
NARAYAN Jitendra
- Big Data and Informatics, CSIR-IGIB, New Delhi, India
- Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Metagenomics, Structural genomics
- recommender
Recommendations: 4
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 4

Chromosome-level reference genome assembly for the mountain hare (Lepus timidus)
The genomic foundations of adaptation: evaluating the mountain hare
Recommended by Jitendra Narayan based on reviews by Theodore Squires and 1 anonymous reviewerFekete et al. (2024) generated a chromosome-level reference genome assembly for the mountain hare (Lepus timidus). This represents a significant advancement in genomic research for non-model organisms, achieving high quality through advanced sequencing and curation techniques. This achievement serves as a foundational blueprint for future efforts in other species, particularly those with ecological or evolutionary importance. The assembly has high continuity and completeness, with an N50 scaffold length of 125.8 Mb and a contig N50 of 4.9 Mb, meeting the Earth BioGenome Project's stringent criteria for reference-grade genomes (Mc Cartney et al., 2024). The combination of PacBio HiFi sequencing and Hi-C scaffolding techniques enabled robust assembly and chromosomal scaffolding of all 23 autosomes and the X and Y sex chromosomes. Additionally, manual curation enhanced the assembly quality, accurately representing genomic sequences. Although the genome provides valuable structural insights, the limited functional annotations highlight a need for further investigation into the genetic underpinnings of the ecological and adaptive traits of the mountain hare.
The ecological and evolutionary implications of resolving this genome are considerable, particularly given the mountain hare’s adaptations to cold, snowy environments and its role in boreal ecosystems. The assembly facilitates the study of adaptations, such as camouflage and snowshoe-like feet, which are critical for survival in its rapidly changing habitat. Comparative genomic analyses reveal the evolutionary relationship between Lepus timidus and closely related species, such as the brown hare (L. europaeus) and Irish hare (L. t. hibernicus), providing insights into gene flow, hybridization, and speciation. These findings have practical implications for conservation genetics, particularly for subspecies threatened by habitat loss and climate change. However, the study does not identify specific adaptive loci or functional variants, limiting its immediate applicability to understanding the molecular basis of traits crucial for survival in extreme environments. Expanding the functional annotation of this genome would significantly enhance its utility in conservation and ecological genomics. Moreover, the high repetitive element content (42.35%) underscores the need for detailed annotation to facilitate downstream studies. These issues suggest that additional refinement and validation are warranted. Despite these limitations, the assembly is invaluable for studying genetic adaptations, hybridization, and hare conservation. Future research should focus on functional annotation, population-level comparisons, and targeted studies of ecological traits to fully realize the potential of this high-quality reference genome.
References
Fekete Z, Absolon DE, Michell C, Wood JMD, Goffart S, Pohjoismäki JLO (2024) Chromosome-level reference genome assembly for the mountain hare (Lepus timidus). bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.10.598177
Mc Cartney AM, Formenti G, Mouton A, De Panis D, Marins LS, Leitão HG, Diedericks G, Kirangwa J, Morselli M, Salces-Ortiz J, Escudero N, Iannucci A, Natali C, Svardal H, Fernández R, De Pooter T, Joris G, Strazisar M, Wood JMD, Herron KE, …, Mazzoni CJ (2024) The European Reference Genome Atlas: piloting a decentralised approach to equitable biodiversity genomics. npj Biodiversity, 3, 28. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44185-024-00054-6
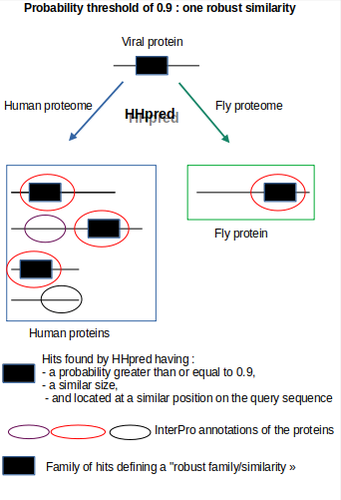
Re-annotation of SARS-CoV-2 proteins using an HHpred-based approach opens new opportunities for a better understanding of this virus
Leveraging HHpred with rigorous validation for improved detection of host-virus homologies
Recommended by Jitendra Narayan based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThe assessment by Brézellec (2024) of the quality of HHpred-based SARS-CoV-2 protein annotations against the traditional Pfam annotations is highly justified and valuable. HHpred’s ability to detect remote homologies offers an expanded view of viral protein similarities, potentially uncovering subtle functional mimicries that Pfam may miss due to its sensitivity limitations when dealing with divergent sequences. However, the accuracy and specificity of HHpred results can be compromised by false positives, especially when dealing with complex viral proteins that feature transmembrane or low-complexity regions prone to spurious matches.
