Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
11 Mar 2021

Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stagesThibault Scalvenzi, Isabelle Clavereau, Mickael Bourge, Nicolas Pollet https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.25.110734A comprehensive look at Xenopus gut microbiota: effects of feed, developmental stages and parental transmissionRecommended by Wirulda Pootakham based on reviews by Vanessa Marcelino and 1 anonymous reviewerIt is well established that the gut microbiota play an important role in the overall health of their hosts (Jandhyala et al. 2015). To date, there are still a limited number of studies on the complex microbial communites inhabiting vertebrate digestive systems, especially the ones that also explored the functional diversity of the microbial community (Bletz et al. 2016). This preprint by Scalvenzi et al. (2021) reports a comprehensive study on the phylogenetic and metabolic profiles of the Xenopus gut microbiota. The author describes significant changes in the gut microbiome communities at different developmental stages and demonstrates different microbial community composition across organs. In addition, the study also investigates the impact of diet on the Xenopus tadpole gut microbiome communities as well as how the bacterial communities are transmitted from parents to the next generation. This is one of the first studies that addresses the interactions between gut bacteria and tadpoles during the development. The authors observe the dynamics of gut microbiome communities during tadpole growth and metamorphosis. They also explore host-gut microbial community metabolic interactions and demostrate the capacity of the microbiome to complement the metabolic pathways of the Xenopus genome. Although this study is limited by the use of Xenopus tadpoles in a laboratory, which are probably different from those in nature, I believe it still provides important and valuable information for the research community working on vertebrate’s microbiota and their interaction with the host. References Bletz et al. (2016). Amphibian gut microbiota shifts differentially in community structure but converges on habitat-specific predicted functions. Nature Communications, 7(1), 1-12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13699 Jandhyala, S. M., Talukdar, R., Subramanyam, C., Vuyyuru, H., Sasikala, M., & Reddy, D. N. (2015). Role of the normal gut microbiota. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG, 21(29), 8787. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748%2Fwjg.v21.i29.8787 Scalvenzi, T., Clavereau, I., Bourge, M. & Pollet, N. (2021) Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stages. bioRxiv, 2020.05.25.110734, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Geonmics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.25.110734 | Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stages | Thibault Scalvenzi, Isabelle Clavereau, Mickael Bourge, Nicolas Pollet | <p><strong>Background</strong> The microorganism world living in amphibians is still largely under-represented and under-studied in the literature. Among anuran amphibians, African clawed frogs of the Xenopus genus stand as well-characterized mode... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Metagenomics, Vertebrates | Wirulda Pootakham | 2020-05-25 14:01:19 | View | |
18 Feb 2021
Traces of transposable element in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networksAgnes Baud, Mariene Wan, Danielle Nouaud, Nicolas Francillonne, Dominique Anxolabehere, Hadi Quesneville https://doi.org/10.1101/547877Using small fragments to discover old TE remnants: the Duster approach empowers the TE detectionRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by Josep Casacuberta and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Josep Casacuberta and 1 anonymous reviewer
Transposable elements are the raw material of the dark matter of the genome, the foundation of the next generation of genes and regulation networks". This sentence could be the essence of the paper of Baud et al. (2021). Transposable elements (TEs) are endogenous mobile genetic elements found in almost all genomes, which were discovered in 1948 by Barbara McClintock (awarded in 1983 the only unshared Medicine Nobel Prize so far). TEs are present everywhere, from a single isolated copy for some elements to more than millions for others, such as Alu. They are founders of major gene lineages (HET-A, TART and telomerases, RAG1/RAG2 proteins from mammals immune system; Diwash et al, 2017), and even of retroviruses (Xiong & Eickbush, 1988). However, most TEs appear as selfish elements that replicate, land in a new genomic region, then start to decay and finally disappear in the midst of the genome, turning into genomic ‘dark matter’ (Vitte et al, 2007). The mutations (single point, deletion, recombination, and so on) that occur during this slow death erase some of their most notable features and signature sequences, rendering them completely unrecognizable after a few million years. Numerous TE detection tools have tried to optimize their detection (Goerner-Potvin & Bourque, 2018), but further improvement is definitely challenging. This is what Baud et al. (2021) accomplished in their paper. They used a simple, elegant and efficient k-mer based approach to find small signatures that, when accumulated, allow identifying very old TEs. Using this method, called Duster, they improved the amount of annotated TEs in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana by 20%, pushing the part of this genome occupied by TEs up from 40 to almost 50%. They further observed that these very old Duster-specific TEs (i.e., TEs that are only detected by Duster) are, among other properties, close to genes (much more than recent TEs), not targeted by small RNA pathways, and highly associated with