Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * ▲ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
27 Apr 2021

Uncovering transposable element variants and their potential adaptive impact in urban populations of the malaria vector Anopheles coluzziiCarlos Vargas-Chavez, Neil Michel Longo Pendy, Sandrine E. Nsango, Laura Aguilera, Diego Ayala, and Josefa González https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.22.393231Anopheles coluzzii, a new system to study how transposable elements may foster adaptation to urban environmentsRecommended by Anne Roulin based on reviews by Yann Bourgeois and 1 anonymous reviewerTransposable elements (TEs) are mobile DNA sequences that can increase their copy number and move from one location to another within the genome [1]. Because of their transposition dynamics, TEs constitute a significant fraction of eukaryotic genomes. TEs are also known to play an important functional role and a wealth of studies has now reported how TEs may influence single host traits [e.g. 2–4]. Given that TEs are more likely than classical point mutations to cause extreme changes in gene expression and phenotypes, they might therefore be especially prone to produce the raw diversity necessary for individuals to respond to challenging environments [5,6] such as the ones found in urban area.
| Uncovering transposable element variants and their potential adaptive impact in urban populations of the malaria vector Anopheles coluzzii | Carlos Vargas-Chavez, Neil Michel Longo Pendy, Sandrine E. Nsango, Laura Aguilera, Diego Ayala, and Josefa González | <p style="text-align: justify;">Background</p> <p style="text-align: justify;">Anopheles coluzzii is one of the primary vectors of human malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Recently, it has colonized the main cities of Central Africa threatening vecto... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Anne Roulin | 2020-12-02 14:58:47 | View | |
12 Jul 2022

Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: steppingstones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert antsHugo Darras, Natalia de Souza Araujo, Lyam Baudry, Nadège Guiglielmoni, Pedro Lorite, Martial Marbouty, Fernando Rodriguez, Irina Arkhipova, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot, Serge Aron https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.07.475286A genomic resource for ants, and moreRecommended by Nadia Ponts based on reviews by Isabel Almudi and Nicolas NègreThe ant species Cataglyphis hispanica is remarkably well adapted to arid habitats of the Iberian Peninsula where two hybridogenetic lineages co-occur, i.e., queens mating with males from the other lineage produce only non-reproductive hybrid workers whereas reproductive males and females are produced by parthenogenesis (Lavanchy and Schwander, 2019). For these two reasons, the genomes of these lineages, Chis1 and Chis2, are potential gold mines to explore the genetic bases of thermal adaptation and the evolution of alternative reproductive modes. Nowadays, sequencing technology enables assembling all kinds of genomes provided genomic DNA can be extracted. More difficult to achieve is high-quality assemblies with just as high-quality annotations that are readily available to the community to be used and re-used at will (Byrne et al., 2019; Salzberg, 2019). The challenge was successfully completed by Darras and colleagues, the generated resource being fully available to the community, including scripts and command lines used to obtain the proposed results. The authors particularly describe that lineage Chis2 has 27 chromosomes, against 26 or 27 for lineage Chis1, with a Robertsonian translocation identified by chromosome conformation capture (Duan et al., 2010, 2012) in the two Queens sequenced. Transcript-supported gene annotation provided 11,290 high-quality gene models. In addition, an ant-tailored annotation pipeline identified 56 different families of repetitive elements in both Chis1 and Chis2 lineages of C. hispanica spread in a little over 15 % of the genome. Altogether, the genomes of Chis1 and Chis2 are highly similar and syntenic, with some level of polymorphism raising questions about their evolutionary story timeline. In particular, the uniform distribution of polymorphisms along the genomes shakes up a previous hypothesis of hybridogenetic lineage pairs determined by ancient non-recombining regions (Linksvayer, Busch and Smith, 2013). I recommend this paper because the science behind is both solid and well-explained. The provided resource is of high quality, and accompanied by a critical exploration of the perspectives brought by the results. These genomes are excellent resources to now go further in exploring the possible events at the genome level that accompanied the remarkable thermal adaptation of the ants Cataglyphis, as well as insights into the genetics of hybridogenetic lineages. Beyond the scientific value of the resources and insights provided by the work performed, I also recommend this article because it is an excellent example of Open Science (Allen and Mehler, 2019; Sarabipour et al., 2019), all data methods and tools being fully and easily accessible to whoever wants/needs it. References Allen C, Mehler DMA (2019) Open science challenges, benefits and tips in early career and beyond. PLOS Biology, 17, e3000246. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000246 Byrne A, Cole C, Volden R, Vollmers C (2019) Realizing the potential of full-length transcriptome sequencing. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 374, 20190097. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2019.0097 Darras H, de Souza Araujo N, Baudry L, Guiglielmoni N, Lorite P, Marbouty M, Rodriguez F, Arkhipova I, Koszul R, Flot J-F, Aron S (2022) Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: stepping stones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert ants. bioRxiv, 2022.01.07.475286, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.07.475286 Duan Z, Andronescu M, Schutz K, Lee C, Shendure J, Fields S, Noble WS, Anthony Blau C (2012) A genome-wide 3C-method for characterizing the three-dimensional architectures of genomes. Methods, 58, 277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.06.018 Duan Z, Andronescu M, Schutz K, McIlwain S, Kim YJ, Lee C, Shendure J, Fields S, Blau CA, Noble WS (2010) A three-dimensional model of the yeast genome. Nature, 465, 363–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08973 Lavanchy G, Schwander T (2019) Hybridogenesis. Current Biology, 29, R9–R11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.11.046 Linksvayer TA, Busch JW, Smith CR (2013) Social supergenes of superorganisms: Do supergenes play important roles in social evolution? BioEssays, 35, 683–689. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201300038 Salzberg SL (2019) Next-generation genome annotation: we still struggle to get it right. Genome Biology, 20, 92. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1715-2 Sarabipour S, Debat HJ, Emmott E, Burgess SJ, Schwessinger B, Hensel Z (2019) On the value of preprints: An early career researcher perspective. PLOS Biology, 17, e3000151. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000151 | Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: steppingstones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert ants | Hugo Darras, Natalia de Souza Araujo, Lyam Baudry, Nadège Guiglielmoni, Pedro Lorite, Martial Marbouty, Fernando Rodriguez, Irina Arkhipova, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot, Serge Aron | <p style="text-align: justify;"><em>Cataglyphis</em> are thermophilic ants that forage during the day when temperatures are highest and sometimes close to their critical thermal limit. Several Cataglyphis species have evolved unusual reproductive ... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Nadia Ponts | Nicolas Nègre, Isabel Almudi | 2022-01-13 16:47:30 | View |
22 Nov 2023
The slow evolving genome of the xenacoelomorph worm Xenoturbella bockiPhilipp H. Schiffer, Paschalis Natsidis, Daniel J. Leite, Helen Robertson, François Lapraz, Ferdinand Marlétaz, Bastian Fromm, Liam Baudry, Fraser Simpson, Eirik Høye, Anne-C. Zakrzewski, Paschalia Kapli, Katharina J. Hoff, Steven Mueller, Martial Marbouty, Heather Marlow, Richard R. Copley, Romain Koszul, Peter Sarkies, Maximilian J. Telford https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.24.497508Genomic idiosyncrasies of Xenoturbella bocki: morphologically simple yet genetically complexRecommended by Rosa Fernandez based on reviews by Christopher Laumer and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Christopher Laumer and 1 anonymous reviewer
Xenoturbella is a genus of morphologically simple bilaterians inhabiting benthic environments. Until very recently, only one species was known from the genus, Xenoturbella bocki Westblad 1949 [1]. Less than a decade ago, five more species were discovered (X. churro, X. monstrosa, X. profunda, X. hollandorum [2] and X. japonica [3]). These enigmatic animals lack an anus, a coelom, reproductive organs, nephrocytes and a centralized nervous system [1]. The systematic classification of the genus has substantially changed in the last decades, with first being considered as its own phylum (Xenoturbellida) and then being clustered together with acoels and nemertodermatids into the phylum Xenacoelomorpha [4,5]. The phylogenetic position of the xenacoelomorphs has been recalcitrant to resolution, with its position ranging from being the sister group to Nephrozoa (ie, protostomes and deuterostomes [6]) to the sister group to Ambulacraria (ie, Hemichordata and Echinodermata) in a clade called Xenambulacraria [4]. Recent studies based on expanded datasets and more refined analyses support either topology [7,8]. Either way, it is clear that additional studies on Xenoturbella could provide important insights into the origins of bilaterian traits such as the anus, the nephrons and the evolution of a centralized nervous system.
In any case, we are approaching a qualitative jump in how we understand phylogenomics thanks to efforts derived from the availability of chromosome-level genome assemblies for a growing number of species. Exciting times are ahead for us, evolutionary biologists, to explore what high-quality genomes - in combination with multiomics datasets - will reveal about animal evolution. I am personally really looking forward to it. References 1. Westblad E. (1949). Xenoturbella bocki n.g., n.sp., a peculiar, primitive Turbellarian type. Arkiv för Zoologi 1, 3-29 (1949). 2. Rouse, G. W., Wilson, N. G., Carvajal, J. I. & Vrijenhoek, R. C. New deep-sea species of Xenoturbella and the position of Xenacoelomorpha. Nature 530, 94–97 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16545 3. Nakano, H. et al. Correction to: A new species of Xenoturbella from the western Pacific Ocean and the evolution of Xenoturbella. BMC Evol. Biol. 18, 1–2 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-018-1190-5https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-018-1190-5 4. Philippe, H. et al. Acoelomorph flatworms are deuterostomes related to Xenoturbella. Nature 470, 255–258 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09676 5. Hejnol, A. et al. Assessing the root of bilaterian animals with scalable phylogenomic methods. Proc. Biol. Sci. 276, 4261–4270 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2009.0896 6. Cannon, J. T. et al. Xenacoelomorpha is the sister group to Nephrozoa. Nature 530, 89–93 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16520 7. Laumer, C. E. et al. Revisiting metazoan phylogeny with genomic sampling of all phyla. Proc. Biol. Sci. 286, 20190831 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2019.0831 8. Philippe, H. et al. Mitigating anticipated effects of systematic errors supports sister-group relationship between Xenacoelomorpha and Ambulacraria. Curr. Biol. 29, 1818–1826.e6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.04.009 9. Schiffer, P. H., Natsidis, P., Leite D. J., Robertson, H., Lapraz, F., Marlétaz, F., Fromm, B., Baudry, L., Simpson, F., Høye, E., Zakrzewski, A-C., Kapli, P., Hoff, K. J., Mueller, S., Marbouty, M., Marlow, H., Copley, R. R., Koszul, R., Sarkies, P. & Telford, M .J. The slow evolving genome of the xenacoelomorph worm Xenoturbella bocki. bioRxiv (2023), ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.24.497508 10. Suga, H. et al. The Capsaspora genome reveals a complex unicellular prehistory of animals. Nat. Commun. 