To address this, the author made a thoughtful decision to implement a multi-step validation protocol. This approach included establishing progressively lower probability thresholds to capture weaker but biologically plausible hits, and organizing hits into “families” of similarly located alignments to validate the robustness of matches. They also cross-verified results by running SARS-CoV-2 protein queries against non-human proteomes (plants, fruit flies, bacteria, and archaea), allowing them to discern between biologically meaningful matches and potentially random alignments. By adding manual verification with InterPro domain annotations, the authors took additional steps to ensure that identified similarities were not only statistically significant but also biologically relevant.
This rigorous validation strategy adds a layer of reliability to HHpred results, demonstrating an effective maximization of sensitivity while maintaining specificity. This approach yielded biologically intriguing and previously undocumented similarities, such as between the Spike-prominin and ORF3a-GPCR, underscoring the quality and depth of the annotation process. These findings highlight a pathway for further experimental validation and illustrate the potential of HHpred to contribute high-quality insights when applied with careful quality control measures.
In summary, the decision to adopt HHpred (Gabler et al. 2020) and enhance its outputs with a robust quality validation process not only improved the depth of SARS-CoV-2 protein annotations but also established a high standard for future viral annotation projects, striking an effective balance between discovery potential and annotation quality. The authors have conducted a study that is methodologically rigorous, well-detailed, and highly pertinent to the field. This work stands as a significant contribution to the scientific community, providing resources and insights that are likely to guide future research in this area.
References
Brézellec, P (2024) Re-annotation of SARS-CoV-2 proteins using an HHpred-based approach opens new opportunities for a better understanding of this virus. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.06.543855
Gabler F, Nam S-Z, Till S, Mirdita M, Steinegger M, Söding J, Lupas AN, Alva V (2020) Protein Sequence Analysis Using the MPI Bioinformatics Toolkit. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 72, e108. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.108
A chromosome-level, haplotype-resolved genome assembly and annotation for the Eurasian minnow (Leuciscidae: Phoxinus phoxinus) provide evidence of haplotype diversity
Exploring evolutionary adaptations through Phoxinus phoxinus genomics
Recommended by Jitendra Narayan based on reviews by Alice Dennis and 2 anonymous reviewersOriowo et al. (2024) offer a thorough and meticulously conducted study that makes a substantial contribution to our understanding of the Eurasian minnow (Phoxinus phoxinus), particularly in terms of its genetic diversity, structural variations, and evolutionary adaptations. The authors have achieved an impressive feat by generating an annotated haplotype-phased, chromosome-level genome assembly (2n = 50). This was accomplished through the integration of high-fidelity long reads with chromosome conformation capture data (Hi-C), resulting in a highly complete and accurate genome assembly. The assembly is characterized by a haploid size of 940 Megabase pairs (Mbp) for haplome one and 929 Mbp for haplome two, with scaffold N50 values of 36.4 Mb and 36.6 Mb, respectively. These metrics, alongside BUSCO scores of 96.9% and 97.2%, highlight the high quality of the genome, making it a robust foundation for further genetic exploration and analyses.
