Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
09 Aug 2023
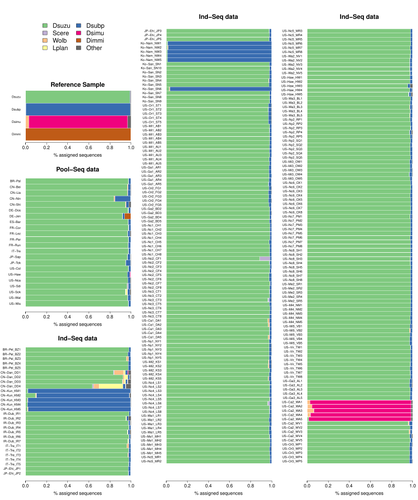
Efficient k-mer based curation of raw sequence data: application in Drosophila suzukiiGautier Mathieu https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.18.537389Decontaminating reads, not contigsRecommended by Nicolas Galtier based on reviews by Marie Cariou and Denis BaurainContamination, the presence of foreign DNA sequences in a sample of interest, is currently a major problem in genomics. Because contamination is often unavoidable at the experimental stage, it is increasingly recognized that the processing of high-throughput sequencing data must include a decontamination step. This is usually performed after the many sequence reads have been assembled into a relatively small number of contigs. Dubious contigs are then discarded based on their composition (e.g. GC-content) or because they are highly similar to a known piece of DNA from a foreign species. Here [1], Mathieu Gautier explores a novel strategy consisting in decontaminating reads, not contigs. Why is this promising? Assembly programs and algorithms are complex, and it is not easy to predict, or monitor, how they handle contaminant reads. Ideally, contaminant reads will be assembled into obvious contaminant contigs. However, there might be more complex situations, such as chimeric contigs with alternating genuine and contaminant segments. Decontaminating at the read level, if possible, should eliminate such unfavorable situations where sequence information from contaminant and target samples are intimately intertwined by an assembler. To achieve this aim, Gautier proposes to use methods initially designed for the analysis of metagenomic data. This is pertinent since the decontamination process involves considering a sample as a mixture of different sources of DNA. The programs used here, CLARK and CLARK-L, are based on so-called k-mer analysis, meaning that the similarity between a read to annotate and a reference sequence is measured by how many sub-sequences (of length 31 base pairs for CLARK and 27 base pairs for CLARK-L) they share. This is notoriously more efficient than traditional sequence alignment algorithms when it comes to comparing a very large number of (most often unrelated) sequences. This is, therefore, a reference-based approach, in which the reads from a sample are assigned to previously sequenced genomes based on k-mer content. This original approach is here specifically applied to the case of Drosophila suzukii, an invasive pest damaging fruit production in Europe and America. Fortunately, Drosophila is a genus of insects with abundant genomic resources, including high-quality reference genomes in dozens of species. Having calibrated and validated his pipeline using data sets of known origins, Gautier quantifies in each of 258 presumed D. suzukii samples the proportion of reads that likely belong to other species of fruit flies, or to fruit fly-associated microbes. This proportion is close to one in 16 samples, which clearly correspond to mis-labelled individuals. It is non-negligible in another ~10 samples, which really correspond to D. suzukii individuals. Most of these reads of unexpected origin are contaminants and should be filtered out. Interestingly, one D. suzukii sample contains a substantial proportion of reads from the closely related D. subpulchera, which might instead reflect a recent episode of gene flow between these two species. The approach, therefore, not only serves as a crucial technical step, but also has the potential to reveal biological processes. Gautier's thorough, well-documented work will clearly benefit the ongoing and future research on D. suzuki, and Drosophila genomics in general. The author and reviewers rightfully note that, like any reference-based approach, this method is heavily dependent on the availability and quality of reference genomes - Drosophila being a favorable case. Building the reference database is a key step, and the interpretation of the output can only be made in the light of its content and gaps, as illustrated by Gautier's careful and detailed discussion of his numerous results. This pioneering study is a striking demonstration of the potential of metagenomic methods for the decontamination of high-throughput sequence data at the read level. The pipeline requires remarkably few computing resources, ensuring low carbon emission. I am looking forward to seeing it applied to a wide range of taxa and samples.
Reference [1] Gautier Mathieu. Efficient k-mer based curation of raw sequence data: application in Drosophila suzukii. bioRxiv, 2023.04.18.537389, ver. 2, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.18.537389 | Efficient k-mer based curation of raw sequence data: application in *Drosophila suzukii* | Gautier Mathieu | <p>Several studies have highlighted the presence of contaminated entries in public sequence repositories, calling for special attention to the associated metadata. Here, we propose and evaluate a fast and efficient kmer-based approach to assess th... |  | Bioinformatics, Population genomics | Nicolas Galtier | 2023-04-20 22:05:13 | View | |
07 Aug 2023
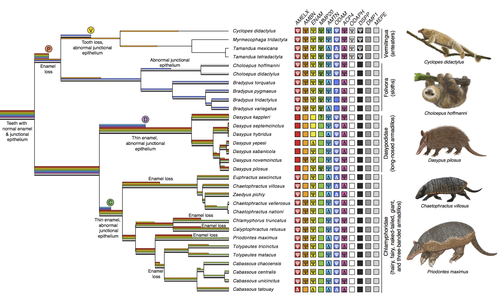
Genomic data suggest parallel dental vestigialization within the xenarthran radiationChristopher A Emerling, Gillian C Gibb, Marie-Ka Tilak, Jonathan J Hughes, Melanie Kuch, Ana T Duggan, Hendrik N Poinar, Michael W Nachman, Frederic Delsuc https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.09.519446What does dental gene decay tell us about the regressive evolution of teeth in South American mammals?Recommended by Didier Casane based on reviews by Juan C. Opazo, Régis Debruyne and Nicolas PolletA group of mammals, Xenathra, evolved and diversified in South America during its long period of isolation in the early to mid Cenozoic era. More recently, as a result of the Great Faunal Interchange between South America and North America, many xenarthran species went extinct. The thirty-one extant species belong to three groups: armadillos, sloths and anteaters. They share dental degeneration. However, the level of degeneration is variable. Anteaters entirely lack teeth, sloths have intermediately regressed teeth and most armadillos have a toothless premaxilla, as well as peg-like, single-rooted teeth that lack enamel in adult animals (Vizcaíno 2009). This diversity raises a number of questions about the evolution of dentition in these mammals. Unfortunately, the fossil record is too poor to provide refined information on the different stages of regressive evolution in these clades. In such cases, the identification of loss-of-function mutations and/or relaxed selection in genes related to a character regression can be very informative (Emerling and Springer 2014; Meredith et al. 2014; Policarpo et al. 2021). Indeed, shared and unique pseudogenes/relaxed selection can tell us to what extent regression has occurred in common ancestors and whether some changes are