4, 2325 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3325 11. Fernández, R. & Gabaldón, T. Gene gain and loss across the metazoan tree of life. Nat Ecol Evol 4, 524–533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-019-1069-x | The slow evolving genome of the xenacoelomorph worm *Xenoturbella bocki* | Philipp H. Schiffer, Paschalis Natsidis, Daniel J. Leite, Helen Robertson, François Lapraz, Ferdinand Marlétaz, Bastian Fromm, Liam Baudry, Fraser Simpson, Eirik Høye, Anne-C. Zakrzewski, Paschalia Kapli, Katharina J. Hoff, Steven Mueller, Martial... | <p style="text-align: justify;">The evolutionary origins of Bilateria remain enigmatic. One of the more enduring proposals highlights similarities between a cnidarian-like planula larva and simple acoel-like flatworms. This idea is based in part o... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Rosa Fernandez | 2022-11-01 12:31:53 | View | |
02 Jun 2023
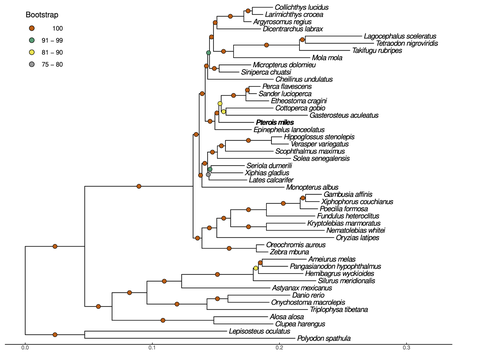
Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois milesChristos V. Kitsoulis, Vasileios Papadogiannis, Jon B. Kristoffersen, Elisavet Kaitetzidou, Aspasia Sterioti, Costas S. Tsigenopoulos, Tereza Manousaki https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.10.523469The genome of a dangerous invader (fish) beautyRecommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Maria Recuerda and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Maria Recuerda and 1 anonymous reviewer
High-quality genomes are currently being generated at an unprecedented speed powered by long-read sequencing technologies. However, sequencing effort is concentrated unequally across the tree of life and several key evolutionary and ecological groups remain largely unexplored. So is the case for fish species of the family Scorpaenidae (Perciformes). Kitsoulis et al. present the genome of the devil firefish, Pterois miles (1). Following current best practices, the assembly relies largely on Oxford Nanopore long reads, aided by Illumina short reads for polishing to increase the per-base accuracy. PacBio’s IsoSeq was used to sequence RNA from a variety of tissues as direct evidence for annotating genes. The reconstructed genome is 902 Mb in size and has high contiguity (N50=14.5 Mb; 660 scaffolds, 90% of the genome covered by the 83 longest scaffolds) and completeness (98% BUSCO completeness). The new genome is used to assess the phylogenetic position of P. miles, explore gene synteny against zebrafish, look at orthogroup expansion and contraction patterns in Perciformes, as well as to investigate the evolution of toxins in scorpaenid fish (2). In addition to its value for better understanding the evolution of scorpaenid and teleost fishes, this new genome is also an important resource for monitoring its invasiveness through the Mediterranean Sea (3) and the Atlantic Ocean, in the latter case forming the invasive lionfish complex with P. volitans (4). REFERENCES 1. Kitsoulis CV, Papadogiannis V, Kristoffersen JB, Kaitetzidou E, Sterioti E, Tsigenopoulos CS, Manousaki T. (2023) Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois miles. BioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.10.523469 2. Kiriake A, Shiomi K. (2011) Some properties and cDNA cloning of proteinaceous toxins from two species of lionfish (Pterois antennata and Pterois volitans). Toxicon, 58(6-7):494–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.08.010 3. Katsanevakis S, et al. (2020) Un- published Mediterranean records of marine alien and cryptogenic species. BioInvasions Records, 9:165–182. https://doi.org/10.3391/bir.2020.9.2.01 4. Lyons TJ, Tuckett QM, Hill JE. (2019) Data quality and quantity for invasive species: A case study of the lionfishes. Fish and Fisheries, 20:748–759. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12374 | Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, *Pterois miles* | Christos V. Kitsoulis, Vasileios Papadogiannis, Jon B. Kristoffersen, Elisavet Kaitetzidou, Aspasia Sterioti, Costas S. Tsigenopoulos, Tereza Manousaki | <p style="text-align: justify;">Devil firefish (<em>Pterois miles</em>), a member of Scorpaenidae family, is one of the most successful marine non-native species, dominating around the world, that was rapidly spread into the Mediterranean Sea, thr... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Iker Irisarri | 2023-01-17 12:37:20 | View | |
15 Mar 2024
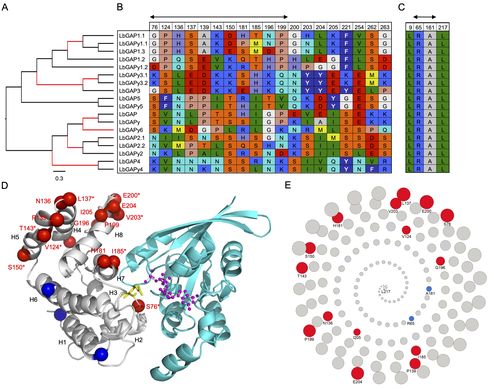
Convergent origin and accelerated evolution of vesicle-associated RhoGAP proteins in two unrelated parasitoid waspsDominique Colinet, Fanny Cavigliasso, Matthieu Leobold, Appoline Pichon, Serge Urbach, Dominique Cazes, Marine Poullet, Maya Belghazi, Anne-Nathalie Volkoff, Jean-Michel Drezen, Jean-Luc Gatti, and Marylène Poirié https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.05.543686Using transcriptomics and proteomics to understand the expansion of a secreted poisonous armoury in parasitoid wasps genomesRecommended by Ignacio Bravo based on reviews by Inacio Azevedo and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Inacio Azevedo and 2 anonymous reviewers
Parasitoid wasps lay their eggs inside another arthropod, whose body is physically consumed by the parasitoid larvae. Phylogenetic inference suggests that Parasitoida are monophyletic, and that this clade underwent a strong radiation shortly after branching off from the Apocrita stem, some 236 million years ago (Peters et al. 2017). The increase in taxonomic diversity during evolutionary radiations is usually concurrent with an increase in genetic/genomic diversity, and is often associated with an increase in phenotypic diversity. Gene (or genome) duplication provides the evolutionary potential for such increase of genomic diversity by neo/subfunctionalisation of one of the gene paralogs, and is often proposed to be related to evolutionary radiations (Ohno 1970; Francino 2005).
