, Siv Nam Khang Hoff, Sissel Jentoft, Mikael Svensson, Eivind Schartum, Ave Tooming-Klunderud, Morten Skage, Anders Krabberød, Leif Asbjørn Vøllestad, Kjetill S. Jakobsen | <p>We present haplotype-resolved whole-genome assemblies from one individual European river lamprey (Lampetra fluviatilis) and one individual brook lamprey (Lampetra planeri), usually regarded as sister species. The genome assembly of L. fluviatil... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Vertebrates | Samuel Abalde | 2024-12-14 14:35:51 | View | |
30 Apr 2025
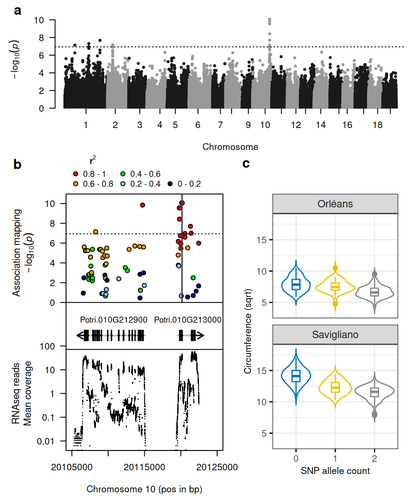
Natural variation in chalcone isomerase defines a major locus controlling radial stem growth variation among Populus nigra populationsHarold Durufle, Annabelle Dejardin, Veronique Jorge, Marie Pegard, Gilles Pilate, Odile Rogier, Leopoldo Sanchez, Vincent Segura https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.21.618920Advancing our understanding of poplar growth using a multi-omics approachRecommended by Wirulda Pootakham based on reviews by Gancho Slavov and 1 anonymous reviewerPoplar is a promising resource, valued not only for wood production and the development of lignocellulosic biomass, but also for its potential role in carbon sequestration. Recognizing the importance of stem growth for wood production and biomass development, Duruflé et al. (2025) present a comprehensive study on the genetic basis of radial stem growth variation in natural populations of black poplar (Populus nigra). They employed a systems biology approach to identify the quantitative trait loci (QTLs) underlying this trait, integrating genomic, transcriptomic, and phenotypic data from a large collection of poplar genotypes. Their genome-wide association study (GWAS) analysis identified single nucleotide polymorphisms linked to two gene models predicted to encode chalcone isomerase, an enzyme involved in the flavonoid pathway. The authors then used the RNA-seq data to test whether the expression of the candidate genes correlated with the phenotypes, and indeed the level of expression of both genes displayed a correlation to the stem circumference. To support their findings, the authors compared the location of the QTLs detected in this study with previously published QTLs. Interestingly, they found a previously reported QTL co-localizing with the newly identified one. The authors have addressed the concerns raised by reviewers on the GWAS analysis and discussed the complication of this QTL study in the manuscript. In essence, the authors have combined the power of GWAS and transcriptomics to locate candidate genes and applied population genetics to explore the evolutionary context of the identified gene. This comprehensive approach provides strong evidence for the role of chalcone isomerase in controlling radial stem growth variation in black poplar. The study opens up avenues for further research into the precise mechanisms by which chalcone isomerase and flavonoid metabolism influence stem growth and provides useful information for future poplar breeding programs.
