Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers▼ | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
09 Oct 2020
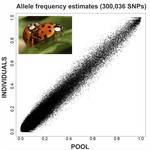
An evaluation of pool-sequencing transcriptome-based exon capture for population genomics in non-model speciesEmeline Deleury, Thomas Guillemaud, Aurélie Blin & Eric Lombaert https://doi.org/10.1101/583534Assessing a novel sequencing-based approach for population genomics in non-model speciesRecommended by Thomas Derrien and Sebastian E. Ramos-Onsins based on reviews by Valentin Wucher and 1 anonymous reviewerDeveloping new sequencing and bioinformatic strategies for non-model species is of great interest in many applications, such as phylogenetic studies of diverse related species, but also for studies in population genomics, where a relatively large number of individuals is necessary. Different approaches have been developed and used in these last two decades, such as RAD-Seq (e.g., Miller et al. 2007), exome sequencing (e.g., Teer and Mullikin 2010) and other genome reduced representation methods that avoid the use of a good reference and well annotated genome (reviewed at Davey et al. 2011). However, population genomics studies require the analysis of numerous individuals, which makes the studies still expensive. Pooling samples was thought as an inexpensive strategy to obtain estimates of variability and other related to the frequency spectrum, thus allowing the study of variability at population level (e.g., Van Tassell et al. 2008), although the major drawback was the loss of information related to the linkage of the variants. In addition, population analysis using all these sequencing strategies require statistical and empirical validations that are not always fully performed. A number of studies aiming to obtain unbiased estimates of variability using reduced representation libraries and/or with pooled data have been performed (e.g., Futschik and Schlötterer 2010, Gautier et al. 2013, Ferretti et al. 2013, Lynch et al. 2014), as well as validation of new sequencing methods for population genetic analyses (e.g., Gautier et al. 2013, Nevado et al. 2014). Nevertheless, empirical validation using both pooled and individual experimental approaches combined with different bioinformatic methods has not been always performed. References [1] Choquet et al. (2019). Towards population genomics in non-model species with large genomes: a case study of the marine zooplankton Calanus finmarchicus. Royal Society open science, 6(2), 180608. doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.180608 | An evaluation of pool-sequencing transcriptome-based exon capture for population genomics in non-model species | Emeline Deleury, Thomas Guillemaud, Aurélie Blin & Eric Lombaert | <p>Exon capture coupled to high-throughput sequencing constitutes a cost-effective technical solution for addressing specific questions in evolutionary biology by focusing on expressed regions of the genome preferentially targeted by selection. Tr... |  | Bioinformatics, Population genomics | Thomas Derrien | 2020-02-26 09:21:11 | View | |
11 Mar 2021

Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stagesThibault Scalvenzi, Isabelle Clavereau, Mickael Bourge, Nicolas Pollet https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.25.110734A comprehensive look at Xenopus gut microbiota: effects of feed, developmental stages and parental transmissionRecommended by Wirulda Pootakham based on reviews by Vanessa Marcelino and 1 anonymous reviewerIt is well established that the gut microbiota play an important role in the overall health of their hosts (Jandhyala et al. 2015). To date, there are still a limited number of studies on the complex microbial communites inhabiting vertebrate digestive systems, especially the ones that also explored the functional diversity of the microbial community (Bletz et al. 2016). This preprint by Scalvenzi et al. (2021) reports a comprehensive study on the phylogenetic and metabolic profiles of the Xenopus gut microbiota. The author describes significant changes in the gut microbiome communities at different developmental stages and demonstrates different microbial community composition across organs. In addition, the study also investigates the impact of diet on the Xenopus tadpole gut microbiome communities as well as how the bacterial communities are transmitted from parents to the next generation. This is one of the first studies that addresses the interactions between gut bacteria and tadpoles during the development. The authors observe the dynamics of gut microbiome communities during tadpole growth and metamorphosis. They also explore host-gut microbial community metabolic interactions and demostrate the capacity of the microbiome to complement the metabolic pathways of the Xenopus genome. Although this study is limited by the use of Xenopus tadpoles in a laboratory, which are probably different from those in nature, I believe it still provides important and valuable information for the research community working on vertebrate’s microbiota and their interaction with the host. References Bletz et al. (2016). Amphibian gut microbiota shifts differentially in community structure but converges on habitat-specific predicted functions. Nature Communications, 7(1), 1-12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13699 Jandhyala, S. M., Talukdar, R., Subramanyam, C., Vuyyuru, H., Sasikala, M., & Reddy, D. N. (2015). Role of the normal gut microbiota. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG, 21(29), 8787. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748%2Fwjg.v21.i29.8787 Scalvenzi, T., Clavereau, I., Bourge, M. & Pollet, N. (2021) Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stages. bioRxiv, 2020.05.25.110734, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Geonmics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.25.110734 | Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stages | Thibault Scalvenzi, Isabelle Clavereau, Mickael Bourge, Nicolas Pollet | <p><strong>Background</strong> The microorganism world living in amphibians is still largely under-represented and under-studied in the literature. Among anuran amphibians, African clawed frogs of the Xenopus genus stand as well-characterized mode... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Metagenomics, Vertebrates | Wirulda Pootakham | 2020-05-25 14:01:19 | View | |
02 Apr 2021

Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detectionLucie Tamisier, Annelies Haegeman, Yoika Foucart, Nicolas Fouillien, Maher Al Rwahnih, Nihal Buzkan, Thierry Candresse, Michela Chiumenti, Kris De Jonghe, Marie Lefebvre, Paolo Margaria, Jean Sébastien Reynard, Kristian Stevens, Denis Kutnjak, Sébastien Massart https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4584718Toward a critical assessment of virus detection in plantsRecommended by Hadi Quesneville based on reviews by Alexander Suh and 1 anonymous reviewerThe advent of High Throughput Sequencing (HTS) since the last decade has revealed previously unsuspected diversity of viruses as well as their (sometimes) unexpected presence in some healthy individuals. These results demonstrate that genomics offers a powerful tool for studying viruses at the individual level, allowing an in-depth inventory of those that are infecting an organism. Such approaches make it possible to study viromes with an unprecedented level of detail, both qualitative and quantitative, which opens new venues for analyses of viruses of humans, animals and plants. Consequently, the diagnostic field is using more and more HTS, fueling the need for efficient and reliable bioinformatics tools. Many such tools have already been developed, but in plant disease diagnostics, validation of the bioinformatics pipelines used for the detection of viruses in HTS datasets is still in its infancy. There is an urgent need for benchmarking the different tools and algorithms using well-designed reference datasets generated for this purpose. This is a crucial step to move forward and to improve existing solutions toward well-standardized bioinformatics protocols. This context has led to the creation of the Plant Health Bioinformatics Network (PHBN), a Euphresco network project aiming to build a bioinformatics community working on plant health. One of their objectives is to provide researchers with open-access reference datasets allowing to compare and validate virus detection pipelines. In this framework, Tamisier et al. [1] present real, semi-artificial, and completely artificial datasets, each aimed at addressing challenges that could affect virus detection. These datasets comprise real RNA-seq reads from virus-infected plants as well as simulated virus reads. Such a work, providing open-access datasets for benchmarking bioinformatics tools, should be encouraged as they are key to software improvement as demonstrated by the well-known success story of the protein structure prediction community: their pioneer community-wide effort, called Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction (CASP)[2], has been providing research groups since 1994 with an invaluable way to objectively test their structure prediction methods, thereby delivering an independent assessment of state-of-art protein-structure modelling tools. Following this success, many other bioinformatic community developed similar “competitions”, such as RNA-puzzles [3] to predict RNA structures, Critical Assessment of Function Annotation [4] to predict gene functions, Critical Assessment of Prediction of Interactions [5] to predict protein-protein interactions, Assemblathon [6] for genome assembly, etc. These are just a few examples from a long list of successful initiatives. Such efforts enable rigorous assessments of tools, stimulate the developers’ creativity, but also provide user communities with a state-of-art evaluation of available tools. Inspired by these success stories, the authors propose a “VIROMOCK challenge” [7], asking researchers in the field to test their tools and to provide feedback on each dataset through a repository. This initiative, if well followed, will undoubtedly improve the field of virus detection in plants, but also probably in many other organisms. This will be a major contribution to the field of viruses, leading to better diagnostics and, consequently, a better understanding of viral diseases, thus participating in promoting human, animal and plant health. References [1] Tamisier, L., Haegeman, A., Foucart, Y., Fouillien, N., Al Rwahnih, M., Buzkan, N., Candresse, T., Chiumenti, M., De Jonghe, K., Lefebvre, M., Margaria, P., Reynard, J.-S., Stevens, K., Kutnjak, D. and Massart, S. (2021) Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detection. Zenodo, 4273791, version 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Genomics. doi: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4273791 [2] Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction” (CASP) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CASP [3] RNA-puzzles - https://www.rnapuzzles.org [4] Critical Assessment of Function Annotation (CAFA) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_Assessment_of_Function_Annotation [5] Critical Assessment of Prediction of Interactions (CAPI) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_Assessment_of_Prediction_of_Interactions [6] Assemblathon - https://assemblathon.org [7] VIROMOCK challenge - https://gitlab.com/ilvo/VIROMOCKchallenge | Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detection | Lucie Tamisier, Annelies Haegeman, Yoika Foucart, Nicolas Fouillien, Maher Al Rwahnih, Nihal Buzkan, Thierry Candresse, Michela Chiumenti, Kris De Jonghe, Marie Lefebvre, Paolo Margaria, Jean Sébastien Reynard, Kristian Stevens, Denis Kutnjak, Séb... | <p>The widespread use of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) for detection of plant viruses and sequencing of plant virus genomes has led to the generation of large amounts of data and of bioinformatics challenges to process them. Many bioinformatics... |  | Bioinformatics, Plants, Viruses and transposable elements | Hadi Quesneville | 2020-11-27 14:31:47 | View | |
27 Apr 2021

Uncovering transposable element variants and their potential adaptive impact in urban populations of the malaria vector Anopheles coluzziiCarlos Vargas-Chavez, Neil Michel Longo Pendy, Sandrine E. Nsango, Laura Aguilera, Diego Ayala, and Josefa González https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.22.393231Anopheles coluzzii, a new system to study how transposable elements may foster adaptation to urban environmentsRecommended by Anne Roulin based on reviews by Yann Bourgeois and 1 anonymous reviewerTransposable elements (TEs) are mobile DNA sequences that can increase their copy number and move from one location to another within the genome [1]. Because of their transposition dynamics, TEs constitute a significant fraction of eukaryotic genomes. TEs are also known to play an important functional role and a wealth of studies has now reported how TEs may influence single host traits [e.g. 2–4]. Given that TEs are more likely than classical point mutations to cause extreme changes in gene expression and phenotypes, they might therefore be especially prone to produce the raw diversity necessary for individuals to respond to challenging environments [5,6] such as the ones found in urban area.