References
| Convergent origin and accelerated evolution of vesicle-associated RhoGAP proteins in two unrelated parasitoid wasps | Dominique Colinet, Fanny Cavigliasso, Matthieu Leobold, Appoline Pichon, Serge Urbach, Dominique Cazes, Marine Poullet, Maya Belghazi, Anne-Nathalie Volkoff, Jean-Michel Drezen, Jean-Luc Gatti, and Marylène Poirié | <p>Animal venoms and other protein-based secretions that perform a variety of functions, from predation to defense, are highly complex cocktails of bioactive compounds. Gene duplication, accompanied by modification of the expression and/or functio... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Ignacio Bravo | 2023-06-12 11:08:31 | View | |
01 May 2024
Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of lifeCristóbal Uribe, Mariana F. Nery, Kattina Zavala, Gonzalo A. Mardones, Gonzalo Riadi & Juan C. Opazo https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.06.15.545160v8Positive selection acted upon cetacean ion channels during the aquatic transitionRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
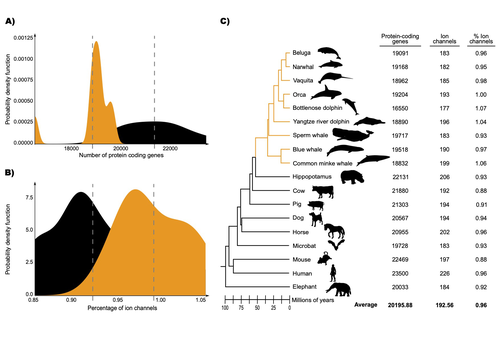
The transition of cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) from terrestrial to aquatic lifestyles is a striking example of natural selection driving major phenotypic changes (Figure 1). For instance, cetaceans have evolved the ability to withstand high pressure and to store oxygen for long periods, among other adaptations (Das et al. 2023). Many phenotypic changes, such as shifts in organ structure, have been well-characterized through fossils (Thewissen et al. 2009). Although such phenotypic transitions are now well understood, we have only a partial understanding of the underlying genetic mechanisms. Scanning for signatures of adaptation in genes related to phenotypes of interest is one approach to better understand these mechanisms. This was the focus of Uribe and colleagues’ (2024) work, who tested for such signatures across cetacean protein-coding genes.
Figure 1: The skeletons of Ambulocetus (an early whale; top) and Pakicetus (the earliest known cetacean, which lived about 50 million years ago; bottom). Copyright: J. G. M. Thewissen. Displayed here with permission from the copyright holder.
The authors were specifically interested in investigating the evolution of ion channels, as these proteins play fundamental roles in physiological processes. An important aspect of their work was to develop a bioinformatic pipeline to identify orthologous ion channel genes across a set of genomes. After applying their bioinformatic workflow to 18 mammalian species (including nine cetaceans), they conducted tests to find out whether these genes showed signatures of positive selection in the cetacean lineage. For many ion channel genes, elevated ratios of non-synonymous to synonymous substitution rates were detected (for at least a subset of sites, and not necessarily the entire coding region of the genes). The genes concerned were enriched for several functions, including heart and nervous system-related phenotypes. One top gene hit among the putatively selected genes was SCN5A, which encodes a sodium channel expressed in the heart. Interestingly, the authors noted a specific amino acid replacement, which is associated with sensitivity to the toxin tetrodotoxin in other lineages. This substitution appears to have occurred in the common ancestor of toothed whales, and then was reversed in the ancestor of bottlenose dolphins. The authors describe known bottlenose dolphin interactions with toxin-producing pufferfish that could result in high tetrodotoxin exposure, and thus perhaps higher selection for tetrodotoxin resistance. Although this observation is intriguing, the authors emphasize it requires experimental confirmation. The authors also recapitulated the previously described observation (Yim et al. 2014; Huelsmann et al. 2019) that cetaceans have fewer protein-coding genes compared to terrestrial mammals, on average. This signal has previously been hypothesized to partially reflect adaptive gene loss. For example, specific gene loss events likely decreased the risk of developing blood clots while diving (Huelsmann et al. 2019). Uribe and colleagues also considered overall gene turnover rate, which encompasses gene copy number variation across lineages, and found the cetacean gene turnover rate to be three times higher than that of terrestrial mammals. Finally, they found that cetaceans have a higher proportion of ion channel genes (relative to all protein-coding genes in a genome) compared to terrestrial mammals. Similar investigations of the relative non-synonymous to synonymous substitution rates across cetacean and terrestrial mammal orthologs have been conducted previously, but these have primarily focused on dolphins as the sole cetacean representative (McGowen et al. 2012; Nery et al. 2013; Sun et al. 2013). These projects have also been conducted across a large proportion of orthologous genes, rather than a subset with a particular function. Performing proteome-wide investigations can be valuable in that they summarize the genome-wide signal, but can suffer from a high multiple testing burden. More generally, investigating a more targeted question, such as the extent of positive selection acting on ion channels in this case, or on genes potentially linked to cetaceans’ increased brain sizes (McGowen et al. 2011) or hypoxia tolerance (Tian et al. 2016), can be easier to interpret, as opposed to summarizing broader signals. However, these smaller-scale studies can also experience a high multiple testing burden, especially as similar tests are conducted across numerous studies, which often is not accounted for (Ioannidis 2005). In addition, integrating signals across the entire genome will ultimately be needed given that many genetic changes undoubtedly underlie cetaceans’ phenotypic diversification. As highlighted by the fact that past genome-wide analyses have produced some differing biological interpretations (McGowen et al. 2012; Nery et al. 2013; Sun et al. 2013), this is not a trivial undertaking. Nonetheless, the work performed in this preprint, and in related research, is valuable for (at least) three reasons. First, although it is a challenging task, a better understanding of the genetic basis of cetacean phenotypes could have benefits for many aspects of cetacean biology, including conservation efforts. In addition, the remarkable phenotypic shifts in cetaceans make the question of what genetic mechanisms underlie these changes intrinsically interesting to a wide audience. Last, since the cetacean fossil record is especially well-documented (Thewissen et al. 2009), cetaceans represent an appealing system to validate and further develop statistical methods for inferring adaptation from genetic data. Uribe and colleagues’ (2024) analyses provide useful insights relevant to each of these points, and have generated intriguing hypotheses for further investigation.