References Duruflé H, Déjardin A, Jorge V, Pégard M, Pilate G, Rogier O, Sanchez L, Segura V (2025) Natural variation in chalcone isomerase defines a major locus controlling radial stem growth variation among Populus nigra populations. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.21.618920 | Natural variation in chalcone isomerase defines a major locus controlling radial stem growth variation among *Populus nigra* populations | Harold Durufle, Annabelle Dejardin, Veronique Jorge, Marie Pegard, Gilles Pilate, Odile Rogier, Leopoldo Sanchez, Vincent Segura | <p>Poplar is a promising resource for wood production and the development of lignocellulosic biomass, but currently available varieties have not been optimized for these purposes. Therefore, it is critical to investigate the genetic variability an... |  | Plants, Population genomics | Wirulda Pootakham | Fernando Guerra , Gancho Slavov | 2024-10-25 09:37:10 | View |
13 Mar 2025
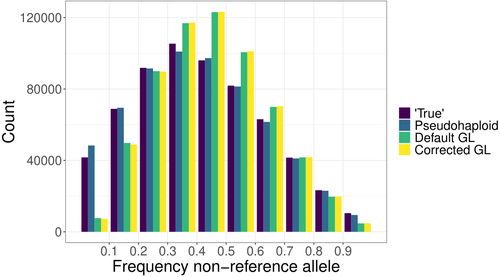
Estimating allele frequencies, ancestry proportions and genotype likelihoods in the presence of mapping biasTorsten Günther, Amy Goldberg, Joshua G. Schraiber https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.01.601500A novel genotype likelihood-based method to reduce mapping bias in low-coverage and ancient DNA studiesRecommended by Sebastian Ernesto Ramos-Onsins based on reviews by Maxime Lefebvre, Michael Westbury and Adrien Oliva based on reviews by Maxime Lefebvre, Michael Westbury and Adrien Oliva
The study of genomic variability within and between populations, as well as among species, relies on comparative analyses of homologous positions—sites that share a common evolutionary origin. Homology is inferred through sequence similarity (Reeck et al. 1987). However, the ability to detect homologous regions can be compromised when sequence mismatches accumulate due to mutations, especially when analyzing short DNA fragments, as in short-read sequencing (Li et al. 2008). In the genomic era, accurately mapping homologous DNA fragments to a reference genome is essential for obtaining precise estimates of genetic variability and evolutionary inferences (e.g., Li et al. 2008; Ellegren 2014). However, short-read, high-throughput sequencing often introduces mapping bias, disproportionately favoring the reference allele. This bias distorts allele frequency estimates, ancestry proportions, and genotype likelihoods, impacting downstream analyses (e.g., Günther & Nettelblad 2019; Martiniano et al. 2020). Mapping bias is particularly problematic in ancient DNA studies, where post-mortem damage exacerbates sequencing errors. DNA fragmentation limits read length, while deamination, causing G to A and C to U transitions, increases mismatches and further complicates homology identification (Dabney & Pääbo 2013). These degradation processes contribute to the misidentification of true variants, confounding evolutionary inferences. Various strategies have been developed to mitigate mapping bias, including the commonly used approach, called pseudo-haploid data, that randomly picks a single read at each analyzed position for each individual, thereby retaining a single allele at each polymorphic site (Günther & Nettelblad 2019; Barlow et al. 2020). Günther et al. (2025) introduce a novel method to correct mapping bias using a genotype likelihood-based approach, incorporating a mapping bias ratio to adjust for reference allele overrepresentation. The method specifically targets known single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) because in population genomic analysis of ancient DNA data, low coverage and post-mortem damage often hinder the ability to identify novel SNPs in most individuals. The analysis focuses on DNA fragmentation, assuming that deamination effects are minimal when considering ascertained SNPs. The proposed method was compared against existing approaches, including pseudo-haploid data and standard genotype likelihood-based probabilistic methods. The evaluation was performed using both empirical and simulated data. For empirical data, low-coverage sequencing data from the 1000 Genomes Project (Finnish in Finland, Japanese in Tokyo, Yoruba in Ibadan, Nigeria populations) was analyzed, while for simulated data, ancient DNA-like datasets were generated using ms-prime (Kelleher et al. 2016), modeling different sequencing depths, divergence times, and reference genome choices. The study assesses the impact of mapping bias on the ratio of reference versus non-reference allele mapping, the accuracy of SNP allele frequency estimates relative to true frequencies, the deviation and variance between estimated and true allele frequencies, population differentiation and the estimation of admixture proportions using supervised and unsupervised methods, considering both genotype likelihoods and genotype calls. Günther et al. (2025) bring to light that all methods analyzed exhibit minor but systematic reference allele bias. The new corrected genotype likelihood method outperforms the standard genotype likelihood approach in correlating with true allele frequencies, although the pseudo-haploid method still provides the most accurate estimates. Mapping bias also affects ancestry estimation, leading to admixture proportion errors of up to 4%, though this effect is smaller than the 10% discrepancy observed across different inference methods. The work performed by Günther et al. (2025) provides a rigorous and innovative evaluation of mapping bias in the context of ascertained SNPs, introducing a probabilistic approach that improves bias correction. Unlike non-probabilistic methods such as pseudo-haploid data, the genotype likelihood framework leverages all sequencing reads for each analyzed SNP, and can incorporate additional bias corrections, enhancing its applicability across different sequencing conditions. While probabilistic approaches offer clear advantages in bias correction, they can be less intuitive to interpret compared to traditional genotype calling methods. This study highlights that mapping bias is pervasive across all methods, influencing evolutionary inferences such as selection signals and population differentiation. Although the improvements in allele frequency recovery may seem modest, the genome-wide impact of mapping bias is significant, especially in ancient DNA studies, making bias correction essential for robust evolutionary analyses.