| Uncovering transposable element variants and their potential adaptive impact in urban populations of the malaria vector Anopheles coluzzii | Carlos Vargas-Chavez, Neil Michel Longo Pendy, Sandrine E. Nsango, Laura Aguilera, Diego Ayala, and Josefa González | <p style="text-align: justify;">Background</p> <p style="text-align: justify;">Anopheles coluzzii is one of the primary vectors of human malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Recently, it has colonized the main cities of Central Africa threatening vecto... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Anne Roulin | 2020-12-02 14:58:47 | View | |
05 May 2021
A primer and discussion on DNA-based microbiome data and related bioinformatics analysesGavin M. Douglas and Morgan G. I. Langille https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/3dybgA hitchhiker’s guide to DNA-based microbiome analysisRecommended by Danny Ionescu based on reviews by Nicolas Pollet, Rafael Cuadrat and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Nicolas Pollet, Rafael Cuadrat and 1 anonymous reviewer
In the last two decades, microbial research in its different fields has been increasingly focusing on microbiome studies. These are defined as studies of complete assemblages of microorganisms in given environments and have been benefiting from increases in sequencing length, quality, and yield, coupled with ever-dropping prices per sequenced nucleotide. Alongside localized microbiome studies, several global collaborative efforts have emerged, including the Human Microbiome Project [1], the Earth Microbiome Project [2], the Extreme Microbiome Project, and MetaSUB [3]. Coupled with the development of sequencing technologies and the ever-increasing amount of data output, multiple standalone or online bioinformatic tools have been designed to analyze these data. Often these tools have been focusing on either of two main tasks: 1) Community analysis, providing information on the organisms present in the microbiome, or 2) Functionality, in the case of shotgun metagenomic data, providing information on the metabolic potential of the microbiome. Bridging between the two types of data, often extracted from the same dataset, is typically a daunting task that has been addressed by a handful of tools only. The extent of tools and approaches to analyze microbiome data is great and may be overwhelming to researchers new to microbiome or bioinformatic studies. In their paper “A primer and discussion on DNA-based microbiome data and related bioinformatics analyses”, Douglas and Langille [4] guide us through the different sequencing approaches useful for microbiome studies. alongside their advantages and caveats and a selection of tools to analyze these data, coupled with examples from their own field of research. Standing out in their primer-style review is the emphasis on the coupling between taxonomic/phylogenetic identification of the organisms and their functionality. This type of analysis, though highly important to understand the role of different microorganisms in an environment as well as to identify potential functional redundancy, is often not conducted. For this, the authors identify two approaches. The first, using shotgun metagenomics, has higher chances of attributing a function to the correct taxon. The second, using amplicon sequencing of marker genes, allows for a deeper coverage of the microbiome at a lower cost, and extrapolates the amplicon data to close relatives with a sequenced genome. As clearly stated, this approach makes the leap between taxonomy and functionality and has been shown to be erroneous in cases where the core genome of the bacterial genus or family does not encompass the functional diversity of the different included species. This practice was already common before the genomic era, but its accuracy is improving thanks to the increasing availability of sequenced reference genomes from cultures, environmentally picked single cells or metagenome-assembled genome. In addition to their description of standalone tools useful for linking taxonomy and functionality, one should mention the existence of online tools that may appeal to researchers who do not have access to adequate bioinformatics infrastructure. Among these are the Integrated Microbial Genomes and Microbiomes (IMG) from the Joint Genome Institute [5], KBase [6] and MG-RAST [7]. A second important point arising from this review is the need for standardization in microbiome data analyses and the complexity of achieving this. As Douglas and Langille [4] state, this has been previously addressed, highlighting the variability in results obtained with different tools. It is often the case that papers describing new bioinformatic tools display their superiority relative to existing alternatives, potentially misleading newcomers to the field that the newest tool is the best and only one to be used. This is often not the case, and while benchmarking against well-defined datasets serves as a powerful testing tool, “real-life” samples are often not comparable. Thus, as done here, future primer-like reviews should highlight possible cross-field caveats, encouraging researchers to employ and test several approaches and validate their results whenever possible. In summary, Douglas and Langille [4] offer both the novice and experienced researcher a detailed guide along the paths of microbiome data analysis, accompanied by informative background information, suggested tools with which analyses can be started, and an insightful view on where the field should be heading. References [1] Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Hamady M, Fraser-Liggett CM, Knight R, Gordon JI (2007) The Human Microbiome Project. Nature, 449, 804–810. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06244 [2] Gilbert JA, Jansson JK, Knight R (2014) The Earth Microbiome project: successes and aspirations. BMC Biology, 12, 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-014-0069-1 [3] Mason C, Afshinnekoo E, Ahsannudin S, Ghedin E, Read T, Fraser C, Dudley J, Hernandez M, Bowler C, Stolovitzky G, Chernonetz A, Gray A, Darling A, Burke C, Łabaj PP, Graf A, Noushmehr H, Moraes s., Dias-Neto E, Ugalde J, Guo Y, Zhou Y, Xie Z, Zheng D, Zhou H, Shi L, Zhu S, Tang A, Ivanković T, Siam R, Rascovan N, Richard H, Lafontaine I, Baron C, Nedunuri N, Prithiviraj B, Hyat S, Mehr S, Banihashemi K, Segata N, Suzuki H, Alpuche Aranda CM, Martinez J, Christopher Dada A, Osuolale O, Oguntoyinbo F, Dybwad M, Oliveira M, Fernandes A, Oliveira M, Fernandes A, Chatziefthimiou AD, Chaker S, Alexeev D, Chuvelev D, Kurilshikov A, Schuster S, Siwo GH, Jang S, Seo SC, Hwang SH, Ossowski S, Bezdan D, Udekwu K, Udekwu K, Lungjdahl PO, Nikolayeva O, Sezerman U, Kelly F, Metrustry S, Elhaik E, Gonnet G, Schriml L, Mongodin E, Huttenhower C, Gilbert J, Hernandez M, Vayndorf E, Blaser M, Schadt E, Eisen J, Beitel C, Hirschberg D, Schriml L, Mongodin E, The MetaSUB International Consortium (2016) The Metagenomics and Metadesign of the Subways and Urban Biomes (MetaSUB) International Consortium inaugural meeting report. Microbiome, 4, 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-016-0168-z [4] Douglas GM, Langille MGI (2021) A primer and discussion on DNA-based microbiome data and related bioinformatics analyses. OSF Preprints, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Genomics. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/3dybg [5] Chen I-MA, Markowitz VM, Chu K, Palaniappan K, Szeto E, Pillay M, Ratner A, Huang J, Andersen E, Huntemann M, Varghese N, Hadjithomas M, Tennessen K, Nielsen T, Ivanova NN, Kyrpides NC (2017) IMG/M: integrated genome and metagenome comparative data analysis system. Nucleic Acids Research, 45, D507–D516. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw929 [6] Arkin AP, Cottingham RW, Henry CS, Harris NL, Stevens RL, Maslov S, Dehal P, Ware D, Perez F, Canon S, Sneddon MW, Henderson ML, Riehl WJ, Murphy-Olson D, Chan SY, Kamimura RT, Kumari S, Drake MM, Brettin TS, Glass EM, Chivian D, Gunter D, Weston DJ, Allen BH, Baumohl J, Best AA, Bowen B, Brenner SE, Bun CC, Chandonia J-M, Chia J-M, Colasanti R, Conrad N, Davis JJ, Davison BH, DeJongh M, Devoid S, Dietrich E, Dubchak I, Edirisinghe JN, Fang G, Faria JP, Frybarger PM, Gerlach W, Gerstein M, Greiner A, Gurtowski J, Haun HL, He F, Jain R, Joachimiak MP, Keegan KP, Kondo S, Kumar V, Land ML, Meyer F, Mills M, Novichkov PS, Oh T, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Parrello B, Pasternak S, Pearson E, Poon SS, Price GA, Ramakrishnan S, Ranjan P, Ronald PC, Schatz MC, Seaver SMD, Shukla M, Sutormin RA, Syed MH, Thomason J, Tintle NL, Wang D, Xia F, Yoo H, Yoo S, Yu D (2018) KBase: The United States Department of Energy Systems Biology Knowledgebase. Nature Biotechnology, 36, 566–569. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4163 [7] Wilke A, Bischof J, Gerlach W, Glass E, Harrison T, Keegan KP, Paczian T, Trimble WL, Bagchi S, Grama A, Chaterji S, Meyer F (2016) The MG-RAST metagenomics database and portal in 2015. Nucleic Acids Research, 44, D590–D594. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1322 | A primer and discussion on DNA-based microbiome data and related bioinformatics analyses | Gavin M. Douglas and Morgan G. I. Langille | <p style="text-align: justify;">The past decade has seen an eruption of interest in profiling microbiomes through DNA sequencing. The resulting investigations have revealed myriad insights and attracted an influx of researchers to the research are... |  | Bioinformatics, Metagenomics | Danny Ionescu | 2021-02-17 00:26:46 | View | |
19 Jul 2021
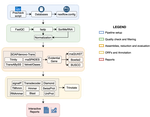
TransPi - a comprehensive TRanscriptome ANalysiS PIpeline for de novo transcriptome assemblyRamon E Rivera-Vicens, Catalina Garcia-Escudero, Nicola Conci, Michael Eitel, Gert Wörheide https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.18.431773TransPI: A balancing act between transcriptome assemblersRecommended by Oleg Simakov based on reviews by Gustavo Sanchez and Juan Daniel Montenegro CabreraEver since the introduction of the first widely usable assemblers for transcriptomic reads (Huang and Madan 1999; Schulz et al. 2012; Simpson et al. 2009; Trapnell et al. 2010, and many more), it has been a technical challenge to compare different methods and to choose the “right” or “best” assembly. It took years until the first widely accepted set of benchmarks beyond raw statistical evaluation became available (e.g., Parra, Bradnam, and Korf 2007; Simão et al. 2015). However, an approach to find the right balance between the number of transcripts or isoforms vs. evolutionary completeness measures has been lacking. This has been particularly pronounced in the field of non-model organisms (i.e., wild species that lack a genomic reference). Often, studies in this area employed only one set of assembly tools (the most often used to this day being Trinity, Haas et al. 2013; Grabherr et al. 2011). While it was relatively straightforward to obtain an initial assembly, its validation, annotation, as well its application to the particular purpose that the study was designed for (phylogenetics, differential gene expression, etc) lacked a clear workflow. This led to many studies using a custom set of tools with ensuing various degrees of reproducibility. TransPi (Rivera-Vicéns et al. 2021) fills this gap by first employing a meta approach using several available transcriptome assemblers and algorithms to produce a