Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers▼ | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
18 Jul 2022
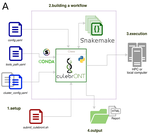
CulebrONT: a streamlined long reads multi-assembler pipeline for prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomesJulie Orjuela, Aurore Comte, Sébastien Ravel, Florian Charriat, Tram Vi, Francois Sabot, Sébastien Cunnac https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.19.452922A flexible and reproducible pipeline for long-read assembly and evaluationRecommended by Raúl Castanera based on reviews by Benjamin Istace and Valentine MurigneuxThird-generation sequencing has revolutionised de novo genome assembly. Thanks to this technology, genome reference sequences have evolved from fragmented drafts to gapless, telomere-to-telomere genome assemblies. Long reads produced by Oxford Nanopore and PacBio technologies can span structural variants and resolve complex repetitive regions such as centromeres, unlocking previously inaccessible genomic information. Nowadays, many research groups can afford to sequence the genome of their working model using long reads. Nevertheless, genome assembly poses a significant computational challenge. Read length, quality, coverage and genomic features such as repeat content can affect assembly contiguity, accuracy, and completeness in almost unpredictable ways. Consequently, there is no best universal software or protocol for this task. Producing a high-quality assembly requires chaining several tools into pipelines and performing extensive comparisons between the assemblies obtained by different tool combinations to decide which one is the best. This task can be extremely challenging, as the number of tools available rises very rapidly, and thorough benchmarks cannot be updated and published at such a fast pace. In their paper, Orjuela and collaborators present CulebrONT [1], a universal pipeline that greatly contributes to overcoming these challenges and facilitates long-read genome assembly for all taxonomic groups. CulebrONT incorporates six commonly used assemblers and allows to perform assembly, circularization (if needed), polishing, and evaluation in a simple framework. One important aspect of CulebrONT is its modularity, which allows the activation or deactivation of specific tools, giving great flexibility to the user. Nevertheless, possibly the best feature of CulebrONT is the opportunity to benchmark the selected tool combinations based on the excellent report generated by the pipeline. This HTML report aggregates the output of several tools for quality evaluation of the assemblies (e.g. BUSCO [2] or QUAST [3]) generated by the different assemblers, in addition to the running time and configuration parameters. Such information is of great help to identify the best-suited pipeline, as exemplified by the authors using four datasets of different taxonomic origins. Finally, CulebrONT can handle multiple samples in parallel, which makes it a good solution for laboratories looking for multiple assemblies on a large scale. References 1. Orjuela J, Comte A, Ravel S, Charriat F, Vi T, Sabot F, Cunnac S (2022) CulebrONT: a streamlined long reads multi-assembler pipeline for prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. bioRxiv, 2021.07.19.452922, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.19.452922 2. Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics, 31, 3210–3212. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351 3. Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 29, 1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086 | CulebrONT: a streamlined long reads multi-assembler pipeline for prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes | Julie Orjuela, Aurore Comte, Sébastien Ravel, Florian Charriat, Tram Vi, Francois Sabot, Sébastien Cunnac | <p style="text-align: justify;">Using long reads provides higher contiguity and better genome assemblies. However, producing such high quality sequences from raw reads requires to chain a growing set of tools, and determining the best workflow is ... |  | Bioinformatics | Raúl Castanera | Valentine Murigneux | 2022-02-22 16:21:25 | View |
06 May 2022
A deep dive into genome assemblies of non-vertebrate animalsNadège Guiglielmoni, Ramón Rivera-Vicéns, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202111.0170.v3Diving, and even digging, into the wild jungle of annotation pathways for non-vertebrate animalsRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by Yann Bourgeois, Cécile Monat, Valentina Peona and Benjamin Istace based on reviews by Yann Bourgeois, Cécile Monat, Valentina Peona and Benjamin Istace
In their paper, Guiglielmoni et al. propose we pick up our snorkels and palms and take "A deep dive into genome assemblies of non-vertebrate animals" (1). Indeed, while numerous assembly-related tools were developed and tested for human genomes (or at least vertebrates such as mice), very few were tested on non-vertebrate animals so far. Moreover, most of the benchmarks are aimed at raw assembly tools, and very few offer a guide from raw reads to an almost finished assembly, including quality control and phasing. This huge and exhaustive review starts with an overview of the current sequencing technologies, followed by the theory of the different approaches for assembly and their implementation. For each approach, the authors present some of the most representative tools, as well as the limits of the approach. The authors additionally present all the steps required to obtain an almost complete assembly at a chromosome-scale, with