References Ellegren H. (2014) Genome sequencing and population genomics in non-model organisms. Trends Ecol Evol. 29(1):51-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2013.09.008 Günther T, Nettelblad C. (2019) The presence and impact of reference bias on population genomic studies of prehistoric human populations. PLoS Genet.15(7):e1008302. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008302 Günther T., Goldberg A., Schraiber J. G. (2025) Estimating allele frequencies, ancestry proportions and genotype likelihoods in the presence of mapping bias. bioRxiv, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.01.601500 Kelleher J., Etheridge A. M., McVean G. (2016) Efficient coalescent simulation and genealogical analysis for large sample sizes. PLoS computational biology, 12(5):e1004842. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004842 Li H, Ruan J, Durbin R. (2008) Mapping short DNA sequencing reads and calling variants using mapping quality scores. Genome Res. 18(11):1851-8. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.078212.108 Reeck GR, de Haën C, Teller DC, Doolittle RF, Fitch WM, Dickerson RE, et al. (1987) "Homology" in proteins and nucleic acids: a terminology muddle and a way out of it. Cell. 50 (5): 667. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(87)90322-9 | Estimating allele frequencies, ancestry proportions and genotype likelihoods in the presence of mapping bias | Torsten Günther, Amy Goldberg, Joshua G. Schraiber | <p>Population genomic analyses rely on an accurate and unbiased characterization of the genetic composition of the studied population. For short-read, high-throughput sequencing data, mapping sequencing reads to a linear reference genome can bias ... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Population genomics | Sebastian Ernesto Ramos-Onsins | 2024-07-02 10:46:19 | View | |
10 Mar 2025

hdmax2, an R package to perform high dimension mediation analysisFlorence Pittion, Basile Jumentier, Aurélie Nakamura, Johanna Lepeule, Olivier François, Magali Richard https://hal.science/hal-04658960High-dimensional mediation analysis: Unraveling pathways linking external exposures to health outcomesRecommended by Guillaume Laval based on reviews by Pierre Neuvial and Gaspard KernerPittion et al. (2025) introduce an R package called hdmax2, which implements an enhanced version of the “High-Dimensional Mediation Analysis using the Max-Squared” (HDMAX2) method originally proposed by Jumentier et al. (2023) for high-dimensional mediation analysis. The goal of mediation analysis is to quantify the indirect effect of a variable M in the causal relationship between exposure X and outcome Y. The fundamental concept behind HDMAX2 methods is to use a latent factor mixed model to estimate the effects of unobserved confounders and a max-squared test to identify significant mediators. The HDMAX2 method represents a significant advancement in the case of high-dimensional mediation, such as DNA methylation or gene expression analysis, where the number of mediators often far exceeds the sample size. The main contributions of this article are the implementation of the HDMAX2 method as an R package, and an extension of the original method to binary outcomes and to binary, categorical, and multivariate exposures, as opposed to only continuous variables. The package includes visualization tools, helper functions for mediator selection, and options for handling multivariate exposures. A key strength of the package lies in its versatility. The new package, hdmax2, accommodates a variety of data types. This flexibility makes it a valuable tool for researchers analyzing high-throughput molecular data. Finally to illustrate this flexibility, the authors present two case studies that were not described in the Jumentier et al. (2023) analysis. In the first case study, the authors employed mediation analysis to assess the potential causal role of DNA methylation in the pathway linking the HER2 status of breast cancer (a marker for an aggressive breast cancer subtype) to a survival risk score, which was derived from a six-gene expression signature and is inversely correlated with patient survival. In the second case study, the authors conducted mediation analysis to explore the role of gene expression in the pathway linking patient gender to the occurrence of multiple sclerosis specific subtypes: clinically isolated syndrome and relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. These illustrate the relevance of hdmax2 to study the transcriptome and the methylome. In conclusion, the hdmax2 R package will be invaluable for handling high-dimensional molecular data in the study of the intricate pathways through which exposures influence health outcomes.