lineage-specific. In addition, the distribution of pseudogenes/relaxed selection on the branches of a phylogenetic tree is related to the evolutionary processes involved. A much higher density of pseudogenes in the most internal branches indicates that degeneration took place early and over a short period of time, consistent with selection against the presence of the morphological character with which they are associated, while pseudogenes distributed evenly in many internal and external branches suggest a more gradual process over many millions of years, in line with relaxed selection and fixation of loss-of-function mutations by genetic drift. In this paper (Emerling et al. 2023), the authors examined the dynamics of decay of 11 dental genes that may parallel teeth regression. The analyses of the data reported in this paper clearly point to xenarthran teeth having repeatedly regressed in parallel in the three clades. In fact, no loss-of-function mutation is shared by all species examined. However, more genes should be studied to confirm the hypothesis that the common ancestor of extant xenarthrans had normal dentition. There are distinct patterns of gene loss in different lineages that are associated with the variation in dentition observed across the clades. These patterns of gene loss suggest that regressive evolution took place both gradually and in relatively rapid, discrete phases during the diversification of xenarthrans. This study underscores the utility of using pseudogenes to reconstruct evolutionary history of morphological characters when fossils are sparse. References Emerling CA, Gibb GC, Tilak M-K, Hughes JJ, Kuch M, Duggan AT, Poinar HN, Nachman MW, Delsuc F. 2023. Genomic data suggest parallel dental vestigialization within the xenarthran radiation. bioRxiv, 2022.12.09.519446, ver 2, peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.09.519446 Emerling CA, Springer MS. 2014. Eyes underground: Regression of visual protein networks in subterranean mammals. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 78: 260-270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2014.05.016 Meredith RW, Zhang G, Gilbert MTP, Jarvis ED, Springer MS. 2014. Evidence for a single loss of mineralized teeth in the common avian ancestor. Science 346: 1254390. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254390 Policarpo M, Fumey J, Lafargeas P, Naquin D, Thermes C, Naville M, Dechaud C, Volff J-N, Cabau C, Klopp C, et al. 2021. Contrasting gene decay in subterranean vertebrates: insights from cavefishes and fossorial mammals. Molecular Biology and Evolution 38: 589-605. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa249 Vizcaíno SF. 2009. The teeth of the “toothless”: novelties and key innovations in the evolution of xenarthrans (Mammalia, Xenarthra). Paleobiology 35: 343-366. https://doi.org/10.1666/0094-8373-35.3.343 | Genomic data suggest parallel dental vestigialization within the xenarthran radiation | Christopher A Emerling, Gillian C Gibb, Marie-Ka Tilak, Jonathan J Hughes, Melanie Kuch, Ana T Duggan, Hendrik N Poinar, Michael W Nachman, Frederic Delsuc | <p style="text-align: justify;">The recent influx of genomic data has provided greater insights into the molecular basis for regressive evolution, or vestigialization, through gene loss and pseudogenization. As such, the analysis of gene degradati... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Vertebrates | Didier Casane | 2022-12-12 16:01:57 | View | |
10 Jul 2023
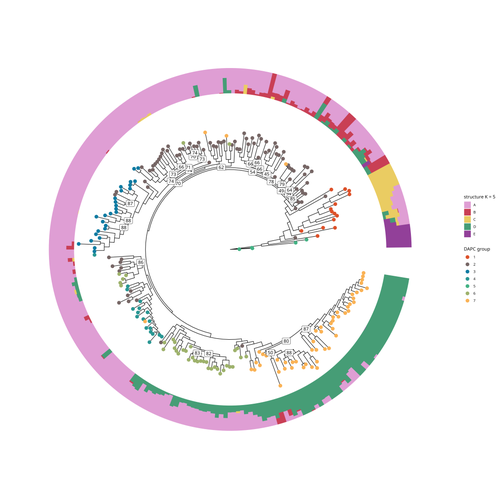
SNP discovery by exome capture and resequencing in a pea genetic resource collectionG. Aubert, J. Kreplak, M. Leveugle, H. Duborjal, A. Klein, K. Boucherot, E. Vieille, M. Chabert-Martinello, C. Cruaud, V. Bourion, I. Lejeune-Hénaut, M.L. Pilet-Nayel, Y. Bouchenak-Khelladi, N. Francillonne, N. Tayeh, J.P. Pichon, N. Rivière, J. Burstin https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.03.502586The value of a large Pisum SNP datasetRecommended by Wanapinun Nawae based on reviews by Rui Borges and 1 anonymous reviewerOne important goal of modern genetics is to establish functional associations between genotype and phenotype. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are numerous and widely distributed in the genome and can be obtained from nucleic acid sequencing (1). SNPs allow for the investigation of genetic diversity, which is critical for increasing crop resilience to the challenges posed by global climate change. The associations between SNPs and phenotypes can be captured in genome-wide association studies. SNPs can also be used in combination with machine learning, which is becoming more popular for predicting complex phenotypic traits like yield and biotic and abiotic stress tolerance from genotypic data (2). The availability of many SNP datasets is important in machine learning predictions because this approach requires big data to build a comprehensive model of the association between genotype and phenotype. Aubert and colleagues have studied, as part of the PeaMUST project, the genetic diversity of 240 Pisum accessions (3). They sequenced exome-enriched genomic libraries, a technique that enables the identification of high-density, high-quality SNPs at a low cost (4). This technique involves capturing and sequencing only the exonic regions of the genome, which are the protein-coding regions. A total of 2,285,342 SNPs were obtained in this study. The analysis of these SNPs with the annotations of the genome sequence of one of the studied pea accessions (5) identified a number of SNPs that could have an impact on gene activity. Additional analyses revealed 647,220 SNPs that were unique to individual pea accessions, which might contribute to the fitness and diversity of accessions in different habitats. Phylogenetic and clustering analyses demonstrated that the SNPs could distinguish Pisum germplasms based on their agronomic and evolutionary histories. These results point out the power of selected SNPs as markers for identifying Pisum individuals. Overall, this study found high-quality SNPs that are meaningful in a biological context. This dataset was derived from a large set of germplasm and is thus particularly useful for studying genotype-phenotype associations, as well as the diversity within Pisum species. These SNPs could also be used in breeding programs to develop new pea varieties that are resilient to abiotic and biotic stressors. References
https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2021-005
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03559-z
https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.03.502586
https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.115.018564