The study’s findings are both novel and significant, providing deep insights into the genetic architecture of P. phoxinus. The authors report heterozygosity rate of 1.43% and a high repeat content of approximately 54%, primarily consisting of DNA transposons. These transposons play a crucial role in genome rearrangements and variations, contributing to the species' adaptability and evolution (Bourque et al. 2018). The research also identifies substantial structural variations within the genome, including insertions, deletions, inversions, and translocations (Oriowo et al. 2024). Beyond these findings, the genome annotation is exceptionally comprehensive, containing 30,980 mRNAs and 23,497 protein-coding genes. The study’s gene family evolution analysis, which compares the P. phoxinus proteome to that of ten other teleost species, reveals immune system gene families that favor histone-based disease prevention mechanisms over NLR-based immune responses. This provides new insight into the evolutionary strategies that have emerged in P. phoxinus, enabling its survival in its environment. Moreover, the demographic analysis conducted in the study reveals historical fluctuations in the effective population size of P. phoxinus, likely correlated with past climatic changes, offering insights into the species' evolutionary history.
This annotated and phased reference genome not only serves as a crucial resource for resolving taxonomic complexities within the genus Phoxinus but also highlights the importance of haplotype-phased assemblies in understanding genetic diversity, particularly in species characterized by high heterozygosity. The authors have delivered a study that is methodologically sound, richly detailed, and highly relevant to the field. The study represents a valuable and impactful contribution to the scientific community, offering resources and knowledge that will likely inform future research in the field.
References
Bourque G, Burns KH, Gehring M, Gorbunova V, Seluanov A, Hammell M, Imbeault M, Izsvák Z, Levin HL, Macfarlan TS, Mager DL, Feschotte C (2018) Ten things you should know about transposable elements. Genome Biology, 19, 199. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1577-z
Oriowo TO, Chrysostomakis I, Martin S, Kukowka S, Brown T, Winkler S, Myers EW, Böhne A, Stange M (2024) A chromosome-level, haplotype-resolved genome assembly and annotation for the Eurasian minnow (Leuciscidae: Phoxinus phoxinus) provide evidence of haplotype diversity. bioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.30.569369
The European Reference Genome Atlas: piloting a decentralised approach to equitable biodiversity genomics
Informed Choices, Cohesive Future: Decisions and Recommendations for ERGA
Recommended by Jitendra Narayan based on reviews by Justin Ideozu and Eric CrandallThe European Reference Genome Atlas (ERGA) (Mc Cartney et al, 2024, Mazzoni et al, 2023) demonstrates the collaborative spirit and intellectual abilities of researchers from 33 European countries. This ambitious project, which is part of the Earth BioGenome Project (Lewin et al., 2018) Phase II, has embarked on an unprecedented mission: to decipher the genetic makeup of 150,000 species over a span of four years. At the heart of ERGA is a decentralized pilot infrastructure specifically built to assist the production of high-quality reference genomes. This structure acts as a scaffold for the massive task of genome sequencing, giving the necessary framework to manage the complexity of genomic research. The research paper under consideration offers a comprehensive narrative of ERGA's evolution, outlining both successes and challenges encountered along the road.
One of the most significant issues addressed in the manuscript is the equitable distribution of resources and expertise among participating laboratories and countries. In a project of this magnitude, it is critical to leverage the pooled talents and capacities of researchers from across Europe. ERGA's pan-European network promotes communications and collaboration, creating an environment in which knowledge flows freely and barriers are overcome. This adoption of strong coordination and communication tactics will be essential to ERGA's success. Scientific collaboration depends on efficient communication channels because they allow researchers to share resources, collaborate on new initiatives, and exchange ideas. Through a diverse range of gatherings, courses, and virtual discussion boards, ERGA fosters an environment of transparency and cooperation among members, enabling scientists to overcome challenges and make significant discoveries. The importance ERGA places on training and information transfer programmes is a pillar of its strategy. Understanding the importance of capacity development, ERGA invests in providing researchers with the knowledge and abilities necessary for effectively navigating the complicated terrain of genomic research. A wide range of subjects are covered in training programmes (Larivière et al. 2023), from sample preparation and collection to data processing methods and sequencing technology. Through the development of a group of highly qualified experts, ERGA creates the foundation for continued advancement and creativity in the genomics sector.