References Jumentier B, Barrot C-C, Estavoyer M, Tost J, Heude B, François O, Lepeule J (2023) High-dimensional mediation analysis: A new method applied to maternal smoking, placental DNA methylation, and birth outcomes. Environmental Health Perspectives, 131, 047011. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP11559 Pittion F, Jumentier B, Nakamura A, Lepeule J, Francois O, Richard M (2025) hdmax2, an R package to perform high dimension mediation analysis. HAL, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://hal.science/hal-04658960 | hdmax2, an R package to perform high dimension mediation analysis | Florence Pittion, Basile Jumentier, Aurélie Nakamura, Johanna Lepeule, Olivier François, Magali Richard | <p>Mediation analysis plays a crucial role in epidemiology, unraveling the intricate pathways through which exposures exert influence on health outcomes. Recent advances in high-throughput sequencing techniques have generated growing interest in a... |  | Bioinformatics | Guillaume Laval | 2024-09-10 11:49:02 | View | |
26 Feb 2025
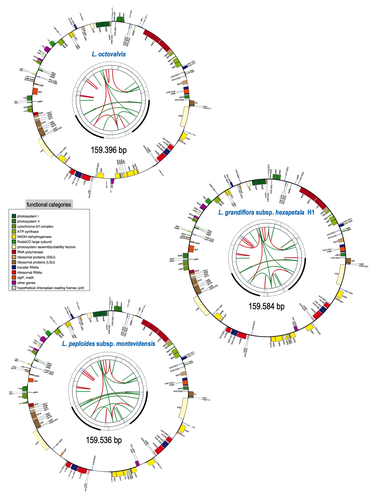
Sequencing, de novo assembly of Ludwigia plastomes, and comparative analysis within the Onagraceae familyF Barloy-Hubler, A-L Le Gac, C Boury, E Guichoux, D Barloy https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.10.20.563230Onagre, monster, invasion and geneticsRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The first time I heard of ”onagres” in French was when I was a teenager, through the books of Pierre Bordage as fantastic monsters, or through historical games as Roman siege weapons (onagers). At this time, I was far from imagining that “onagre” also refers to a very large flowering plant family, as it is the French term for evening primroses. In this family, the genus Ludwigia comprises species that are invasive (resembling in that way the ancient armies using onagers to invade cities) in aquatic environments, degrading ecosystems already fragilized by human activities. To counteract this phenomenon, it is of high importance to understand their propagation of these species. However, the knowledge about their genetics and diversity is very scarce, and thus tracking their dispersal using genetic information is complicated, and in fact almost impossible. Barloy-Hubler et al. (2024) proposed in the present manuscript a new set of chloroplastic genomes from two of these species, Ludwigia grandiflora subsp. hexapetala and Ludwigia peploides subsp. montevidensis, and compared them to the published chloroplastic genome of Ludwigia octovalis. They explored the possibility of assembling these genomes relying solely on short reads and showed that long reads were necessary to obtain an almost complete assembly for these plastid genomes. In addition, through this approach, they detected two haplotypes in Ludwigia grandiflora subsp. hexapetala as compared to one in a short-read assembly. This highlights the need for long reads data to assess the structure and diversity of chloroplastic genomes. The authors were also able to clarify the phylogeny of the genus Ludwigia. Finally, they identified multiple potential single nucleotide polymorphisms and simple sequence repeats for future evaluation of diversity and dispersal of those invasive species. This analysis, while appearing more technical than biological at first glance, is in fact of high importance for the understanding of ecology and preservation of fragile ecosystems, such as the European watersheds. Indeed, new scientific results and insights are generally linked to a reevaluation of previously analyzed data or samples through new technologies, and this paper is a quite clever example of that matter.