| SNP discovery by exome capture and resequencing in a pea genetic resource collection | G. Aubert, J. Kreplak, M. Leveugle, H. Duborjal, A. Klein, K. Boucherot, E. Vieille, M. Chabert-Martinello, C. Cruaud, V. Bourion, I. Lejeune-Hénaut, M.L. Pilet-Nayel, Y. Bouchenak-Khelladi, N. Francillonne, N. Tayeh, J.P. Pichon, N. Rivière, J. B... | <p style="text-align: justify;"><strong>Background & Summary</strong></p> <p style="text-align: justify;">In addition to being the model plant used by Mendel to establish genetic laws, pea (<em>Pisum sativum</em> L., 2n=14) is a major pulse c... |  | Plants, Population genomics | Wanapinun Nawae | 2022-11-29 09:29:06 | View | |
02 Jun 2023
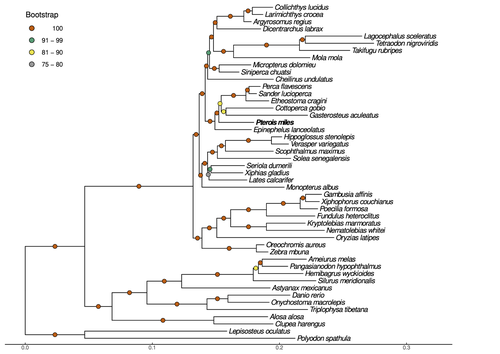
Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois milesChristos V. Kitsoulis, Vasileios Papadogiannis, Jon B. Kristoffersen, Elisavet Kaitetzidou, Aspasia Sterioti, Costas S. Tsigenopoulos, Tereza Manousaki https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.10.523469The genome of a dangerous invader (fish) beautyRecommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Maria Recuerda and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Maria Recuerda and 1 anonymous reviewer
High-quality genomes are currently being generated at an unprecedented speed powered by long-read sequencing technologies. However, sequencing effort is concentrated unequally across the tree of life and several key evolutionary and ecological groups remain largely unexplored. So is the case for fish species of the family Scorpaenidae (Perciformes). Kitsoulis et al. present the genome of the devil firefish, Pterois miles (1). Following current best practices, the assembly relies largely on Oxford Nanopore long reads, aided by Illumina short reads for polishing to increase the per-base accuracy. PacBio’s IsoSeq was used to sequence RNA from a variety of tissues as direct evidence for annotating genes. The reconstructed genome is 902 Mb in size and has high contiguity (N50=14.5 Mb; 660 scaffolds, 90% of the genome covered by the 83 longest scaffolds) and completeness (98% BUSCO completeness). The new genome is used to assess the phylogenetic position of P. miles, explore gene synteny against zebrafish, look at orthogroup expansion and contraction patterns in Perciformes, as well as to investigate the evolution of toxins in scorpaenid fish (2). In addition to its value for better understanding the evolution of scorpaenid and teleost fishes, this new genome is also an important resource for monitoring its invasiveness through the Mediterranean Sea (3) and the Atlantic Ocean, in the latter case forming the invasive lionfish complex with P. volitans (4). REFERENCES 1. Kitsoulis CV, Papadogiannis V, Kristoffersen JB, Kaitetzidou E, Sterioti E, Tsigenopoulos CS, Manousaki T. (2023) Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois miles. BioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.10.523469 2. Kiriake A, Shiomi K. (2011) Some properties and cDNA cloning of proteinaceous toxins from two species of lionfish (Pterois antennata and Pterois volitans). Toxicon, 58(6-7):494–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.08.010 3. Katsanevakis S, et al. (2020) Un- published Mediterranean records of marine alien and cryptogenic species. BioInvasions Records, 9:165–182. https://doi.org/10.3391/bir.2020.9.2.01 4. Lyons TJ, Tuckett QM, Hill JE. (2019) Data quality and quantity for invasive species: A case study of the lionfishes. Fish and Fisheries, 20:748–759. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12374 | Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, *Pterois miles* | Christos V. Kitsoulis, Vasileios Papadogiannis, Jon B. Kristoffersen, Elisavet Kaitetzidou, Aspasia Sterioti, Costas S. Tsigenopoulos, Tereza Manousaki | <p style="text-align: justify;">Devil firefish (<em>Pterois miles</em>), a member of Scorpaenidae family, is one of the most successful marine non-native species, dominating around the world, that was rapidly spread into the Mediterranean Sea, thr... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Iker Irisarri | 2023-01-17 12:37:20 | View | |
22 May 2023

Genetic bases of resistance to the rice hoja blanca disease deciphered by a QTL approachAlexander Silva, Maria Elker Montoya, Constanza Quintero, Juan Cuasquer, Joe Tohme, Eduardo Graterol, Maribel Cruz, Mathias Lorieux https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.07.515427Scoring symptoms of a plant viral diseaseRecommended by Olivier Panaud based on reviews by Grégoire Aubert and Valérie GeffroyThe paper from Silva et al. (2023) provides new insights into the genetic bases of natural resistance of rice to the Rice Hoja Blanca (RHB) disease, one of its most serious diseases in tropical countries of the American continent and the Caribbean. This disease is caused by the Rice Hoja Blanca Virus, or RHBV, the vector of which is the planthopper insect Tagosodes orizicolus Müir. It is responsible for serious damage to the rice crop (Morales and Jennings 2010). The authors take a Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) detection approach to find genomic regions statistically associated with the resistant phenotype. To this aim, they use four resistant x susceptible crosses (the susceptible parent being the same in all four crosses) to maximize the chances to find new QTLs. The F2 populations derived from the crosses are genotyped using Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) extracted from whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data of the resistant parents, and the F3 families derived from the F2 individuals are scored for disease symptoms. For this, they use a computer-aided image analysis protocol that they designed so they can estimate the severity of the damages in the plant. They find several new QTLs, some being apparently more associated with disease severity, others with disease incidence. They also find that a previously identified QTL of Oryza sativa ssp. japonica origin is also present in the indica cluster (Romero et al. 2014). Finally, they discuss the candidate genes that could underlie the QTLs and provide a simple model for resistance. It has to be noted that scoring symptoms of a viral disease such as RHB is very challenging. It requires maintaining populations of viruliferous insect vectors, mastering times and conditions for infestation by nymphs, and precise symptom scoring. It also requires the preparation of segregating populations, their genotyping with enough genetic markers, and mastering QTL detection methods. All these aspects are present in this work. In particular, the phenotyping of symptom severity implemented using computer-aided image processing represents an impressive, enormous amount of work. From the genomics side, the fine-scale genotyping is based on the WGS of the parental lines (resistant and susceptible), followed by the application of suitable bioinformatic tools for SNP extraction and primers prediction that can be used on their Fluidigm platform. It also required implementing data correction algorithms to achieve precise genetic maps in the four crosses. The QTL detection itself required careful statistical pre-processing of phenotypic data. The authors then used a combination of several QTL detection methods, including an