combined and reduced transcriptome assembly, then validating and annotating the resulting transcriptome. Notably, TransPI performs an extensive analysis/detection of chimeric transcripts, the results of which show that this new tool often produces fewer misassemblies compared to Trinity. TransPI not only generates a final report that includes the most important plots (in clickable/zoomable format) but also stores all relevant intermediate files, allowing advanced users to take a deeper look and/or experiment with different settings. As running TransPi is largely automated (including its installation via several popular package managers), it is very user-friendly and is likely to become the new "gold standard" for transcriptome analyses, especially of non-model organisms. References Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, di Palma F, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nature Biotechnology, 29, 644–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1883 Haas BJ, Papanicolaou A, Yassour M, Grabherr M, Blood PD, Bowden J, Couger MB, Eccles D, Li B, Lieber M, MacManes MD, Ott M, Orvis J, Pochet N, Strozzi F, Weeks N, Westerman R, William T, Dewey CN, Henschel R, LeDuc RD, Friedman N, Regev A (2013) De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nature Protocols, 8, 1494–1512. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.084 Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: A DNA Sequence Assembly Program. Genome Research, 9, 868–877. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.9.9.868 Parra G, Bradnam K, Korf I (2007) CEGMA: a pipeline to accurately annotate core genes in eukaryotic genomes. Bioinformatics, 23, 1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm071 Rivera-Vicéns RE, Garcia-Escudero CA, Conci N, Eitel M, Wörheide G (2021) TransPi – a comprehensive TRanscriptome ANalysiS PIpeline for de novo transcriptome assembly. bioRxiv, 2021.02.18.431773, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.18.431773 Schulz MH, Zerbino DR, Vingron M, Birney E (2012) Oases: robust de novo RNA-seq assembly across the dynamic range of expression levels. Bioinformatics, 28, 1086–1092. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts094 Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics, 31, 3210–3212. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351 Simpson JT, Wong K, Jackman SD, Schein JE, Jones SJM, Birol İ (2009) ABySS: A parallel assembler for short read sequence data. Genome Research, 19, 1117–1123. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.089532.108 Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L (2010) Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nature Biotechnology, 28, 511–515. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1621 | TransPi - a comprehensive TRanscriptome ANalysiS PIpeline for de novo transcriptome assembly | Ramon E Rivera-Vicens, Catalina Garcia-Escudero, Nicola Conci, Michael Eitel, Gert Wörheide | <p style="text-align: justify;">The use of RNA-Seq data and the generation of de novo transcriptome assemblies have been pivotal for studies in ecology and evolution. This is distinctly true for non-model organisms, where no genome information is ... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics | Oleg Simakov | 2021-02-18 20:56:08 | View | |
06 Jul 2021
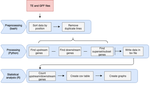
A pipeline to detect the relationship between transposable elements and adjacent genes in host genomesCaroline Meguerditchian, Ayse Ergun, Veronique Decroocq, Marie Lefebvre, Quynh-Trang Bui https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.25.432867A new tool to cross and analyze TE and gene annotationsRecommended by Emmanuelle Lerat based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersTransposable elements (TEs) are important components of genomes. Indeed, they are now recognized as having a major role in gene and genome evolution (Biémont 2010). In particular, several examples have shown that the presence of TEs near genes may influence their functioning, either by recruiting particular epigenetic modifications (Guio et al. 2018) or by directly providing new regulatory sequences allowing new expression patterns (Chung et al. 2007; Sundaram et al. 2014). Therefore, the study of the interaction between TEs and their host genome requires tools to easily cross-annotate both types of entities. In particular, one needs to be able to identify all TEs located in the close vicinity of genes or inside them. Such task may not always be obvious for many biologists, as it requires informatics knowledge to develop their own script codes. In their work, Meguerdichian et al. (2021) propose a command-line pipeline that takes as input the annotations of both genes and TEs for a given genome, then detects and reports the positional relationships between each TE insertion and their closest genes. The results are processed into an R script to provide tables displaying some statistics and graphs to visualize these relationships. This tool has the potential to be very useful for performing preliminary analyses before studying the impact of TEs on gene functioning, especially for biologists. Indeed, it makes it possible to identify genes close to TE insertions. These identified genes could then be specifically considered in order to study in more detail the link between the presence of TEs and their functioning. For example, the identification of TEs close to genes may allow to determine their potential role on gene expression. References Biémont C (2010). A brief history of the status of transposable elements: from junk DNA to major players in evolution. Genetics, 186, 1085–1093. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.110.124180 Chung H, Bogwitz MR, McCart C, Andrianopoulos A, ffrench-Constant RH, Batterham P, Daborn PJ (2007). Cis-regulatory elements in the Accord retrotransposon result in tissue-specific expression of the Drosophila melanogaster insecticide resistance gene Cyp6g1. Genetics, 175, 1071–1077. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.106.066597 Guio L, Vieira C, González J (2018). Stress affects the epigenetic marks added by natural transposable element insertions in Drosophila melanogaster. Scientific Reports, 8, 12197. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30491-w Meguerditchian C, Ergun A, Decroocq V, Lefebvre M, Bui Q-T (2021). A pipeline to detect the relationship between transposable elements and adjacent genes in host genomes. bioRxiv, 2021.02.25.432867, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.25.432867 Sundaram V, Cheng Y, Ma Z, Li D, Xing X, Edge P, Snyder MP, Wang T (2014). Widespread contribution of transposable elements to the innovation of gene regulatory networks. Genome Research, 24, 1963–1976. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.168872.113 | A pipeline to detect the relationship between transposable elements and adjacent genes in host genomes | Caroline Meguerditchian, Ayse Ergun, Veronique Decroocq, Marie Lefebvre, Quynh-Trang Bui | <p>Understanding the relationship between transposable elements (TEs) and their closest positional genes in the host genome is a key point to explore their potential role in genome evolution. Transposable elements can regulate and affect gene expr... |  | Bioinformatics, Viruses and transposable elements | Emmanuelle Lerat | 2021-03-03 15:08:34 | View | |
23 Mar 2022
Chromosomal rearrangements with stable repertoires of genes and transposable elements in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungusArthur Demene, Benoit Laurent, Sandrine Cros-Arteil, Christophe Boury, Cyril Dutech https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.09.434572Comparative genomics in the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria parasitica reveals large chromosomal rearrangements and a stable genome organizationRecommended by Sebastien Duplessis based on reviews by Benjamin Schwessinger and 1 anonymous reviewerAbout twenty-five years after the sequencing of the first fungal genome and a dozen years after the first plant pathogenic fungi genomes were sequenced, unprecedented international efforts have led to an impressive collection of genomes available for the community of mycologists in international databases (Goffeau et al. 1996, Dean et al. 2005; Spatafora et al. 2017). For instance, to date, the Joint Genome Institute Mycocosm database has collected more than 2,100 fungal genomes over the fungal tree of life (https://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov). Such resources are paving the way for comparative genomics, population genomics and phylogenomics to address a large panel of questions regarding the biology and the ecology of fungal species. Early on, population genomics applied to pathogenic fungi revealed a great diversity of genome content and organization and a wide variety of variants and rearrangements (Raffaele and Kamoun 2012, Hartmann 2022). Such plasticity raises questions about how to choose a representative genome to serve as an ideal reference to address pertinent biological questions. Cryphonectria parasitica is a fungal pathogen that is infamous for the devastation of chestnut forests in North America after its accidental introduction more than a century ago (Anagnostakis 1987). Since then, it has been a quarantine species under surveillance in various parts of the world. As for other fungi causing diseases on forest trees, the study of adaptation to its host in the forest ecosystem and of its reproduction and dissemination modes is more complex than for crop-targeting pathogens. A first reference genome was published in 2020 for the chestnut blight fungus C. parasitica strain EP155 in the frame of an international project with the DOE JGI (Crouch et al. 2020). Another genome was then sequenced from the French isolate YVO003, which showed a few differences in the assembly suggesting possible rearrangements (Demené et al. 2019). Here the sequencing of a third isolate ESM015 from the native area of C. parasitica in Japan allows to draw broader comparative analysis and particularly to compare between native and introduced isolates (Demené et al. 2022). Demené and collaborators report on a new genome sequence using up-to-date long-read sequencing technologies and they provide an improved genome assembly. Comparison with previously published C. parasitica genomes did not reveal dramatic changes in the overall chromosomal landscapes, but large rearrangements could be spotted. Despite these rearrangements, the genome content and organization – i.e. genes and repeats – remain stable, with a limited number of genes gains and losses. As in any fungal plant pathogen genome, the repertoire of candidate effectors predicted among secreted proteins was more particularly scrutinized. Such effector genes have previously been reported in other pathogens in repeat-enriched plastic genomic regions with accelerated evolutionary rates under the pressure of the host immune system (Raffaele and Kamoun 2012). Demené and collaborators established a list of priority candidate effectors in the C. parasitica gene catalog likely involved in the interaction with the host plant which will require more attention in future functional studies. Six major inter-chromosomal translocations were detected and are likely associated with double break strands repairs. The authors speculate on the possible effects that these translocations may have on gene organization and expression