Das K, Sköld H, Lorenz A, Parmentier E (2023) Who are the marine mammals? In: “Marine Mammals: A Deep Dive into the World of Science”. Brennecke D, Knickmeier K, Pawliczka I, Siebert U, Wahlberg, M (editors). Springer, Cham. p. 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06836-2_1 Huelsmann M, Hecker N, Springer MS, Gatesy J, Sharma V, Hiller M (2019) Genes lost during the transition from land to water in cetaceans highlight genomic changes associated with aquatic adaptations. Science Advances, 5, eaaw6671. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw6671 Ioannidis JPA (2005) Why most published research findings are false. PLOS Medicine, 2, e124. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020124 McGowen MR, Montgomery SH, Clark C, Gatesy J (2011) Phylogeny and adaptive evolution of the brain-development gene microcephalin (MCPH1) in cetaceans. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 11, 98. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-98 McGowen MR, Grossman LI, Wildman DE (2012) Dolphin genome provides evidence for adaptive evolution of nervous system genes and a molecular rate slowdown. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279, 3643–3651. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.0869 Nery MF, González DJ, Opazo JC (2013) How to make a dolphin: molecular signature of positive selection in cetacean genome. PLOS ONE, 8, e65491. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065491 Sun YB, Zhou WP, Liu HQ, Irwin DM, Shen YY, Zhang YP (2013) Genome-wide scans for candidate genes involved in the aquatic adaptation of dolphins. Genome Biology and Evolution, 5, 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evs123 Tian R, Wang Z, Niu X, Zhou K, Xu S, Yang G (2016) Evolutionary genetics of hypoxia tolerance in cetaceans during diving. Genome Biology and Evolution, 8, 827–839. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evw037 Thewissen JGM, Cooper LN, George JC, Bajpai (2009) From land to water: the origin of whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Evolution: Education and Outreach, 2, 272–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12052-009-0135-2 Uribe C, Nery M, Zavala K, Mardones G, Riadi G, Opazo J (2024) Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of life. bioRxiv, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.15.545160 Yim HS, Cho YS, Guang X, Kang SG, Jeong JY, Cha SS, Oh HM, Lee JH, Yang EC, Kwon KK, et al. (2014) Minke whale genome and aquatic adaptation in cetaceans. Nature Genetics, 46, 88–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2835
| Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of life | Cristóbal Uribe, Mariana F. Nery, Kattina Zavala, Gonzalo A. Mardones, Gonzalo Riadi & Juan C. Opazo | <p>Cetaceans could be seen as a natural experiment within the tree of life in which a mammalian lineage changed from terrestrial to aquatic habitats. This shift involved extensive phenotypic modifications, which represent an opportunity to explore... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Gavin Douglas | 2023-07-04 20:53:46 | View | |
26 Jun 2024
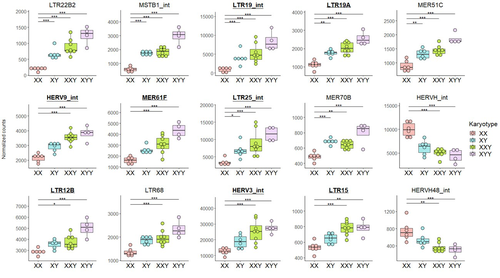
Transposable element expression with variation in sex chromosome number supports a toxic Y effect on human longevityJordan Teoli, Miriam Merenciano, Marie Fablet, Anamaria Necsulea, Daniel Siqueira-de-Oliveira, Alessandro Brandulas-Cammarata, Audrey Labalme, Hervé Lejeune, Jean-François Lemaitre, François Gueyffier, Damien Sanlaville, Claire Bardel, Cristina Vieira, Gabriel AB Marais, Ingrid Plotton https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.03.550779The number of Y chromosomes is positively associated with transposable element expression in humans, in line with the toxic Y hypothesisRecommended by Anna-Sophie Fiston-Lavier based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers
The study of human longevity has long been a source of fascination for scientists, particularly in relation to the genetic factors that contribute to differences in lifespan between the sexes. One particularly intriguing area of research concerns the Y chromosome and its impact on male longevity. The Y chromosome expresses genes that are essential for male development and reproduction. However, it may also influence various physiological processes and health outcomes. It is therefore of great importance to investigate the impact of the Y chromosome on longevity. This may assist in elucidating the biological mechanisms underlying sex-specific differences in aging and disease susceptibility. As longevity research progresses, the Y chromosome's role presents a promising avenue for elucidating the complex interplay between genetics and aging. Transposable elements (TEs), often referred to as "jumping genes", are DNA sequences that can move within the genome, potentially causing mutations and genomic instability. In young, healthy cells, various mechanisms, including DNA methylation and histone modifications, suppress TE activity to maintain genomic integrity. However, as individuals age, these regulatory mechanisms may deteriorate, leading to increased TE activity. This dysregulation could contribute to age-related genomic instability, cellular dysfunction, and the onset of diseases such as cancer. Understanding how TE repression changes with age is crucial for uncovering the molecular underpinnings of aging (De Cecco et al. 2013; Van Meter et al. 2014). The lower recombination rates observed on Y chromosomes result in the accumulation of TE insertions, which in turn leads to an enrichment of TEs and potentially higher TE activity. To ascertain whether the number of Y chromosomes is associated with TE activity in humans, Teoli et al. (2024) studied the TE expression level, as a proxy of the TE activity, in several karyotype compositions (i.e. with differing numbers of Y chromosomes). They used transcriptomic data from blood samples collected