This manuscript also covers in detail the technological workflows and sequencing techniques used in ERGA's pilot infrastructure. With the aid of cutting-edge sequencing technologies based on both long-read and short-read sequencing, they are working to unravel the complex structure of the genetic code with a level of accuracy and precision never before possible. To guarantee the accuracy of genetic data and prevent mistakes and flaws that can jeopardize the findings' integrity, quality control methods are put in place. Despite having a focus on genome sequencing due to its technological complexities, ERGA also remains firm in its dedication to metadata collection and sample validation. Metadata serves as a critical link between raw genetic data and useful scientific insights, giving necessary context and allowing researchers to draw practical findings from their investigations. Sample validation approaches improve the reliability and reproducibility of the results, providing users confidence in the quality of the genetic data provided by ERGA.
Looking ahead, ERGA envisions its decentralized infrastructure serving as a model for global collaborative research efforts. By embracing diversity, encouraging cooperation, and pushing for open access to data and resources, ERGA hopes to catalyze scientific discovery and generate positive change in the field of biodiversity genomics. ERGA aims to promote a more equitable and sustainable future for all by ongoing interaction with stakeholders, intensive outreach and education activities, and policy change advocacy. In addition to its immediate goals, ERGA considers the long-term implications of its work. As genomic technology progresses, the potential application of high-quality reference genomes will continue to grow. From informing conservation efforts and illuminating evolutionary histories to revolutionizing healthcare and agriculture, it is likely that ERGA's contributions will have far-reaching consequences for people and the planet as a whole.
Furthermore, ERGA understands the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in addressing the difficult challenges of the twenty-first century. ERGA aims to integrate genetic research into larger initiatives to promote sustainability and biodiversity conservation by forming relationships with stakeholders from other areas, such as policymakers, conservationists, and indigenous groups. Through shared knowledge and community action, ERGA seeks to create a future in which mankind coexists peacefully with the natural world, guided by a thorough grasp of its genetic legacy and ecological interconnectivity.
Finally, the manuscript exemplifies ERGA's collaborative ambitions and achievements, capturing the spirit of creativity and collaboration that defines this ground-breaking effort. As ERGA continues to push the boundaries of genetic research, it remains dedicated to scientific excellence, inclusivity, and the quest of knowledge for the benefit of society. I wholeheartedly recommend the publication of this groundbreaking initiative, offering my enthusiastic endorsement for its valuable contribution to the scientific community.
References
Larivière, D., Abueg, L., Brajuka, N. et al. (2024). Scalable, accessible and reproducible reference genome assembly and evaluation in Galaxy. Nature Biotechnology 42, 367-370. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-023-02100-3
Lewin, H. A., Robinson, G. E., Kress, W. J., Baker, W. J., Coddington, J., Crandall, K. A., Durbin, R., Edwards, S. V., Forest, F., Gilbert, M. T. P., Goldstein, M. M., Grigoriev, I. V., Hackett, K. J., Haussler, D., Jarvis, E. D., Johnson, W. E., Patrinos, A., Richards, S., Castilla-Rubio, J. C., … Zhang, G. (2018). Earth BioGenome Project: Sequencing life for the future of life. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(17), 4325–4333. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1720115115
Mazzoni, C. J., Claudio, C.i, Waterhouse, R. M. (2023). Biodiversity: an atlas of European reference genomes. Nature 619 : 252-252. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-02229-w
Mc Cartney, A. M., Formenti, G., Mouton, A., Panis, D. de, Marins, L. S., Leitão, H. G., Diedericks, G., Kirangwa, J., Morselli, M., Salces-Ortiz, J., Escudero, N., Iannucci, A., Natali, C., Svardal, H., Fernández, R., Pooter, T. de, Joris, G., Strazisar, M., Wood, J., … Mazzoni, C. J. (2024). The European Reference Genome Atlas: piloting a decentralised approach to equitable biodiversity genomics. bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.09.25.559365