regulation leading to dramatic phenotypic changes in relation to introduction and invasion in new continents and the impact regarding sexual reproduction in this fungus (Demené et al. 2022). I recommend this article not only because it is providing an improved assembly of a reference genome for C. parasitica, but also because it adds diversity in terms of genome references availability, with a third high-quality assembly. Such an effort in the tree pathology community for a pathogen under surveillance is of particular importance for future progress in post-genomic analysis, e.g. in further genomic population studies (Hartmann 2022). References Anagnostakis SL (1987) Chestnut Blight: The Classical Problem of an Introduced Pathogen. Mycologia, 79, 23–37. https://doi.org/10.2307/3807741 Crouch JA, Dawe A, Aerts A, Barry K, Churchill ACL, Grimwood J, Hillman BI, Milgroom MG, Pangilinan J, Smith M, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Yadav JS, Grigoriev IV, Nuss DL (2020) Genome Sequence of the Chestnut Blight Fungus Cryphonectria parasitica EP155: A Fundamental Resource for an Archetypical Invasive Plant Pathogen. Phytopathology®, 110, 1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-12-19-0478-A Dean RA, Talbot NJ, Ebbole DJ, Farman ML, Mitchell TK, Orbach MJ, Thon M, Kulkarni R, Xu J-R, Pan H, Read ND, Lee Y-H, Carbone I, Brown D, Oh YY, Donofrio N, Jeong JS, Soanes DM, Djonovic S, Kolomiets E, Rehmeyer C, Li W, Harding M, Kim S, Lebrun M-H, Bohnert H, Coughlan S, Butler J, Calvo S, Ma L-J, Nicol R, Purcell S, Nusbaum C, Galagan JE, Birren BW (2005) The genome sequence of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Nature, 434, 980–986. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03449 Demené A., Laurent B., Cros-Arteil S., Boury C. and Dutech C. 2022. Chromosomal rearrangements with stable repertoires of genes and transposable elements in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungus. bioRxiv, 2021.03.09.434572, ver.6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.09.434572 Goffeau A, Barrell BG, Bussey H, Davis RW, Dujon B, Feldmann H, Galibert F, Hoheisel JD, Jacq C, Johnston M, Louis EJ, Mewes HW, Murakami Y, Philippsen P, Tettelin H, Oliver SG (1996) Life with 6000 Genes. Science, 274, 546–567. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.274.5287.546 Hartmann FE (2022) Using structural variants to understand the ecological and evolutionary dynamics of fungal plant pathogens. New Phytologist, 234, 43–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17907 Raffaele S, Kamoun S (2012) Genome evolution in filamentous plant pathogens: why bigger can be better. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 417–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2790 Spatafora JW, Aime MC, Grigoriev IV, Martin F, Stajich JE, Blackwell M (2017) The Fungal Tree of Life: from Molecular Systematics to Genome-Scale Phylogenies. Microbiology Spectrum, 5, 5.5.03. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0053-2016 | Chromosomal rearrangements with stable repertoires of genes and transposable elements in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungus | Arthur Demene, Benoit Laurent, Sandrine Cros-Arteil, Christophe Boury, Cyril Dutech | <p style="text-align: justify;">Chromosomal rearrangements have been largely described among eukaryotes, and may have important consequences on evolution of species. High genome plasticity has been often reported in Fungi, which may explain their ... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Fungi | Sebastien Duplessis | 2021-03-12 14:18:20 | View | |
13 Jul 2022
Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structuresColin Clairet, Nicolas Lapalu, Adeline Simon, Jessica L. Soyer, Muriel Viaud, Enric Zehraoui, Berengere Dalmais, Isabelle Fudal, Nadia Ponts https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.16.439968Genome-wide chromatin and expression datasets of various pathogenic ascomycetesRecommended by Sébastien Bloyer and Romain Koszul based on reviews by Ricardo C. Rodríguez de la Vega and 1 anonymous reviewerPlant pathogenic fungi represent serious economic threats. These organisms are rapidly adaptable, with plastic genomes containing many variable regions and evolving rapidly. It is, therefore, useful to characterize their genetic regulation in order to improve their control. One of the steps to do this is to obtain omics data that link their DNA structure and gene expression. Clairet C, Lapalu N, Simon A, Soyer JL, Viaud M, Zehraoui E, Dalmais B, Fudal I, Ponts N (2022) Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structures. bioRxiv, 2021.04.16.439968, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.16.439968 | Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structures | Colin Clairet, Nicolas Lapalu, Adeline Simon, Jessica L. Soyer, Muriel Viaud, Enric Zehraoui, Berengere Dalmais, Isabelle Fudal, Nadia Ponts | <p style="text-align: justify;">Fungal pathogens represent a serious threat towards agriculture, health, and environment. Control of fungal diseases on crops necessitates a global understanding of fungal pathogenicity determinants and their expres... |  | Epigenomics, Fungi | Sébastien Bloyer | 2021-04-17 10:32:41 | View | |
20 Jul 2021