References Barloy-Hubler F, Gac A-LL, Boury C, Guichoux E, Barloy D (2024) Sequencing, de novo assembly of Ludwigia plastomes, and comparative analysis within the Onagraceae family. bioRxiv, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.10.20.563230 Bordage, P (1993) Les Guerriers du Silence, L'Atalante, ISBN 9782905158697
| Sequencing, de novo assembly of *Ludwigia* plastomes, and comparative analysis within the Onagraceae family | F Barloy-Hubler, A-L Le Gac, C Boury, E Guichoux, D Barloy | <p>The Onagraceae family, which belongs to the order Myrtales, consists of approximately 657 species and 17 genera. This family includes the genus <em>Ludwigia </em>L., which is comprised of 82 species. In this study, we focused on the two aquatic... |  | Bioinformatics, Plants | Francois Sabot | 2023-12-12 18:05:20 | View | |
22 Jan 2025
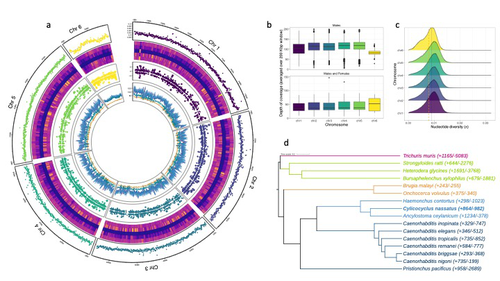
Spatio-temporal diversity and genetic architecture of pyrantel resistance in Cylicocyclus nassatus, the most abundant horse parasiteGuillaume Sallé, Élise Courtot, Cédric Cabau, Hugues Parrinello, Delphine Serreau, Fabrice Reigner, Amandine Gesbert, Lauriane Jacquinot, Océane Lenhof, Annabelle Aimé, Valérie Picandet, Tetiana Kuzmina, Oleksandr Holovachov, Jennifer Bellaw, Martin K. Nielsen, Georg von Samson-Himmelstjerna, Sophie Valière, Marie Gislard, Jérôme Lluch, Claire Kuchly, Christophe Klopp https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.19.549683Genomic and transcriptomic insights into the genetic basis of anthelmintic resistance in a cyathostomin parasitic nematodeRecommended by Nicolas Pollet based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersParasitic worms infect billions of animals worldwide. While parasitism is now considered a context-dependent relation along a symbiosis continuum, most of these parasitic worms, also known as helminths, can cause diseases that have a significant impact (Hopkins et al. 2017; Selzer, Epe 2021). When considering livestock animals, these impacts have a high economic cost, and therefore, prophylactic drugs are widely used (Selzer and Epe 2021). Consequently, drug resistance has become increasingly common across all parasites and concerns about drug effects on non-target organisms have been raised (de Souza and Guimarães 2022). This is why understanding the relationship between parasitic worms and their animal hosts and the diseases they cause at the genetic and molecular level is high on the agenda of parasitologists (Doyle 2022). The development of genomics resources plays a pivotal role in this agenda and is at the origin of Sallé and colleagues' article (2025). The most common intestinal parasites in equids are helminths of the cyathostomin nematode complex. These are the primary parasitic cause of death in young horses and also exhibit a reduced sensitivity to anthelmintic drugs. Therefore, Sallé and colleagues embarked on the arduous journey to build a reference annotated genome of the Cylicocylus nassatus nematode. They used cutting-edge molecular genetics methods to amplify and sequence the genome of a single individual and obtained chromosomal-level contiguity using Hi-C technology for six chromosomes and an assembly of 514.7 Mbp. Remarkably, transposable elements occupy more than half of the C. nassatus genome and may have led to an increase in genome size in this nematode. In parallel, the authors built a gene catalogue using transcriptomic data, reaching a BUSCO gene completion score of 94.1% with 22,718 protein-coding genes. They quantified allele frequencies based on the resequencing of nine populations, including an ancient Egyptian worm from the 19th century, indicating a recent loss of genetic diversity in European cyathostomin even if geographical sampling was limited. They also analysed transcriptomic differences between sexes and found differences linked with drug treatment. While there may be confounding effects due to global differences between sex that could explain this finding, these results will likely fuel future transcriptomic analyses investigating the response to antiparasitic drugs. The Cylicocylus nassatus genome assembly obtained will be invaluable for studying nematode genome evolution and analysing the genetic and molecular basis of drug resistance in these parasites.
