
IRISARRI Iker
- Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales, Madrid, Spain
- Bioinformatics, ERGA, Evolutionary genomics, Plants, Vertebrates
- recommender, manager, administrator
Recommendations: 4
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 4

Chromosome level genome reference of the Caucasian dwarf goby Knipowitschia cf. caucasica, a new alien Gobiidae invading the River Rhine
New chromosome-scale genome assembly for the Dwarf Goby, a River Rhine invader
Recommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Tereza Manousaki, Ruiqi Li and 1 anonymous reviewerSince the opening of the Rhine-Main-Danube-Channel, four goby species are known to have invaded the River Rhine. Of these, the most recent and numerous is the Caucasian Dwarf Goby, which has been found in the Rhine since 2019. This study presents a new high-quality genome for this species (Knipowitschia cf. caucasica) (Schoenle et al. 2024). Currently, chromosome-scale genome assemblies represent a key first step in invasion biology, allowing the reconstruction of a species’ invasion history and monitoring its progress, as well as identifying and characterizing candidate genes that control invasiveness (McCartney et al. 2019).
The authors sequenced the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes of this species using state-of-the art methods including long-read sequencing techniques, scaffolded based on chromatin conformation data, and annotated using both direct transcriptomic and protein homology evidence. Data analyses follow currently established pipelines for genome assembly, scaffolding, annotation, and downstream bioinformatic analyses. The quality of the final genome was thoroughly assessed and conforms to what is expected from other genomes of fishes in the family Gobiidae. This study follows other recent endeavors that generated high-quality genomes to improve our understanding of invasion biology (e.g. Shao et al. 2020 and Kitsoulis et al. 2023). These studies are successfully contributing to increasing the genomic resources for the world’s most damaging invasive species, which were not available for even a third of the top 100 invasive species just five years ago (McCarthy et al. 2019). Beyond invasion biology, the Dwarf Goby genome is also an important resource for many other applications, including evolutionary genomic analyses and phylogeography of this species and closely related ones in their native ranges.
References
Kitsoulis CV, Papadogiannis V, Kristoffersen JB, Kaitetzidou E, Sterioti A, Tsigenopoulos CS, Manousaki T (2023) Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois miles. Peer Community Journal 3:e64. https://doi.org/10.24072/pcjournal.295
McCartney MA, Mallez S, Gohl DM (2019) Genome projects in invasion biology. Conservation Genetics 20:1201–1222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-019-01224-x
Schoenle A, Guiglielmoni N, Mainz T, Greve C, Hamadou AB, Heermann L, Borcherding J, Waldvogel A-M (2024) Chromosome level genome reference of the Caucasian dwarf goby Knipowitschia cf. caucasica, a new alien Gobiidae invading the River Rhine. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.22.590508
Shao F, Ludwig A, Mao Y, Liu N, Peng Z (2020). Chromosome-level genome assembly of the female western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). GigaScience 9:giaa092. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giaa092

High quality genome assembly and annotation (v1) of the eukaryotic terrestrial microalga Coccomyxa viridis SAG 216-4
Reference genome for the lichen-forming green alga Coccomyxa viridis SAG 216–4
Recommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Elisa Goldbecker, Fabian Haas and 2 anonymous reviewersGreen algae of the genus Coccomyxa (family Trebouxiophyceae) are extremely diverse in their morphology, habitat (i.e., in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments) and lifestyle, including free-living and mutualistic forms. Coccomyxa viridis (strain SAG 216–4) is a photobiont in the lichen Peltigera aphthosa, which was isolated in Switzerland more than 70 years ago (cf. SAG, the Culture Collection of Algae at the University of Göttingen, Germany). Despite the high diversity and plasticity in Coccomyxa, integrative taxonomic analyses led Darienko et al. (2015) to propose clear species boundaries. These authors also showed that symbiotic strains that form lichens evolved multiple times independently in Coccomyxa.
Using state-of-the-art sequencing data and bioinformatic methods, including Pac-Bio HiFi and ONT long reads, as well as Hi-C chromatin conformation information, Kraege et al. (2024) generated a high-quality genome assembly for the Coccomyxa viridis strain SAG 216–4. They reconstructed 19 complete nuclear chromosomes, flanked by telomeric regions, totaling 50.9 Mb, plus the plastid and mitochondrial genomes. The performed quality controls leave no doubt of the high quality of the genome assemblies and structural annotations. An interesting observation is the lack of conserved synteny with the close relative Coccomyxa subellipsoidea, but further comparative studies with additional Coccomyxa strains will be required to grasp the genomic evolution in this genus of green algae. This project is framed within the ERGA pilot project, which aims to establish a pan-European genomics infrastructure and contribute to cataloging genomic biodiversity and producing resources that can inform conservation strategies (Formenti et al. 2022). This complete reference genome represents an important step towards this goal, in addition to contributing to future genomic analyses of Coccomyxa more generally.