original meta-QTL method they developed in the software MapDisto. The authors then perform a very complete and convincing analysis of candidate genes, which includes genes already identified for a similar disease (RSV) on chromosome 11 of rice. What remains to elucidate is whether the candidate genes are actually involved or not in the disease resistance process. The team has already started implementing gene knockout strategies to study some of them in more detail. It will be interesting to see whether those genes act against the virus itself, or against the insect vector. Overall the work is of high quality and represents an important advance in the knowledge of disease resistance. In addition, it has many implications for crop breeding, allowing the setup of large-scale, marker-assisted strategies, for new resistant elite varieties of rice. References Morales F and Jennings P (2010) Rice hoja blanca: a complex plant-virus-vector pathosystem. CAB Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1079/PAVSNNR20105043 Romero LE, Lozano I, Garavito A, et al (2014) Major QTLs control resistance to Rice hoja blanca virus and its vector Tagosodes orizicolus. G3 | Genes, Genomes, Genetics 4:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.113.009373 Silva A, Montoya ME, Quintero C, Cuasquer J, Tohme J, Graterol E, Cruz M, Lorieux M (2023) Genetic bases of resistance to the rice hoja blanca disease deciphered by a QTL approach. bioRxiv, 2022.11.07.515427, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.07.515427 | Genetic bases of resistance to the rice hoja blanca disease deciphered by a QTL approach | Alexander Silva, Maria Elker Montoya, Constanza Quintero, Juan Cuasquer, Joe Tohme, Eduardo Graterol, Maribel Cruz, Mathias Lorieux | <p style="text-align: justify;">Rice hoja blanca (RHB) is one of the most serious diseases in rice growing areas in tropical Americas. Its causal agent is Rice hoja blanca virus (RHBV), transmitted by the planthopper <em>Tagosodes orizicolus </em>... |  | Functional genomics, Plants | Olivier Panaud | 2022-11-09 09:13:30 | View | |
24 Feb 2023

MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomesBertrand Néron, Rémi Denise, Charles Coluzzi, Marie Touchon, Eduardo P. C. Rocha, Sophie S. Abby https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.02.506364A unique and customizable approach for functionally annotating prokaryotic genomesRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by Kwee Boon Brandon Seah and Max Emil Schön based on reviews by Kwee Boon Brandon Seah and Max Emil Schön
Macromolecular System Finder (MacSyFinder) v2 (Néron et al., 2023) is a newly updated approach for performing functional annotation of prokaryotic genomes (Abby et al., 2014). This tool parses an input file of protein sequences from a single genome (either ordered by genome location or unordered) and identifies the presence of specific cellular functions (referred to as “systems”). These systems are called based on two criteria: (1) that the "quorum" of a minimum set of core proteins involved is reached the “quorum” of a minimum set of core proteins being involved that are present, and (2) that the genes encoding these proteins are in the expected genomic organization (e.g., within the same order in an operon), when ordered data is provided. I believe the MacSyFinder approach represents an improvement over more commonly used methods exactly because it can incorporate such information on genomic organization, and also because it is more customizable. Before properly appreciating these points, it is worth noting the norms and key challenges surrounding high-throughput functional annotation of prokaryotic genomes. Genome sequences are being added to online repositories at increasing rates, which has led to an enormous amount of bacterial genome diversity available to investigate (Altermann et al., 2022). A key aspect of understanding this diversity is the functional annotation step, which enables genes to be grouped into more biologically interpretable categories. For instance, gene calls can be mapped against existing Clusters of Orthologous Genes, which are themselves grouped into general categories such as ‘Transcription’ and ‘Lipid metabolism’ (Galperin et al., 2021). This approach is valuable but is primarily used for global summaries of functional annotations within a genome: for example, it could be useful to know that a genome is particularly enriched for genes involved in lipid metabolism. However, knowing that a particular gene is involved in the general process of lipid metabolism is less likely to be actionable. In other words, the desired specificity of a gene’s functional annotation will depend on the exact question being investigated. There is no shortage of functional ontologies in genomics that can be applied for this purpose (Douglas and Langille, 2021), and researchers are often overwhelmed by the choice of which functional ontology to use. In this context, giving researchers the ability to precisely specify the gene families and operon structures they are interested in identifying across genomes provides useful control over what precise functions they are profiling. Of course, most researchers will lack the information and/or expertise to fully take advantage of MacSyFinder’s customizable features, but having this option for specialized purposes is valuable. The other MacSyFinder feature that I find especially noteworthy is that it can incorporate genomic organization (e.g., of genes ordered in operons) when calling systems. This is a rare feature among commonly used tools for functional annotation and likely results in much higher specificity. As the authors note, this capability makes the co-occurrence of paralogs, and other divergent genes that share sequence similarity, to contribute less noise (i.e., they result in fewer false positive calls). It is important to emphasize that these features are not new additions in MacSyFinder v2, but there are many other valuable changes. Most practically, this release is written in Python 3, rather than the obsolete Python 2.7, and was made more computationally efficient, which will enable MacSyFinder to be more widely used and more easily maintained moving forward. In addition, the search algorithm for analyzing individual proteins was fundamentally updated as well. The authors show that their improvements to the search algorithm result in an 8% and 20% increase in the number of identified calls for single and multi-locus secretion systems, respectively. Taken together, MacSyFinder v2 represents both practical and scientific improvements over the previous version, which will be of great value to the field. References Abby SS, Néron B, Ménager H, Touchon M, Rocha EPC (2014) MacSyFinder: A Program to Mine Genomes for Molecular Systems with an Application to CRISPR-Cas Systems. PLOS ONE, 9, e110726. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110726 Altermann E, Tegetmeyer HE, Chanyi RM (2022) The evolution of bacterial genome assemblies - where do we need to go next? Microbiome Research Reports, 1, 15. https://doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2022.02 Douglas GM, Langille MGI (2021) A primer and discussion on DNA-based microbiome data and related bioinformatics analyses. Peer Community Journal, 1. https://doi.org/10.24072/pcjournal.2 Galperin MY, Wolf YI, Makarova KS, Vera Alvarez R, Landsman D, Koonin EV (2021) COG database update: focus on microbial diversity, model organisms, and widespread pathogens. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, D274–D281. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1018 Néron B, Denise R, Coluzzi C, Touchon M, Rocha EPC, Abby SS (2023) MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomes. bioRxiv, 2022.09.02.506364, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.02.506364 | MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomes | Bertrand Néron, Rémi Denise, Charles Coluzzi, Marie Touchon, Eduardo P. C. Rocha, Sophie S. Abby | <p style="text-align: justify;">Complex cellular functions are usually encoded by a set of genes in one or a few organized genetic loci in microbial genomes. Macromolecular System Finder (MacSyFinder) is a program that uses these properties to mod... |  | Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Functional genomics | Gavin Douglas | Kwee Boon Brandon Seah, Max Emil Schön | 2022-09-09 10:30:31 | View |
24 Feb 2023
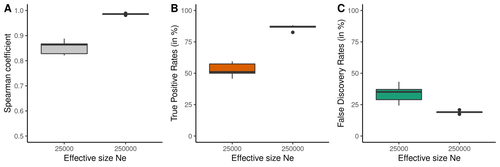
Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation studyMarie Raynaud, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Nicolas Galtier https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.30.486352How to interpret the inference of recombination landscapes on methods based on linkage disequilibrium?Recommended by Sebastian Ernesto Ramos-Onsins based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Data interpretation depends on previously established and validated tools, designed for a specific type of data. These methods, however, are usually based on simple models with validity subject to a set of theoretical parameterized conditions and data types. Accordingly, the tool developers provide the potential users with guidelines for data interpretations within the tools’ limitation. Nevertheless, once the methodology is accepted by the community, it is employed in a large variety of empirical studies outside of the method’s original scope or that typically depart from the standard models used for its design, thus potentially leading to the wrong interpretation of the results. Numerous empirical studies inferred recombination rates across genomes, detecting hotspots of recombination and comparing related species (e.g., Shanfelter et al. 2019, Spence and Song 2019). These studies used indirect methodologies based on the signals that recombination left in the genome, such as linkage disequilibrium and the patterns of haplotype segregation (e.g.,Chan et al. 2012). The conclusions from these analyses have been used, for example, to interpret the evolution of the chromosomal structure or the evolution of recombination among closely related species. Indirect methods have the advantage of collecting a large quantity of recombination events, and thus have a better resolution than direct methods (which only detect the few recombination events occurring at that time). On the other hand, indirect methods are affected by many different evolutionary events, such as demographic changes and selection. Indeed, the inference of recombination levels across the genome has not been studied accurately in non-standard conditions. Linkage disequilibrium is affected by several factors that can modify the recombination inference, such as demographic history, events of selection, population size, and mutation rate, but is also related to the size of the studied sample, and other technical parameters defined for each specific methodology. Raynaud et al (2023) analyzed the reliability of the recombination rate inference when considering the violation of several standard assumptions (evolutionary and methodological) in one of the most popular families of methods based on LDhat (McVean et al. 2004), specifically its improved version, LDhelmet (Chan et al. 2012). These methods cover around 70 % of the studies that infer recombination rates. The authors used recombination maps, obtained from empirical studies on humans, and included hotspots, to perform a detailed simulation study of the capacity of this methodology to correctly infer the pattern of recombination and the location of these hotspots. Correlations between the real, and inferred values from simulations were obtained, as well as several rates, such as the true positive and false discovery rate to detect hotspots. The authors of this work send a message of caution to researchers that are applying this methodology to interpret data from the inference of recombination landscapes and the location of hotspots. The inference of recombination landscapes and hotspots can differ considerably even in standard model conditions. In addition, demographic processes, like bottleneck or admixture, but also the level of population size and mutation rates, can substantially affect the estimation accuracy of the level of recombination and the location of hotspots. Indeed, the inference of the location of hotspots in simulated data with the same landscape, can be very imprecise when standard assumptions are violated or not considered. These effects may lead to incorrect interpretations, for example about the conservation of recombination maps between closely related species. Finally, Raynaud et al (2023) included a useful guide with advice on how to obtain accurate recombination estimations with methods based on linkage disequilibrium, also emphasizing the limitations of such approaches. REFERENCES Chan AH, Jenkins PA, Song YS (2012) Genome-Wide Fine-Scale Recombination Rate Variation in Drosophila melanogaster. PLOS Genetics, 8, e1003090. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003090 McVean GAT, Myers SR, Hunt S, Deloukas P, Bentley DR, Donnelly P (2004) The Fine-Scale Structure of Recombination Rate Variation in the Human Genome. Science, 304, 581–584. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1092500 Raynaud M, Gagnaire P-A, Galtier N (2023) Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation study. bioRxiv, 2022.03.30.486352, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.30.486352 Spence JP, Song YS (2019) Inference and analysis of population-specific fine-scale recombination maps across 26 diverse human populations. Science Advances, 5, eaaw9206. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw9206 | Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation study | Marie Raynaud, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Nicolas Galtier | <p style="text-align: justify;">Knowledge of recombination rate variation along the genome provides important insights into genome and phenotypic evolution. Population genomic approaches offer an attractive way to infer the population-scaled recom... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Population genomics | Sebastian Ernesto Ramos-Onsins | 2022-04-05 14:59:14 | View | |