all the different technologies currently available for scaffolding, QC, and phasing, and the way these tools can be applied to non-vertebrates animals. Finally, they propose some useful advice on the choice of the different approaches (but not always tools, see below), and advocate for a robust genome database with all information on the way the assembly was obtained. This review is a very complete one for now and is a very good starting point for any student or scientist interested to start working on genome assembly, from either model or non-model organisms. However, the authors do not provide a list of tools or a benchmark of them as a recommendation. Why? Because such a proposal may be obsolete in less than a year.... Indeed, with the explosion of the 3rd generation of sequencing technology, assembly tools (from different steps) are constantly evolving, and their relative performance increases on a monthly basis. In addition, some tools are really efficient at the time of a review or of an article, but are not further developed later on, and thus will not evolve with the technology. We have all seen it with wonderful tools such as Chiron (2) or TopHat (3), which were very promising ones, but cannot be developed further due to the stop of the project, the end of the contract of the post-doc in charge of the development, or the decision of the developer to switch to another paradigm. Such advice would, therefore, need to be constantly updated. Thus, the manuscript from Guiglielmoni et al will be an almost intemporal one (up to the next sequencing revolution at last), and as they advocated for a more informed genome database, I think we should consider a rolling benchmarking system (tools, genome and sequence dataset) allowing to keep the performance of the tools up-to-date, and to propose the best set of assembly tools for a given type of genome. References 1. Guiglielmoni N, Rivera-Vicéns R, Koszul R, Flot J-F (2022) A Deep Dive into Genome Assemblies of Non-vertebrate Animals. Preprints, 2021110170, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202111.0170 2. Teng H, Cao MD, Hall MB, Duarte T, Wang S, Coin LJM (2018) Chiron: translating nanopore raw signal directly into nucleotide sequence using deep learning. GigaScience, 7, giy037. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giy037 3. Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics, 25, 1105–1111. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120 | A deep dive into genome assemblies of non-vertebrate animals | Nadège Guiglielmoni, Ramón Rivera-Vicéns, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot | <p style="text-align: justify;">Non-vertebrate species represent about ∼95% of known metazoan (animal) diversity. They remain to this day relatively unexplored genetically, but understanding their genome structure and function is pivotal for expan... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics | Francois Sabot | Valentina Peona, Benjamin Istace, Cécile Monat, Yann Bourgeois | 2021-11-10 17:47:31 | View |
12 Jul 2022

Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: steppingstones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert antsHugo Darras, Natalia de Souza Araujo, Lyam Baudry, Nadège Guiglielmoni, Pedro Lorite, Martial Marbouty, Fernando Rodriguez, Irina Arkhipova, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot, Serge Aron https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.07.475286A genomic resource for ants, and moreRecommended by Nadia Ponts based on reviews by Isabel Almudi and Nicolas NègreThe ant species Cataglyphis hispanica is remarkably well adapted to arid habitats of the Iberian Peninsula where two hybridogenetic lineages co-occur, i.e., queens mating with males from the other lineage produce only non-reproductive hybrid workers whereas reproductive males and females are produced by parthenogenesis (Lavanchy and Schwander, 2019). For these two reasons, the genomes of these lineages, Chis1 and Chis2, are potential gold mines to explore the genetic bases of thermal adaptation and the evolution of alternative reproductive modes. Nowadays, sequencing technology enables assembling all kinds of genomes provided genomic DNA can be extracted. More difficult to achieve is high-quality assemblies with just as high-quality annotations that are readily available to the community to be used and re-used at will (Byrne et al., 2019; Salzberg, 2019). The challenge was successfully completed by Darras and colleagues, the generated resource being fully available to the community, including scripts and command lines used to obtain the proposed results. The authors particularly describe that lineage Chis2 has 27 chromosomes, against 26 or 27 for lineage Chis1, with a Robertsonian translocation identified by chromosome conformation capture (Duan et al., 2010, 2012) in the two Queens sequenced. Transcript-supported gene annotation provided 11,290 high-quality gene models. In addition, an ant-tailored annotation pipeline identified 56 different families of repetitive elements in both Chis1 and Chis2 lineages of C. hispanica spread in a little over 15 % of the genome. Altogether, the genomes of Chis1 and Chis2 are highly similar and syntenic, with some level of polymorphism raising questions about their evolutionary story timeline. In particular, the uniform distribution of polymorphisms along the genomes shakes up a previous hypothesis of hybridogenetic lineage pairs determined by ancient non-recombining regions (Linksvayer, Busch and Smith, 2013). I recommend this paper because the science behind is