References Doyle SR (2022) Improving helminth genome resources in the post-genomic era. Trends in Parasitology, 38, 831–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2022.06.002 Hopkins SR, Wojdak JM, Belden LK (2017) Defensive symbionts mediate host–parasite interactions at multiple scales. Trends in Parasitology, 33, 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2016.10.003 Sallé G, Courtot É, Cabau C, Parrinello H, Serreau D, Reigner F, Gesbert A, Jacquinot L, Lenhof O, Aimé A, Picandet V, Kuzmina T, Holovachov O, Bellaw J, Nielsen MK, Samson-Himmelstjerna G von, Valière S, Gislard M, Lluch J, Kuchly C, Klopp C (2024) Spatio-temporal diversity and genetic architecture of pyrantel resistance in Cylicocyclus nassatus, the most abundant horse parasite. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.19.549683 Selzer PM, Epe C (2021) Antiparasitics in animal health: quo vadis? Trends in Parasitology, 37, 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2020.09.004 de Souza RB, Guimarães JR (2022) Effects of avermectins on the environment based on its toxicity to plants and soil invertebrates–a review. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 233, 259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05744-0
| Spatio-temporal diversity and genetic architecture of pyrantel resistance in *Cylicocyclus nassatus*, the most abundant horse parasite | Guillaume Sallé, Élise Courtot, Cédric Cabau, Hugues Parrinello, Delphine Serreau, Fabrice Reigner, Amandine Gesbert, Lauriane Jacquinot, Océane Lenhof, Annabelle Aimé, Valérie Picandet, Tetiana Kuzmina, Oleksandr Holovachov, Jennifer Bellaw, Mart... | <p>Cyathostomins are a complex of 50 intestinal parasite species infecting horses and wild equids. The massive administration of modern anthelmintic drugs has increased their relative abundance in horse helminth communities and selected drug-resis... |  | Terrestrial invertebrates | Nicolas Pollet | Jane Hodgkinson, Anonymous | 2023-07-27 20:45:09 | View |
14 Jan 2025

Chromosome-level reference genome assembly for the mountain hare (Lepus timidus)Zsofia Fekete, Dominic E. Absolon, Craig Michell, Jonathan M. D. Wood, Steffi Goffart, Jaakko L. O. Pohjoismaki https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.10.598177The genomic foundations of adaptation: evaluating the mountain hareRecommended by Jitendra Narayan based on reviews by Theodore Squires and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Theodore Squires and 1 anonymous reviewer
Fekete et al. (2024) generated a chromosome-level reference genome assembly for the mountain hare (Lepus timidus). This represents a significant advancement in genomic research for non-model organisms, achieving high quality through advanced sequencing and curation techniques. This achievement serves as a foundational blueprint for future efforts in other species, particularly those with ecological or evolutionary importance. The assembly has high continuity and completeness, with an N50 scaffold length of 125.8 Mb and a contig N50 of 4.9 Mb, meeting the Earth BioGenome Project's stringent criteria for reference-grade genomes (Mc Cartney et al., 2024). The combination of PacBio HiFi sequencing and Hi-C scaffolding techniques enabled robust assembly and chromosomal scaffolding of all 23 autosomes and the X and Y sex chromosomes. Additionally, manual curation enhanced the assembly quality, accurately representing genomic sequences. Although the genome provides valuable structural insights, the limited functional annotations highlight a need for further investigation into the genetic underpinnings of the ecological and adaptive traits of the mountain hare. The ecological and evolutionary implications of resolving this genome are considerable, particularly given the mountain hare’s adaptations to cold, snowy environments and its role in boreal ecosystems. The assembly facilitates the study of adaptations, such as camouflage and snowshoe-like feet, which are critical for survival in its rapidly changing habitat. Comparative genomic analyses reveal the evolutionary relationship between Lepus timidus and closely related species, such as the brown hare (L. europaeus) and Irish hare (L. t. hibernicus), providing insights into gene flow, hybridization, and speciation. These findings have practical implications for conservation genetics, particularly for subspecies threatened by habitat loss and climate change. However, the study does not identify specific adaptive loci or functional variants, limiting its immediate applicability to understanding the molecular basis of traits crucial for survival in extreme environments. Expanding the functional annotation of this genome would significantly enhance its utility in conservation and ecological genomics. Moreover, the high repetitive element content (42.35%) underscores the need for detailed annotation to facilitate downstream studies. These issues suggest that additional refinement and validation are warranted. Despite these limitations, the assembly is invaluable for studying genetic adaptations, hybridization, and hare conservation. Future research should focus on functional annotation, population-level comparisons, and targeted studies of ecological traits to fully realize the potential of this high-quality reference genome.