07 Feb 2023
RAREFAN: A webservice to identify REPINs and RAYTs in bacterial genomesFrederic Bertels, Julia von Irmer, Carsten Fortmann-Grote https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.22.493013A workflow for studying enigmatic non-autonomous transposable elements across bacteriaRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by Sophie Abby and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Sophie Abby and 1 anonymous reviewer
Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences (REPs) are common repetitive elements in bacterial genomes (Gilson et al., 1984; Stern et al., 1984). In 2011, Bertels and Rainey identified that REPs are overrepresented in pairs of inverted repeats, which likely form hairpin structures, that they referred to as “REP doublets forming hairpins” (REPINs). Based on bioinformatics analyses, they argued that REPINs are likely selfish elements that evolved from REPs flanking particular transposes (Bertels and Rainey, 2011). These transposases, so-called REP-associated tyrosine transposases (RAYTs), were known to be highly associated with the REP content in a genome and to have characteristic upstream and downstream flanking REPs (Nunvar et al., 2010). The flanking REPs likely enable RAYT transposition, and their horizontal replication is physically linked to this process. In contrast, Bertels and Rainey hypothesized that REPINs are selfish elements that are highly replicated due to the similarity in arrangement to these RAYT-flanking REPs, but independent of RAYT transposition and generally with no impact on bacterial fitness (Bertels and Rainey, 2011). This last point was especially contentious, as REPINs are highly conserved within species (Bertels and Rainey, 2023), which is unusual for non-beneficial bacterial DNA (Mira et al., 2001). Bertels and Rainey have since refined their argument to be that REPINs must provide benefits to host cells, but that there are nonetheless signatures of intragenomic conflict in genomes associated with these elements (Bertels and Rainey, 2023). These signatures reflect the divergent levels of selections driving REPIN distribution: selection at the level of each DNA element and selection on each individual bacterium. I found this observation particularly interesting as I and my colleague recently argued that these divergent levels of selection, and the interaction between them, is key to understanding bacterial pangenome diversity (Douglas and Shapiro, 2021). REPINs could be an excellent system for investigating these levels of selection across bacteria more generally. The problem is that REPINs have not been widely characterized in bacterial genomes, partially because no bioinformatic workflow has been available for this purpose. To address this problem, Fortmann-Grote et al. (2023) developed RAREFAN, which is a web server for identifying RAYTs and associated REPINs in a set of input genomes. The authors showcase their tool by applying it to 49 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia genomes and providing examples of how to identify and assess RAYT-REPIN hits. The workflow requires several manual steps, but nonetheless represents a straightforward and standardized approach. Overall, this workflow should enable RAYTs and REPINs to be identified across diverse bacterial species, which will facilitate further investigation into the mechanisms driving their maintenance and spread. References Bertels F, Rainey PB (2023) Ancient Darwinian replicators nested within eubacterial genomes. BioEssays, 45, 2200085. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.202200085 Bertels F, Rainey PB (2011) Within-Genome Evolution of REPINs: a New Family of Miniature Mobile DNA in Bacteria. PLOS Genetics, 7, e1002132. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002132 Douglas GM, Shapiro BJ (2021) Genic Selection Within Prokaryotic Pangenomes. Genome Biology and Evolution, 13, evab234. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evab234 Fortmann-Grote C, Irmer J von, Bertels F (2023) RAREFAN: A webservice to identify REPINs and RAYTs in bacterial genomes. bioRxiv, 2022.05.22.493013, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.22.493013 Gilson E, Clément J m., Brutlag D, Hofnung M (1984) A family of dispersed repetitive extragenic palindromic DNA sequences in E. coli. The EMBO Journal, 3, 1417–1421. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01986.x Mira A, Ochman H, Moran NA (2001) Deletional bias and the evolution of bacterial genomes. Trends in Genetics, 17, 589–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(01)02447-7 Nunvar J, Huckova T, Licha I (2010) Identification and characterization of repetitive extragenic palindromes (REP)-associated tyrosine transposases: implications for REP evolution and dynamics in bacterial genomes. BMC Genomics, 11, 44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-44 Stern MJ, Ames GF-L, Smith NH, Clare Robinson E, Higgins CF (1984) Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: A major component of the bacterial genome. Cell, 37, 1015–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7 | RAREFAN: A webservice to identify REPINs and RAYTs in bacterial genomes | Frederic Bertels, Julia von Irmer, Carsten Fortmann-Grote | <p style="text-align: justify;">Compared to eukaryotes, repetitive sequences are rare in bacterial genomes and usually do not persist for long. Yet, there is at least one class of persistent prokaryotic mobile genetic elements: REPINs. REPINs are ... | Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Gavin Douglas | 2022-06-07 08:21:34 | View | ||
16 Dec 2022
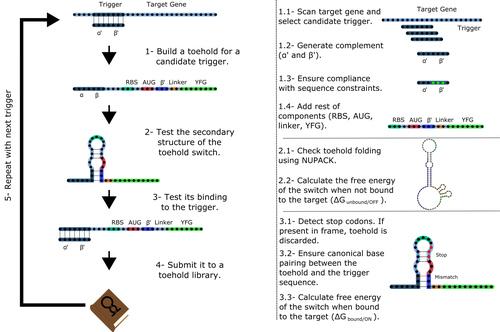
Toeholder: a Software for Automated Design and In Silico Validation of Toehold RiboswitchesAngel F. Cisneros, François D. Rouleau, Carla Bautista, Pascale Lemieux, Nathan Dumont-Leblond https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.09.467922A novel approach for engineering biological systems by interfacing computer science with synthetic biologyRecommended by Sahar Melamed based on reviews by Wim Wranken and 1 anonymous reviewerBiological systems depend on finely tuned interactions of their components. Thus, regulating these components is critical for the system's functionality. In prokaryotic cells, riboswitches are regulatory elements controlling transcription or translation. Riboswitches are RNA molecules that are usually located in the 5′-untranslated region of protein-coding genes. They generate secondary structures leading to the regulation of the expression of the downstream protein-coding gene (Kavita and Breaker, 2022). Riboswitches are very versatile and can bind a wide range of small molecules; in many cases, these are metabolic byproducts from the gene’s enzymatic or signaling