References
Darienko T, Gustavs L, Eggert A, Wolf W, Pröschold T (2015) Evaluating the species boundaries of green microalgae (Coccomyxa, Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) using integrative taxonomy and DNA barcoding with further implications for the species identification in environmental samples. PLOS ONE, 10, e0127838. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127838
Formenti G, Theissinger K, Fernandes C, Bista I, Bombarely A, Bleidorn C, Ciofi C, Crottini A, Godoy JA, Höglund J, Malukiewicz J, Mouton A, Oomen RA, Paez S, Palsbøll PJ, Pampoulie C, Ruiz-López MJ, Svardal H, Theofanopoulou C, de Vries J, Waldvogel A-M, Zhang G, Mazzoni CJ, Jarvis ED, Bálint M, European Reference Genome Atlas Consortium (2022) The era of reference genomes in conservation genomics. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 37, 197–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2021.11.008
Kraege A, Chavarro-Carrero EA, Guiglielmoni N, Schnell E, Kirangwa J, Heilmann-Heimbach S, Becker K, Köhrer K, WGGC Team, DeRGA Community, Schiffer P, Thomma BPHJ, Rovenich H (2024) High quality genome assembly and annotation (v1) of the eukaryotic terrestrial microalga Coccomyxa viridis SAG 216-4. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.11.548521
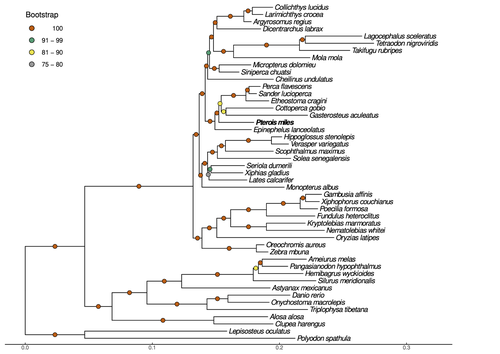
Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois miles
The genome of a dangerous invader (fish) beauty
Recommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Maria Recuerda and 1 anonymous reviewerHigh-quality genomes are currently being generated at an unprecedented speed powered by long-read sequencing technologies. However, sequencing effort is concentrated unequally across the tree of life and several key evolutionary and ecological groups remain largely unexplored. So is the case for fish species of the family Scorpaenidae (Perciformes). Kitsoulis et al. present the genome of the devil firefish, Pterois miles (1). Following current best practices, the assembly relies largely on Oxford Nanopore long reads, aided by Illumina short reads for polishing to increase the per-base accuracy. PacBio’s IsoSeq was used to sequence RNA from a variety of tissues as direct evidence for annotating genes. The reconstructed genome is 902 Mb in size and has high contiguity (N50=14.5 Mb; 660 scaffolds, 90% of the genome covered by the 83 longest scaffolds) and completeness (98% BUSCO completeness). The new genome is used to assess the phylogenetic position of P. miles, explore gene synteny against zebrafish, look at orthogroup expansion and contraction patterns in Perciformes, as well as to investigate the evolution of toxins in scorpaenid fish (2). In addition to its value for better understanding the evolution of scorpaenid and teleost fishes, this new genome is also an important resource for monitoring its invasiveness through the Mediterranean Sea (3) and the Atlantic Ocean, in the latter case forming the invasive lionfish complex with P. volitans (4).