References Fekete Z, Absolon DE, Michell C, Wood JMD, Goffart S, Pohjoismäki JLO (2024) Chromosome-level reference genome assembly for the mountain hare (Lepus timidus). bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.10.598177 Mc Cartney AM, Formenti G, Mouton A, De Panis D, Marins LS, Leitão HG, Diedericks G, Kirangwa J, Morselli M, Salces-Ortiz J, Escudero N, Iannucci A, Natali C, Svardal H, Fernández R, De Pooter T, Joris G, Strazisar M, Wood JMD, Herron KE, …, Mazzoni CJ (2024) The European Reference Genome Atlas: piloting a decentralised approach to equitable biodiversity genomics. npj Biodiversity, 3, 28. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44185-024-00054-6
| Chromosome-level reference genome assembly for the mountain hare (*Lepus timidus*) | Zsofia Fekete, Dominic E. Absolon, Craig Michell, Jonathan M. D. Wood, Steffi Goffart, Jaakko L. O. Pohjoismaki | <p> We present here a high-quality genome assembly of a male mountain hare (<em>Lepus timidus</em> Linnaeus), from Ilomantsi, Eastern Finland, utilizing an isolated fibroblast cell line as the source for high quality DNA and RNA. Following th... |  | Bioinformatics, ERGA Pilot, Evolutionary genomics, Vertebrates | Jitendra Narayan | 2024-06-11 08:52:32 | View | |
28 Nov 2024
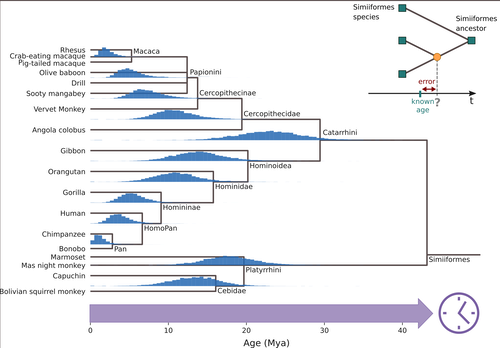
Factors influencing the accuracy and precision in dating single gene treesGuillaume Louvel and Hugues Roest Crollius https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.24.264671Dating single gene trees in the age of phylogenomicsRecommended by Federico Hoffmann based on reviews by Sishuo Wang, David Duchêne and 1 anonymous reviewerDating evolutionary trees is a critical task that allows us to connect biological history to ecological and geological events, helping us explore connections between environmental change and genetic innovations. The central idea behind these techniques is to link changes at the sequence level to divergence times, under the general assumption that substitutions accumulate steadily over time. So, sequences that diverged earlier are expected to be more different than sequences that diverged more recently. For a number of biological and statistical reasons, the relationship between sequence divergence and time is not linear, so it is not always the case that more divergent sequences have accumulated more substitutions than less divergent ones. In the case of organismal-level divergences, a natural approach to mitigate these challenges is to incorporate as many genes as possible into the analyses. However, this route is not available when we are focusing our interest on a single gene or a gene family. Thus, exploring how different features of single gene trees impact the accuracy and precision of divergence time estimates is of interest. In this study, Louvel and Roest Crollius (2024), select a well-studied group of mammals, primates, extract single copy genes from their genomes, and explore how different factors such as alignment size, evolutionary rate variation and discordance between the gene and species trees impact divergence time estimates. There are many strengths of this study. The central ones are the number of factors considered and the transparent discussion of the limitations. In this regard, the study is an elegant combination of empirical and simulated data. Some of the results match intuitive expectations. For example, the authors find that longer alignments are more informative than shorter ones, that differences in evolutionary rate among branches lead to loss in precision, and that slow-evolving genes perform worse. Intriguingly, they also find differences in performance among genes with different ontologies. The empirical data used in this study is limited to a single group, and generally considers genes that have apparently remained as single copies. Accordingly, the conclusions that can be drawn are somewhat limited, calling for future studies building on and expanding the concepts of the study by Louvel and colleagues. For example, including genes that have been lost or duplicated would be of interest because changes in gene complement are a prevalent source of variation at the genome level in mammals in general (Demuth et al. 2006), and particularly in primates (Hahn et al. 2007).