pathway. Their versatility and abundance in many species make them attractive for synthetic biological circuits. One class that has been drawing the attention of synthetic biologists is toehold switches (Ekdahl et al., 2022; Green et al., 2014). These are single-stranded RNA molecules harboring the necessary elements for translation initiation of the downstream gene: a ribosome-binding site and a start codon. Conformation change of toehold switches is triggered by an RNA molecule, which enables translation. To exploit the most out of toehold switches, automation of their design would be highly advantageous. Cisneros and colleagues (Cisneros et al., 2022) developed a tool, “Toeholder”, that automates the design of toehold switches and performs in silico tests to select switch candidates for a target gene. Toeholder is an open-source tool that provides a comprehensive and automated workflow for the design of toehold switches. While web tools have been developed for designing toehold switches (To et al., 2018), Toeholder represents an intriguing approach to engineering biological systems by coupling synthetic biology with computational biology. Using molecular dynamics simulations, it identified the positions in the toehold switch where hydrogen bonds fluctuate the most. Identifying these regions holds great potential for modifications when refining the design of the riboswitches. To be effective, toehold switches should provide a strong ON signal and a weak OFF signal in the presence or the absence of a target, respectively. Toeholder nicely ranks the candidate toehold switches based on experimental evidence that correlates with toehold performance (based on good ON/OFF ratios). Riboswitches are highly appealing for a broad range of applications, including pharmaceutical and medical purposes (Blount and Breaker, 2006; Giarimoglou et al., 2022; Tickner and Farzan, 2021), thanks to their adaptability and inexpensiveness. The Toeholder tool developed by Cisneros and colleagues is expected to promote the implementation of toehold switches into these various applications. References Blount KF, Breaker RR (2006) Riboswitches as antibacterial drug targets. Nature Biotechnology, 24, 1558–1564. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1268 Cisneros AF, Rouleau FD, Bautista C, Lemieux P, Dumont-Leblond N, ULaval 2019 T iGEM (2022) Toeholder: a Software for Automated Design and In Silico Validation of Toehold Riboswitches. bioRxiv, 2021.11.09.467922, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.09.467922 Ekdahl AM, Rojano-Nisimura AM, Contreras LM (2022) Engineering Toehold-Mediated Switches for Native RNA Detection and Regulation in Bacteria. Journal of Molecular Biology, 434, 167689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167689 Giarimoglou N, Kouvela A, Maniatis A, Papakyriakou A, Zhang J, Stamatopoulou V, Stathopoulos C (2022) A Riboswitch-Driven Era of New Antibacterials. Antibiotics, 11, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091243 Green AA, Silver PA, Collins JJ, Yin P (2014) Toehold Switches: De-Novo-Designed Regulators of Gene Expression. Cell, 159, 925–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.002 Kavita K, Breaker RR (2022) Discovering riboswitches: the past and the future. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2022.08.009 Tickner ZJ, Farzan M (2021) Riboswitches for Controlled Expression of Therapeutic Transgenes Delivered by Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors. Pharmaceuticals, 14, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060554 To AC-Y, Chu DH-T, Wang AR, Li FC-Y, Chiu AW-O, Gao DY, Choi CHJ, Kong S-K, Chan T-F, Chan K-M, Yip KY (2018) A comprehensive web tool for toehold switch design. Bioinformatics, 34, 2862–2864. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty216 | Toeholder: a Software for Automated Design and In Silico Validation of Toehold Riboswitches | Angel F. Cisneros, François D. Rouleau, Carla Bautista, Pascale Lemieux, Nathan Dumont-Leblond | <p>Abstract: Synthetic biology aims to engineer biological circuits, which often involve gene expression. A particularly promising group of regulatory elements are riboswitches because of their versatility with respect to their targets, but e... |  | Bioinformatics | Sahar Melamed | 2022-02-16 14:40:13 | View | |
15 Dec 2022

Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAsAdeline Simon, Alex Mercier, Pierre Gladieux, Benoit Poinssot, Anne-Sophie Walker, Muriel Viaud https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.07.483234Exploring genomic determinants of host specialization in Botrytis cinereaRecommended by Sebastien Duplessis based on reviews by Cecile Lorrain and Thorsten LangnerThe genomics era has pushed forward our understanding of fungal biology. Much progress has been made in unraveling new gene functions and pathways, as well as the evolution or adaptation of fungi to their hosts or environments through population studies (Hartmann et al. 2019; Gladieux et al. 2018). Closing gaps more systematically in draft genomes using the most recent long-read technologies now seems the new standard, even with fungal species presenting complex genome structures (e.g. large and highly repetitive dikaryotic genomes; Duan et al. 2022). Understanding the genomic dynamics underlying host specialization in phytopathogenic fungi is of utmost importance as it may open new avenues to combat diseases. A strong host specialization is commonly observed for biotrophic and hemi-biotrophic fungal species or for necrotrophic fungi with a narrow host range, whereas necrotrophic fungi with broad host range are considered generalists (Liang and Rollins, 2018; Newman and Derbyshire, 2020). However, some degrees of specialization towards given hosts have been reported in generalist fungi and the underlying mechanisms remain to be determined. Botrytis cinerea is a polyphagous necrotrophic phytopathogen with a particularly wide host range and it is notably responsible for grey mould disease on many fruits, such as tomato and grapevine. Because of its importance as a plant pathogen, its relatively small genome size and its taxonomical position, it has been targeted for early genome sequencing and a first reference genome was provided in 2011 (Amselem et al. 2011). Other genomes were subsequently sequenced for other strains, and most importantly a gapless assembled version of the initial reference genome B05.10 was provided to the community (van Kan et al. 2017). This genomic resource has supported advances in various aspects of the biology of B. cinerea such as the production of specialized metabolites, which plays an important role in host-plant colonization, or more recently in the production of small RNAs which interfere with the host immune system, representing a new class of non-proteinaceous virulence effectors (Dalmais et al. 2011; Weiberg et al. 2013). In the present study, Simon et al. (2022) use PacBio long-read sequencing for Sl3 and Vv3 strains, which represent