conserved regions across the rosid family. In addition, they are highly associated with flowering or stress response genes, and may be involved through exaptation in the evolution of responses to environmental changes. TEs are not just selfish elements: more and more studies have shown their key role in the evolution of their hosts, and tools such as Duster will help us better understand their impact. References Baud, A., Wan, M., Nouaud, D., Francillonne, N., Anxolabéhère, D. and Quesneville, H. (2021). Traces of transposable elements in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networks. bioRxiv, 547877, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics.doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/547877 | Traces of transposable element in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networks | Agnes Baud, Mariene Wan, Danielle Nouaud, Nicolas Francillonne, Dominique Anxolabehere, Hadi Quesneville | <p>Transposable elements (TEs) are mobile, repetitive DNA sequences that make the largest contribution to genome bulk. They thus contribute to the so-called 'dark matter of the genome', the part of the genome in which nothing is immediately recogn... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics, Plants, Structural genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Francois Sabot | Anonymous, Josep Casacuberta | 2020-04-07 17:12:12 | View |
09 Oct 2020
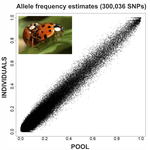
An evaluation of pool-sequencing transcriptome-based exon capture for population genomics in non-model speciesEmeline Deleury, Thomas Guillemaud, Aurélie Blin & Eric Lombaert https://doi.org/10.1101/583534Assessing a novel sequencing-based approach for population genomics in non-model speciesRecommended by Thomas Derrien and Sebastian Ernesto Ramos-Onsins and Sebastian Ernesto Ramos-Onsins based on reviews by Valentin Wucher and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Valentin Wucher and 1 anonymous reviewer
Developing new sequencing and bioinformatic strategies for non-model species is of great interest in many applications, such as phylogenetic studies of diverse related species, but also for studies in population genomics, where a relatively large number of individuals is necessary. Different approaches have been developed and used in these last two decades, such as RAD-Seq (e.g., Miller et al. 2007), exome sequencing (e.g., Teer and Mullikin 2010) and other genome reduced representation methods that avoid the use of a good reference and well annotated genome (reviewed at Davey et al. 2011). However, population genomics studies require the analysis of numerous individuals, which makes the studies still expensive. Pooling samples was thought as an inexpensive strategy to obtain estimates of variability and other related to the frequency spectrum, thus allowing the study of variability at population level (e.g., Van Tassell et al. 2008), although the major drawback was the loss of information related to the linkage of the variants. In addition, population analysis using all these sequencing strategies require statistical and empirical validations that are not always fully performed. A number of studies aiming to obtain unbiased estimates of variability using reduced representation libraries and/or with pooled data have been performed (e.g., Futschik and Schlötterer 2010, Gautier et al. 2013, Ferretti et al. 2013, Lynch et al. 2014), as well as validation of new sequencing methods for population genetic analyses (e.g., Gautier et al. 2013, Nevado et al. 2014). Nevertheless, empirical validation using both pooled and individual experimental approaches combined with different bioinformatic methods has not been always performed. References [1] Choquet et al. (2019). Towards population genomics in non-model species with large genomes: a case study of the marine zooplankton Calanus finmarchicus. Royal Society open science, 6(2), 180608. doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.180608 | An evaluation of pool-sequencing transcriptome-based exon capture for population genomics in non-model species | Emeline Deleury, Thomas Guillemaud, Aurélie Blin & Eric Lombaert | <p>Exon capture coupled to high-throughput sequencing constitutes a cost-effective technical solution for addressing specific questions in evolutionary biology by focusing on expressed regions of the genome preferentially targeted by selection. Tr... |  | Bioinformatics, Population genomics | Thomas Derrien | 2020-02-26 09:21:11 | View | |
24 Sep 2020

A rapid and simple method for assessing and representing genome sequence relatednessM Briand, M Bouzid, G Hunault, M Legeay, M Fischer-Le Saux, M Barret https://doi.org/10.1101/569640A quick alternative method for resolving bacterial taxonomy using short identical DNA sequences in genomes or metagenomesRecommended by B. Jesse Shapiro based on reviews by Gavin Douglas and 1 anonymous reviewerThe bacterial species problem can be summarized as follows: bacteria recombine too little, and yet too much (Shapiro 2019). References Arevalo P, VanInsberghe D, Elsherbini J, Gore J, Polz MF (2019) A Reverse Ecology Approach Based on a Biological Definition of Microbial Populations. Cell, 178, 820-834.e14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.033 | A rapid and simple method for assessing and representing genome sequence relatedness | M Briand, M Bouzid, G Hunault, M Legeay, M Fischer-Le Saux, M Barret | <p>Coherent genomic groups are frequently used as a proxy for bacterial species delineation through computation of overall genome relatedness indices (OGRI). Average nucleotide identity (ANI) is a widely employed method for estimating relatedness ... |  | Bioinformatics, Metagenomics | B. Jesse Shapiro | Gavin Douglas | 2019-11-07 16:37:56 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Gavin Douglas
Jean-François Flot
Danny Ionescu










