
NAWAE Wanapinun
- National Omics Center, National Science and Technology Development Agency, Pathum Thani, Thailand
- Bioinformatics, Plants
- recommender
Recommendation: 1
Reviews: 0
Recommendation: 1
SNP discovery by exome capture and resequencing in a pea genetic resource collection
The value of a large Pisum SNP dataset
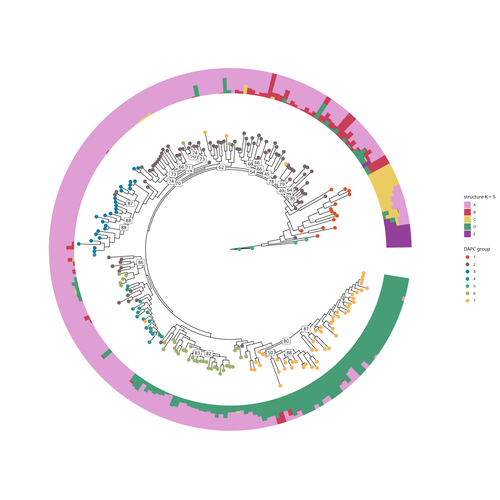
Recommended by Wanapinun Nawae based on reviews by Rui Borges and 1 anonymous reviewerOne important goal of modern genetics is to establish functional associations between genotype and phenotype. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are numerous and widely distributed in the genome and can be obtained from nucleic acid sequencing (1). SNPs allow for the investigation of genetic diversity, which is critical for increasing crop resilience to the challenges posed by global climate change. The associations between SNPs and phenotypes can be captured in genome-wide association studies. SNPs can also be used in combination with machine learning, which is becoming more popular for predicting complex phenotypic traits like yield and biotic and abiotic stress tolerance from genotypic data (2). The availability of many SNP datasets is important in machine learning predictions because this approach requires big data to build a comprehensive model of the association between genotype and phenotype.
Aubert and colleagues have studied, as part of the PeaMUST project, the genetic diversity of 240 Pisum accessions (3). They sequenced exome-enriched genomic libraries, a technique that enables the identification of high-density, high-quality SNPs at a low cost (4). This technique involves capturing and sequencing only the exonic regions of the genome, which are the protein-coding regions. A total of 2,285,342 SNPs were obtained in this study. The analysis of these SNPs with the annotations of the genome sequence of one of the studied pea accessions (5) identified a number of SNPs that could have an impact on gene activity. Additional analyses revealed 647,220 SNPs that were unique to individual pea accessions, which might contribute to the fitness and diversity of accessions in different habitats. Phylogenetic and clustering analyses demonstrated that the SNPs could distinguish Pisum germplasms based on their agronomic and evolutionary histories. These results point out the power of selected SNPs as markers for identifying Pisum individuals.
Overall, this study found high-quality SNPs that are meaningful in a biological context. This dataset was derived from a large set of germplasm and is thus particularly useful for studying genotype-phenotype associations, as well as the diversity within Pisum species. These SNPs could also be used in breeding programs to develop new pea varieties that are resilient to abiotic and biotic stressors.
References
1. Fallah M, Jean M, Boucher St-Amour VT, O’Donoughue L, Belzile F. The construction of a high-density consensus genetic map for soybean based on SNP markers derived from genotyping-by-sequencing. Genome. 2022 Aug;65(8):413–25.
https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2021-005
2. Gill M, Anderson R, Hu H, Bennamoun M, Petereit J, Valliyodan B, et al. Machine learning models outperform deep learning models, provide interpretation and facilitate feature selection for soybean trait prediction. BMC Plant Biology. 2022 Apr 8;22(1):180.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03559-z
3. Aubert G, Kreplak J, Leveugle M, Duborjal H, Klein A, Boucherot K, et al. SNP discovery by exome capture and resequencing in a pea genetic resource collection., biorxiv, ver. 4, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics.
https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.03.502586
4. Warr A, Robert C, Hume D, Archibald A, Deeb N, Watson M. Exome sequencing: current and future perspectives. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics. 2015 Aug 1;5(8):1543–50.
https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.115.018564
5. Kreplak J, Madoui MA, Cápal P, Novák P, Labadie K, Aubert G, et al. A reference genome for pea provides insight into legume genome evolution. Nat Genet. 2019 Sep;51(9):1411–22.