Genetic mapping of sex and self-incompatibility determinants in the androdioecious plant Phillyrea angustifoliaAmelie Carre, Sophie Gallina, Sylvain Santoni, Philippe Vernet, Cecile Gode, Vincent Castric, Pierre Saumitou-Laprade https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.15.439943Identification of distinct YX-like loci for sex determination and self-incompatibility in an androdioecious shrubRecommended by Tatiana Giraud and Ricardo C. Rodríguez de la Vega based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersA wide variety of systems have evolved to control mating compatibility in sexual organisms. Their genetic determinism and the factors controlling their evolution represent fascinating questions in evolutionary biology and genomics. The plant Phillyrea angustifolia (Oleaeceae family) represents an exciting model organism, as it displays two distinct and rare mating compatibility systems [1]: 1) males and hermaphrodites co-occur in populations of this shrub (a rare system called androdioecy), while the evolution and maintenance of purely hermaphroditic plants or mixtures of females and hermaphrodites (a system called gynodioecy) are easier to explain [2]; 2) a homomorphic diallelic self-incompatibility system acts in hermaphrodites, while such systems are usually multi-allelic, as rare alleles are advantageous, being compatible with all other alleles. Previous analyses of crosses brought some interesting answers to these puzzles, showing that males benefit from the ability to mate with all hermaphrodites regardless of their allele at the self-incompatibility system, and suggesting that both sex and self incompatibility are determined by XY-like genetic systems, i.e. with each a dominant allele; homozygotes for a single allele and heterozygotes therefore co-occur in natural populations at both sex and self-incompatibility loci [3]. Here, Carré et al. used genotyping-by-sequencing to build a genome linkage map of P. angustifolia [4]. The elegant and original use of a probabilistic model of segregating alleles (implemented in the SEX-DETector method) allowed to identify both the sex and self-incompatibility loci [4], while this tool was initially developed for detecting sex-linked genes in species with strictly separated sexes (dioecy) [5]. Carré et al. [4] confirmed that the sex and self-incompatibility loci are located in two distinct linkage groups and correspond to XY-like systems. A comparison with the genome of the closely related Olive tree indicated that their self-incompatibility systems were homologous. Such a XY-like system represents a rare genetic determination mechanism for self-incompatibility and has also been recently found to control mating types in oomycetes [6]. This study [4] paves the way for identifying the genes controlling the sex and self-incompatibility phenotypes and for understanding why and how self-incompatibility is only expressed in hermaphrodites and not in males. It will also be fascinating to study more finely the degree and extent of genomic differentiation at these two loci and to assess whether recombination suppression has extended stepwise away from the sex and self-incompatibility loci, as can be expected under some hypotheses, such as the sheltering of deleterious alleles near permanently heterozygous alleles [7]. Furthermore, the co-occurrence in P. angustifolia of sex and mating types can contribute to our understanding of the factor controlling their evolution [8]. References [1] Saumitou-Laprade P, Vernet P, Vassiliadis C, Hoareau Y, Magny G de, Dommée B, Lepart J (2010) A Self-Incompatibility System Explains High Male Frequencies in an Androdioecious Plant. Science, 327, 1648–1650. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1186687 [2] Pannell JR, Voillemot M (2015) Plant Mating Systems: Female Sterility in the Driver’s Seat. Current Biology, 25, R511–R514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.04.044 [3] Billiard S, Husse L, Lepercq P, Godé C, Bourceaux A, Lepart J, Vernet P, Saumitou-Laprade P (2015) Selfish male-determining element favors the transition from hermaphroditism to androdioecy. Evolution, 69, 683–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/evo.12613 [4] Carre A, Gallina S, Santoni S, Vernet P, Gode C, Castric V, Saumitou-Laprade P (2021) Genetic mapping of sex and self-incompatibility determinants in the androdioecious plant Phillyrea angustifolia. bioRxiv, 2021.04.15.439943, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.15.439943 [5] Muyle A, Käfer J, Zemp N, Mousset S, Picard F, Marais GA (2016) SEX-DETector: A Probabilistic Approach to Study Sex Chromosomes in Non-Model Organisms. Genome Biology and Evolution, 8, 2530–2543. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evw172 [6] Dussert Y, Legrand L, Mazet ID, Couture C, Piron M-C, Serre R-F, Bouchez O, Mestre P, Toffolatti SL, Giraud T, Delmotte F (2020) Identification of the First Oomycete Mating-type Locus Sequence in the Grapevine Downy Mildew Pathogen, Plasmopara viticola. Current Biology, 30, 3897-3907.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.07.057 [7] Jay P, Tezenas E, Giraud T (2021) A deleterious mutation-sheltering theory for the evolution of sex chromosomes and supergenes. bioRxiv, 2021.05.17.444504. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.17.444504 [8] Billiard S, López-Villavicencio M, Devier B, Hood ME, Fairhead C, Giraud T (2011) Having sex, yes, but with whom? Inferences from fungi on the evolution of anisogamy and mating types. Biological Reviews, 86, 421–442. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.2010.00153.x | Genetic mapping of sex and self-incompatibility determinants in the androdioecious plant Phillyrea angustifolia | Amelie Carre, Sophie Gallina, Sylvain Santoni, Philippe Vernet, Cecile Gode, Vincent Castric, Pierre Saumitou-Laprade | <p style="text-align: justify;">The diversity of mating and sexual systems in angiosperms is spectacular, but the factors driving their evolution remain poorly understood. In plants of the Oleaceae family, an unusual self-incompatibility (SI) syst... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Plants | Tatiana Giraud | 2021-05-04 10:37:26 | View |