genetic clusters in B. cinerea populations found on tomato and grapevine. The authors combined these complete and high-quality genome assemblies with the B05.10 reference genome and population sequencing data to perform a comparative genomic analysis of specialization towards the two host plants. Transposable elements generate genomic diversity due to their mobile and repetitive nature and they are of utmost importance in the evolution of fungi as they deeply reshape the genomic landscape (Lorrain et al. 2021). Accessory chromosomes are also known drivers of adaptation in fungi (Möller and Stukenbrock, 2017). Here, the authors identify several genomic features such as the presence of different sets of accessory chromosomes, the presence of differentiated repertoires of transposable elements, as well as related small RNAs in the tomato and grapevine populations, all of which may be involved in host specialization. Whereas core chromosomes are highly syntenic between strains, an accessory chromosome validated by pulse-field electrophoresis is specific of the strains isolated from grapevine. Particularly, they show that two particular retrotransposons are discriminant between the strains and that they allow the production of small RNAs that may act as effectors. The discriminant accessory chromosome of the Vv3 strain harbors one of the unraveled retrotransposons as well as new genes of yet unidentified function. I recommend this article because it perfectly illustrates how efforts put into generating reference genomic sequences of higher quality can lead to new discoveries and allow to build strong hypotheses about biology and evolution in fungi. Also, the study combines an up-to-date genomics approach with a classical methodology such as pulse-field electrophoresis to validate the presence of accessory chromosomes. A major input of this investigation of the genomic determinants of B. cinerea is that it provides solid hints for further analysis of host-specialization at the population level in a broad-scale phytopathogenic fungus. References Amselem J, Cuomo CA, Kan JAL van, Viaud M, Benito EP, Couloux A, Coutinho PM, Vries RP de, Dyer PS, Fillinger S, Fournier E, Gout L, Hahn M, Kohn L, Lapalu N, Plummer KM, Pradier J-M, Quévillon E, Sharon A, Simon A, Have A ten, Tudzynski B, Tudzynski P, Wincker P, Andrew M, Anthouard V, Beever RE, Beffa R, Benoit I, Bouzid O, Brault B, Chen Z, Choquer M, Collémare J, Cotton P, Danchin EG, Silva CD, Gautier A, Giraud C, Giraud T, Gonzalez C, Grossetete S, Güldener U, Henrissat B, Howlett BJ, Kodira C, Kretschmer M, Lappartient A, Leroch M, Levis C, Mauceli E, Neuvéglise C, Oeser B, Pearson M, Poulain J, Poussereau N, Quesneville H, Rascle C, Schumacher J, Ségurens B, Sexton A, Silva E, Sirven C, Soanes DM, Talbot NJ, Templeton M, Yandava C, Yarden O, Zeng Q, Rollins JA, Lebrun M-H, Dickman M (2011) Genomic Analysis of the Necrotrophic Fungal Pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLOS Genetics, 7, e1002230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002230 Dalmais B, Schumacher J, Moraga J, Le Pêcheur P, Tudzynski B, Collado IG, Viaud M (2011) The Botrytis cinerea phytotoxin botcinic acid requires two polyketide synthases for production and has a redundant role in virulence with botrydial. Molecular Plant Pathology, 12, 564–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00692.x Duan H, Jones AW, Hewitt T, Mackenzie A, Hu Y, Sharp A, Lewis D, Mago R, Upadhyaya NM, Rathjen JP, Stone EA, Schwessinger B, Figueroa M, Dodds PN, Periyannan S, Sperschneider J (2022) Physical separation of haplotypes in dikaryons allows benchmarking of phasing accuracy in Nanopore and HiFi assemblies with Hi-C data. Genome Biology, 23, 84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-022-02658-2 Gladieux P, Condon B, Ravel S, Soanes D, Maciel JLN, Nhani A, Chen L, Terauchi R, Lebrun M-H, Tharreau D, Mitchell T, Pedley KF, Valent B, Talbot NJ, Farman M, Fournier E (2018) Gene Flow between Divergent Cereal- and Grass-Specific Lineages of the Rice Blast Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. mBio, 9, e01219-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01219-17 Hartmann FE, Rodríguez de la Vega RC, Carpentier F, Gladieux P, Cornille A, Hood ME, Giraud T (2019) Understanding Adaptation, Coevolution, Host Specialization, and Mating System in Castrating Anther-Smut Fungi by Combining Population and Comparative Genomics. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 57, 431–457. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082718-095947 Liang X, Rollins JA (2018) Mechanisms of Broad Host Range Necrotrophic Pathogenesis in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathology®, 108, 1128–1140. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-06-18-0197-RVW Lorrain C, Oggenfuss U, Croll D, Duplessis S, Stukenbrock E (2021) Transposable Elements in Fungi: Coevolution With the Host Genome Shapes, Genome Architecture, Plasticity and Adaptation. In: Encyclopedia of Mycology (eds Zaragoza Ó, Casadevall A), pp. 142–155. Elsevier, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819990-9.00042-1 Möller M, Stukenbrock EH (2017) Evolution and genome architecture in fungal plant pathogens. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 15, 756–771. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.76 Newman TE, Derbyshire MC (2020) The Evolutionary and Molecular Features of Broad Host-Range Necrotrophy in Plant Pathogenic Fungi. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.591733 Simon A, Mercier A, Gladieux P, Poinssot B, Walker A-S, Viaud M (2022) Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAs. bioRxiv, 2022.03.07.483234, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.07.483234 Van Kan JAL, Stassen JHM, Mosbach A, Van Der Lee TAJ, Faino L, Farmer AD, Papasotiriou DG, Zhou S, Seidl MF, Cottam E, Edel D, Hahn M, Schwartz DC, Dietrich RA, Widdison S, Scalliet G (2017) A gapless genome sequence of the fungus Botrytis cinerea. Molecular Plant Pathology, 18, 75–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12384 Weiberg A, Wang M, Lin F-M, Zhao H, Zhang Z, Kaloshian I, Huang H-D, Jin H (2013) Fungal Small RNAs Suppress Plant Immunity by Hijacking Host RNA Interference Pathways. Science, 342, 118–123. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1239705 | Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAs | Adeline Simon, Alex Mercier, Pierre Gladieux, Benoit Poinssot, Anne-Sophie Walker, Muriel Viaud | <p style="text-align: justify;">The fungus <em>Botrytis cinerea</em> is a polyphagous pathogen that encompasses multiple host-specialized lineages. While several secreted proteins, secondary metabolites and retrotransposons-derived small RNAs have... |  | Fungi, Structural genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Sebastien Duplessis | Cecile Lorrain, Thorsten Langner | 2022-03-15 11:15:48 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Gavin Douglas
Jean-François Flot
Danny Ionescu