in 24 individuals (six females 46,XX, six males 46,XY, eight males 47,XXY and four males 47,XYY). Even though they did not observe a significant correlation between the number of Y chromosomes and TE expression, their results suggest an impact of the presence of the Y chromosome on the overall TE expression. The presence of Y chromosomes also affected the type (family) of TE present/expressed. To ensure that the TE expression level was not biased by the expression of a gene in proximity due to intron retention or pervasive intragenic transcription, the authors also tested whether the TE expression variation observed between the different karyotypes could be explained by gene (i.e. here non-TE gene) expression. As TE repression mechanisms are known to decrease over time, the authors also tested whether TE repression is weaker in older individuals, which would support a compelling link between genomic stability and aging. They investigated the TE expression differently between males and females, hypothesizing that old males should exhibit a stronger TE activity than old females. Using selected 45 males (47,XY) and 35 females (46,XX) blood samples of various ages (from 20 to 70) from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, the authors studied the effect of age on TE expression using 10-year range to group the study subjects. Based on these data, they fail to find an overall increase of TE expression in old males compared to old females. Notwithstanding the small number of samples, the study is well-designed and innovative, and its findings are highly promising. It marks an initial step towards understanding the impact of Y-chromosome ‘toxicity’ on human longevity. Despite the relatively small sample size, which is a consequence of the difficulty of obtaining samples from individuals with sex chromosome aneuploidies, the results are highly intriguing and will be of interest to a broad range of biologists.
References De Cecco M, Criscione SW, Peckham EJ, Hillenmeyer S, Hamm EA, Manivannan J, Peterson AL, Kreiling JA, Neretti N, Sedivy JM (2013) Genomes of replicatively senescent cells undergo global epigenetic changes leading to gene silencing and activation of transposable elements. Aging Cell, 12, 247–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12047 Teoli J, Merenciano M, Fablet M, Necsulea A, Siqueira-de-Oliveira D, Brandulas-Cammarata A, Labalme A, Lejeune H, Lemaitre J-F, Gueyffier F, Sanlaville D, Bardel C, Vieira C, Marais GAB, Plotton I (2024) Transposable element expression with variation in sex chromosome number supports a toxic Y effect on human longevity. bioRxiv, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.03.550779 Van Meter M, Kashyap M, Rezazadeh S, Geneva AJ, Morello TD, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V (2014) SIRT6 represses LINE1 retrotransposons by ribosylating KAP1 but this repression fails with stress and age. Nature Communications, 5, 5011. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6011
| Transposable element expression with variation in sex chromosome number supports a toxic Y effect on human longevity | Jordan Teoli, Miriam Merenciano, Marie Fablet, Anamaria Necsulea, Daniel Siqueira-de-Oliveira, Alessandro Brandulas-Cammarata, Audrey Labalme, Hervé Lejeune, Jean-François Lemaitre, François Gueyffier, Damien Sanlaville, Claire Bardel, Cristina Vi... | <p>Why women live longer than men is still an open question in human biology. Sex chromosomes have been proposed to play a role in the observed sex gap in longevity, and the Y male chromosome has been suspected of having a potential toxic genomic ... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Anna-Sophie Fiston-Lavier | Anonymous, Igor Rogozin , Paul Jay , Anonymous | 2023-08-18 15:01:38 | View |
07 Sep 2023
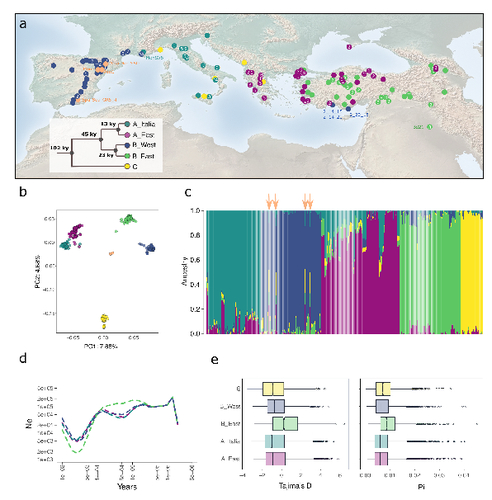
The demographic history of the wild crop relative Brachypodium distachyon is shaped by distinct past and present ecological nichesNikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.01.543285Natural variation and adaptation in Brachypodium distachyonRecommended by Josep Casacuberta based on reviews by Thibault Leroy and 1 anonymous reviewerIdentifying the genetic factors that allow plant adaptation is a major scientific question that is particularly relevant in the face of the climate change that we are already experiencing. To address this, it is essential to have genetic information on a high number of accessions (i.e., plants registered with unique accession numbers) growing under contrasting environmental conditions. There is already an important number of studies addressing these issues in the plant Arabidopsis thaliana, but there is a need to expand these analyses to species that play key roles in wild ecosystems and are close to very relevant crops, as is the case of grasses. The work of Minadakis, Roulin and co-workers (1) presents a Brachypodium distachyon panel of 332 fully sequences accessions that covers the whole species distribution across a wide range of bioclimatic conditions, which will be an invaluable tool to fill this gap. In addition, the authors use this data to start analyzing the population structure and demographic history of this plant, suggesting that the species experienced a shift of its distribution following the Last Glacial Maximum, which may have forced the species into new habitats. The authors also present a modeling of the niches occupied by B. distachyon together with an analysis of the genetic clades found in each of them, and start analyzing the different adaptive loci that may have allowed the species’ expansion into different bioclimatic areas. In addition to the importance of the resources made available by the authors for the scientific community, the analyses presented are well done and carefully discussed, and they highlight the potential of these new resources to investigate the genetic bases of plant adaptation. References 1. Nikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin. The demographic history of the wild crop relative Brachypodium distachyon is shaped by distinct past and present ecological niches. bioRxiv, 2023.06.01.543285, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.01.543285 | The demographic history of the wild crop relative *Brachypodium distachyon* is shaped by distinct past and present ecological niches | Nikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin | <p style="text-align: justify;">Closely related to economically important crops, the grass <em>Brachypodium distachyon</em> has been originally established as a pivotal species for grass genomics but more recently flourished as a model for develop... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics, Plants, Population genomics | Josep Casacuberta | 2023-06-14 15:28:30 | View | |