References Demuth JP, De Bie T, Stajich JE, Cristianini N, Hahn MW (2006) The evolution of mammalian gene families. PLoS One, e85. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000085 Hahn MW, Demuth JP, Han SG (2007) Accelerated rate of gene gain and loss in primates. Genetics, 177,1941-1949. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.080077 Louvel, G and Roest Crollius, H (2024) Factors influencing the accuracy and precision in dating single gene trees. bioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.24.264671
| Factors influencing the accuracy and precision in dating single gene trees | Guillaume Louvel and Hugues Roest Crollius | <p>Molecular dating is the inference of divergence time from genetic sequences. Knowing the time of appearance of a taxon sets the evolutionary context by connecting it with past ecosystems and species. Knowing the divergence times of gene lineage... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Vertebrates | Federico Hoffmann | 2023-08-15 12:06:09 | View | |
13 Nov 2024
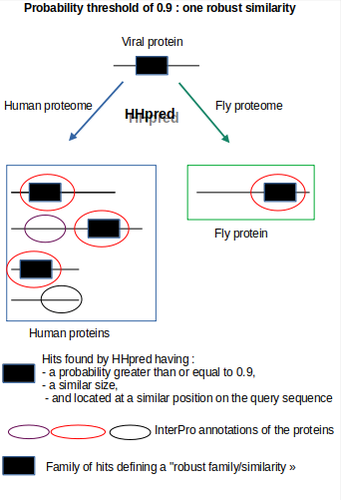
Re-annotation of SARS-CoV-2 proteins using an HHpred-based approach opens new opportunities for a better understanding of this virusPierre Brézellec https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.06.543855Leveraging HHpred with rigorous validation for improved detection of host-virus homologiesRecommended by Jitendra Narayan based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The assessment by Brézellec (2024) of the quality of HHpred-based SARS-CoV-2 protein annotations against the traditional Pfam annotations is highly justified and valuable. HHpred’s ability to detect remote homologies offers an expanded view of viral protein similarities, potentially uncovering subtle functional mimicries that Pfam may miss due to its sensitivity limitations when dealing with divergent sequences. However, the accuracy and specificity of HHpred results can be compromised by false positives, especially when dealing with complex viral proteins that feature transmembrane or low-complexity regions prone to spurious matches. To address this, the author made a thoughtful decision to implement a multi-step validation protocol. This approach included establishing progressively lower probability thresholds to capture weaker but biologically plausible hits, and organizing hits into “families” of similarly located alignments to validate the robustness of matches. They also cross-verified results by running SARS-CoV-2 protein queries against non-human proteomes (plants, fruit flies, bacteria, and archaea), allowing them to discern between biologically meaningful matches and potentially random alignments. By adding manual verification with InterPro domain annotations, the authors took additional steps to ensure that identified similarities were not only statistically significant but also biologically relevant. This rigorous validation strategy adds a layer of reliability to HHpred results, demonstrating an effective maximization of sensitivity while maintaining specificity. This approach yielded biologically intriguing and previously undocumented similarities, such as between the Spike-prominin and ORF3a-GPCR, underscoring the quality and depth of the annotation process. These findings highlight a pathway for further experimental validation and illustrate the potential of HHpred to contribute high-quality insights when applied with careful quality control measures. In summary, the decision to adopt HHpred (Gabler et al. 2020) and enhance its outputs with a robust quality validation process not only improved the depth of SARS-CoV-2 protein annotations but also established a high standard for future viral annotation projects, striking an effective balance between discovery potential and annotation quality. The authors have conducted a study that is methodologically rigorous, well-detailed, and highly pertinent to the field. This work stands as a significant contribution to the scientific community, providing resources and insights that are likely to guide future research in this area. Brézellec, P (2024) Re-annotation of SARS-CoV-2 proteins using an HHpred-based approach opens new opportunities for a better understanding of this virus. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.06.543855 Gabler F, Nam S-Z, Till S, Mirdita M, Steinegger M, Söding J, Lupas AN, Alva V (2020) Protein Sequence Analysis Using the MPI Bioinformatics Toolkit. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 72, e108. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.108
| Re-annotation of SARS-CoV-2 proteins using an HHpred-based approach opens new opportunities for a better understanding of this virus | Pierre Brézellec | <p>Since the publication of the genome of SARS-CoV-2 – the causative agent of COVID-19 – in January 2020, many bioinformatic tools have been applied to annotate its proteins. Although efficient methods have been used, such as the identification of... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Jitendra Narayan | 2023-06-08 10:17:04 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Gavin Douglas
Jean-François Flot
Danny Ionescu