REFERENCES
1. Kitsoulis CV, Papadogiannis V, Kristoffersen JB, Kaitetzidou E, Sterioti E, Tsigenopoulos CS, Manousaki T. (2023) Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois miles. BioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.10.523469
2. Kiriake A, Shiomi K. (2011) Some properties and cDNA cloning of proteinaceous toxins from two species of lionfish (Pterois antennata and Pterois volitans). Toxicon, 58(6-7):494–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.08.010
3. Katsanevakis S, et al. (2020) Un- published Mediterranean records of marine alien and cryptogenic species. BioInvasions Records, 9:165–182. https://doi.org/10.3391/bir.2020.9.2.01
4. Lyons TJ, Tuckett QM, Hill JE. (2019) Data quality and quantity for invasive species: A case study of the lionfishes. Fish and Fisheries, 20:748–759. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12374
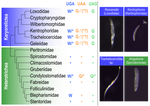
Karyorelict ciliates use an ambiguous genetic code with context-dependent stop/sense codons
An accident frozen in time: the ambiguous stop/sense genetic code of karyorelict ciliates
Recommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Vittorio Boscaro and 2 anonymous reviewersSeveral variations of the “universal” genetic code are known. Among the most striking are those where a codon can either encode for an amino acid or a stop signal depending on the context. Such ambiguous codes are known to have evolved in eukaryotes multiple times independently, particularly in ciliates – eight different codes have so far been discovered (1). We generally view such genetic codes are rare ‘variants’ of the standard code restricted to single species or strains, but this might as well reflect a lack of study of closely related species. In this study, Seah and co-authors (2) explore the possibility of codon reassignment in karyorelict ciliates closely related to Parduczia sp., which has been shown to contain an ambiguous genetic code (1). Here, single-cell transcriptomics are used, along with similar available data, to explore the possibility of codon reassignment across the diversity of Karyorelictea (four out of the six recognized families). Codon reassignments were inferred from their frequencies within conserved Pfam (3) protein domains, whereas stop codons were inferred from full-length transcripts with intact 3’-UTRs.
Results show the reassignment of UAA and UAG stop codons to code for glutamine (Q) and the reassignment of the UGA stop codon into tryptophan (W). This occurs only within the coding sequences, whereas the end of transcription is marked by UGA as the main stop codon, and to a lesser extent by UAA. In agreement with a previous model proposed that explains the functioning of ambiguous codes (1,4), the authors observe a depletion of in-frame UGAs before the UGA codon that indicates the stop, thus avoiding premature termination of transcription. The inferred codon reassignments occur in all studied karyorelicts, including the previously studied Parduczia sp. Despite the overall clear picture, some questions remain. Data for two out of six main karyorelict lineages are so far absent and the available data for Cryptopharyngidae was inconclusive; the phylogenetic affinities of Cryptopharyngidae have also been questioned (5). This indicates the need for further study of this interesting group of organisms. As nicely discussed by the authors, experimental evidence could further strengthen the conclusions of this paper, including ribosome profiling, mass spectrometry – as done for Condylostoma (1) – or even direct genetic manipulation.
The uniformity of the ambiguous genetic code across karyorelicts might at first seem dull, but when viewed in a phylogenetic context character distribution strongly suggest that this genetic code has an ancient origin in the karyorelict ancestor ~455 Ma in the Proterozoic (6). This ambiguous code is also not a rarity of some obscure species, but it is shared by ciliates that are very diverse and ecologically important. The origin of the karyorelict code is also intriguing. Adaptive arguments suggest that it could confer robustness to mutations causing premature stop codons. However, we lack evidence for ambiguous codes being linked to specific habitats of lifestyles that could account for it. Instead, the authors favor the neutral view of an ancient “frozen accident”, fixed stochastically simply because it did not pose a significant selective disadvantage. Once a stop codon is reassigned to an amino acid, it is increasingly difficult to revert this without the deleterious effect of prematurely terminating translation. At the end, the origin of the genetic code itself is thought to be a frozen accident too (7).
References
1. Swart EC, Serra V, Petroni G, Nowacki M. Genetic codes with no dedicated stop codon: Context-dependent translation termination. Cell 2016;166: 691–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.020
2. Seah BKB, Singh A, Swart EC (2022) Karyorelict ciliates use an ambiguous genetic code with context-dependent stop/sense codons. bioRxiv, 2022.04.12.488043. ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.12.488043
3. Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, Qureshi M, Salazar GA, Sonnhammer ELL, Tosatto SCE, Paladin L, Raj S, Richardson LJ, Finn RD, Bateman A. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021, Nuc Acids Res 2020;49: D412-D419. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa913
4. Alkalaeva E, Mikhailova T. Reassigning stop codons via translation termination: How a few eukaryotes broke the dogma. Bioessays. 2017;39. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201600213
5. Xu Y, Li J, Song W, Warren A. Phylogeny and establishment of a new ciliate family, Wilbertomorphidae fam. nov. (Ciliophora, Karyorelictea), a highly specialized taxon represented by Wilbertomorpha colpoda gen. nov., spec. nov. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2013;60: 480–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12055
6. Fernandes NM, Schrago CG. A multigene timescale and diversification dynamics of Ciliophora evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2019;139: 106521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106521
7. Crick FH. The origin of the genetic code. J Mol Biol. 1968;38: 367–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(68)90392-6