23 Mar 2022
Chromosomal rearrangements with stable repertoires of genes and transposable elements in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungusArthur Demene, Benoit Laurent, Sandrine Cros-Arteil, Christophe Boury, Cyril Dutech https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.09.434572Comparative genomics in the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria parasitica reveals large chromosomal rearrangements and a stable genome organizationRecommended by Sebastien Duplessis based on reviews by Benjamin Schwessinger and 1 anonymous reviewerAbout twenty-five years after the sequencing of the first fungal genome and a dozen years after the first plant pathogenic fungi genomes were sequenced, unprecedented international efforts have led to an impressive collection of genomes available for the community of mycologists in international databases (Goffeau et al. 1996, Dean et al. 2005; Spatafora et al. 2017). For instance, to date, the Joint Genome Institute Mycocosm database has collected more than 2,100 fungal genomes over the fungal tree of life (https://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov). Such resources are paving the way for comparative genomics, population genomics and phylogenomics to address a large panel of questions regarding the biology and the ecology of fungal species. Early on, population genomics applied to pathogenic fungi revealed a great diversity of genome content and organization and a wide variety of variants and rearrangements (Raffaele and Kamoun 2012, Hartmann 2022). Such plasticity raises questions about how to choose a representative genome to serve as an ideal reference to address pertinent biological questions. Cryphonectria parasitica is a fungal pathogen that is infamous for the devastation of chestnut forests in North America after its accidental introduction more than a century ago (Anagnostakis 1987). Since then, it has been a quarantine species under surveillance in various parts of the world. As for other fungi causing diseases on forest trees, the study of adaptation to its host in the forest ecosystem and of its reproduction and dissemination modes is more complex than for crop-targeting pathogens. A first reference genome was published in 2020 for the chestnut blight fungus C. parasitica strain EP155 in the frame of an international project with the DOE JGI (Crouch et al. 2020). Another genome was then sequenced from the French isolate YVO003, which showed a few differences in the assembly suggesting possible rearrangements (Demené et al. 2019). Here the sequencing of a third isolate ESM015 from the native area of C. parasitica in Japan allows to draw broader comparative analysis and particularly to compare between native and introduced isolates (Demené et al. 2022). Demené and collaborators report on a new genome sequence using up-to-date long-read sequencing technologies and they provide an improved genome assembly. Comparison with previously published C. parasitica genomes did not reveal dramatic changes in the overall chromosomal landscapes, but large rearrangements could be spotted. Despite these rearrangements, the genome content and organization – i.e. genes and repeats – remain stable, with a limited number of genes gains and losses. As in any fungal plant pathogen genome, the repertoire of candidate effectors predicted among secreted proteins was more particularly scrutinized. Such effector genes have previously been reported in other pathogens in repeat-enriched plastic genomic regions with accelerated evolutionary rates under the pressure of the host immune system (Raffaele and Kamoun 2012). Demené and collaborators established a list of priority candidate effectors in the C. parasitica gene catalog likely involved in the interaction with the host plant which will require more attention in future functional studies. Six major inter-chromosomal translocations were detected and are likely associated with double break strands repairs. The authors speculate on the possible effects that these translocations may have on gene organization and expression regulation leading to dramatic phenotypic changes in relation to introduction and invasion in new continents and the impact regarding sexual reproduction in this fungus (Demené et al. 2022). I recommend this article not only because it is providing an improved assembly of a reference genome for C. parasitica, but also because it adds diversity in terms of genome references availability, with a third high-quality assembly. Such an effort in the tree pathology community for a pathogen under surveillance is of particular importance for future progress in post-genomic analysis, e.g. in further genomic population studies (Hartmann 2022). References Anagnostakis SL (1987) Chestnut Blight: The Classical Problem of an Introduced Pathogen. Mycologia, 79, 23–37. https://doi.org/10.2307/3807741 Crouch JA, Dawe A, Aerts A, Barry K, Churchill ACL, Grimwood J, Hillman BI, Milgroom MG, Pangilinan J, Smith M, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Yadav JS, Grigoriev IV, Nuss DL (2020) Genome Sequence of the Chestnut Blight Fungus Cryphonectria parasitica EP155: A Fundamental Resource for an Archetypical Invasive Plant Pathogen. Phytopathology®, 110, 1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-12-19-0478-A Dean RA, Talbot NJ, Ebbole DJ, Farman ML, Mitchell TK, Orbach MJ, Thon M, Kulkarni R, Xu J-R, Pan H, Read ND, Lee Y-H, Carbone I, Brown D, Oh YY, Donofrio N, Jeong JS, Soanes DM, Djonovic S, Kolomiets E, Rehmeyer C, Li W, Harding M, Kim S, Lebrun M-H, Bohnert H, Coughlan S, Butler J, Calvo S, Ma L-J, Nicol R, Purcell S, Nusbaum C, Galagan JE, Birren BW (2005) The genome sequence of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Nature, 434, 980–986. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03449 Demené A., Laurent B., Cros-Arteil S., Boury C. and Dutech C. 2022. Chromosomal rearrangements with stable repertoires of genes and transposable elements in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungus. bioRxiv, 2021.03.09.434572, ver.6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.09.434572 Goffeau A, Barrell BG, Bussey H, Davis RW, Dujon B, Feldmann H, Galibert F, Hoheisel JD, Jacq C, Johnston M, Louis EJ, Mewes HW, Murakami Y, Philippsen P, Tettelin H, Oliver SG (1996) Life with 6000 Genes. Science, 274, 546–567. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.274.5287.546 Hartmann FE (2022) Using structural variants to understand the ecological and evolutionary dynamics of fungal plant pathogens. New Phytologist, 234, 43–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17907 Raffaele S, Kamoun S (2012) Genome evolution in filamentous plant pathogens: why bigger can be better. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 417–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2790 Spatafora JW, Aime MC, Grigoriev IV, Martin F, Stajich JE, Blackwell M (2017) The Fungal Tree of Life: from Molecular Systematics to Genome-Scale Phylogenies. Microbiology Spectrum, 5, 5.5.03. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0053-2016 | Chromosomal rearrangements with stable repertoires of genes and transposable elements in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungus | Arthur Demene, Benoit Laurent, Sandrine Cros-Arteil, Christophe Boury, Cyril Dutech | <p style="text-align: justify;">Chromosomal rearrangements have been largely described among eukaryotes, and may have important consequences on evolution of species. High genome plasticity has been often reported in Fungi, which may explain their ... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Fungi | Sebastien Duplessis | 2021-03-12 14:18:20 | View | |
11 Mar 2021

Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stagesThibault Scalvenzi, Isabelle Clavereau, Mickael Bourge, Nicolas Pollet https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.25.110734A comprehensive look at Xenopus gut microbiota: effects of feed, developmental stages and parental transmissionRecommended by Wirulda Pootakham based on reviews by Vanessa Marcelino and 1 anonymous reviewerIt is well established that the gut microbiota play an important role in the overall health of their hosts (Jandhyala et al. 2015). To date, there are still a limited number of studies on the complex microbial communites inhabiting vertebrate digestive systems, especially the ones that also explored the functional diversity of the microbial community (Bletz et al. 2016). This preprint by Scalvenzi et al. (2021) reports a comprehensive study on the phylogenetic and metabolic profiles of the Xenopus gut microbiota. The author describes significant changes in the gut microbiome communities at different developmental stages and demonstrates different microbial community composition across organs. In addition, the study also investigates the impact of diet on the Xenopus tadpole gut microbiome communities as well as how the bacterial communities are transmitted from parents to the next generation. This is one of the first studies that addresses the interactions between gut bacteria and tadpoles during the development. The authors observe the dynamics of gut microbiome communities during tadpole growth and metamorphosis. They also explore host-gut microbial community metabolic interactions and demostrate the capacity of the microbiome to complement the metabolic pathways of the Xenopus genome. Although this study is limited by the use of Xenopus tadpoles in a laboratory, which are probably different from those in nature, I believe it still provides important and valuable information for the research community working on vertebrate’s microbiota and their interaction with the host. References Bletz et al. (2016). Amphibian gut microbiota shifts differentially in community structure but converges on habitat-specific predicted functions. Nature Communications, 7(1), 1-12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13699 Jandhyala, S. M., Talukdar, R., Subramanyam, C., Vuyyuru, H., Sasikala, M., & Reddy, D. N. (2015). Role of the normal gut microbiota. World journal of gastroenterology: WJG, 21(29), 8787. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748%2Fwjg.v21.i29.8787 Scalvenzi, T., Clavereau, I., Bourge, M. & Pollet, N. (2021) Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stages. bioRxiv, 2020.05.25.110734, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Geonmics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.25.110734 | Gut microbial ecology of Xenopus tadpoles across life stages | Thibault Scalvenzi, Isabelle Clavereau, Mickael Bourge, Nicolas Pollet | <p><strong>Background</strong> The microorganism world living in amphibians is still largely under-represented and under-studied in the literature. Among anuran amphibians, African clawed frogs of the Xenopus genus stand as well-characterized mode... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Metagenomics, Vertebrates | Wirulda Pootakham | 2020-05-25 14:01:19 | View |