both solid and well-explained. The provided resource is of high quality, and accompanied by a critical exploration of the perspectives brought by the results. These genomes are excellent resources to now go further in exploring the possible events at the genome level that accompanied the remarkable thermal adaptation of the ants Cataglyphis, as well as insights into the genetics of hybridogenetic lineages. Beyond the scientific value of the resources and insights provided by the work performed, I also recommend this article because it is an excellent example of Open Science (Allen and Mehler, 2019; Sarabipour et al., 2019), all data methods and tools being fully and easily accessible to whoever wants/needs it. References Allen C, Mehler DMA (2019) Open science challenges, benefits and tips in early career and beyond. PLOS Biology, 17, e3000246. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000246 Byrne A, Cole C, Volden R, Vollmers C (2019) Realizing the potential of full-length transcriptome sequencing. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 374, 20190097. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2019.0097 Darras H, de Souza Araujo N, Baudry L, Guiglielmoni N, Lorite P, Marbouty M, Rodriguez F, Arkhipova I, Koszul R, Flot J-F, Aron S (2022) Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: stepping stones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert ants. bioRxiv, 2022.01.07.475286, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.07.475286 Duan Z, Andronescu M, Schutz K, Lee C, Shendure J, Fields S, Noble WS, Anthony Blau C (2012) A genome-wide 3C-method for characterizing the three-dimensional architectures of genomes. Methods, 58, 277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.06.018 Duan Z, Andronescu M, Schutz K, McIlwain S, Kim YJ, Lee C, Shendure J, Fields S, Blau CA, Noble WS (2010) A three-dimensional model of the yeast genome. Nature, 465, 363–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08973 Lavanchy G, Schwander T (2019) Hybridogenesis. Current Biology, 29, R9–R11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.11.046 Linksvayer TA, Busch JW, Smith CR (2013) Social supergenes of superorganisms: Do supergenes play important roles in social evolution? BioEssays, 35, 683–689. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201300038 Salzberg SL (2019) Next-generation genome annotation: we still struggle to get it right. Genome Biology, 20, 92. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1715-2 Sarabipour S, Debat HJ, Emmott E, Burgess SJ, Schwessinger B, Hensel Z (2019) On the value of preprints: An early career researcher perspective. PLOS Biology, 17, e3000151. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000151 | Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: steppingstones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert ants | Hugo Darras, Natalia de Souza Araujo, Lyam Baudry, Nadège Guiglielmoni, Pedro Lorite, Martial Marbouty, Fernando Rodriguez, Irina Arkhipova, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot, Serge Aron | <p style="text-align: justify;"><em>Cataglyphis</em> are thermophilic ants that forage during the day when temperatures are highest and sometimes close to their critical thermal limit. Several Cataglyphis species have evolved unusual reproductive ... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Nadia Ponts | Nicolas Nègre, Isabel Almudi | 2022-01-13 16:47:30 | View |
24 Feb 2023

MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomesBertrand Néron, Rémi Denise, Charles Coluzzi, Marie Touchon, Eduardo P. C. Rocha, Sophie S. Abby https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.02.506364A unique and customizable approach for functionally annotating prokaryotic genomesRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by Kwee Boon Brandon Seah and Max Emil Schön based on reviews by Kwee Boon Brandon Seah and Max Emil Schön
Macromolecular System Finder (MacSyFinder) v2 (Néron et al., 2023) is a newly updated approach for performing functional annotation of prokaryotic genomes (Abby et al., 2014). This tool parses an input file of protein sequences from a single genome (either ordered by genome location or unordered) and identifies the presence of specific cellular functions (referred to as “systems”). These systems are called based on two criteria: (1) that the "quorum" of a minimum set of core proteins involved is reached the “quorum” of a minimum set of core proteins being involved that are present, and (2) that the genes encoding these proteins are in the expected genomic organization (e.g., within the same order in an operon), when ordered data is provided. I believe the MacSyFinder approach represents an improvement over more commonly used methods exactly because it can incorporate such information on genomic organization, and also because it is more customizable. Before properly appreciating these points, it is worth noting the norms and key challenges surrounding high-throughput functional annotation of prokaryotic genomes. Genome sequences are being added to online repositories at increasing rates, which has led to an enormous amount of bacterial genome diversity available to investigate (Altermann et al., 2022). A key aspect of understanding this diversity is the functional annotation step, which enables genes to be grouped into more biologically interpretable categories. For instance, gene calls can be mapped against existing Clusters of Orthologous Genes, which are themselves grouped into general categories such as ‘Transcription’ and ‘Lipid metabolism’ (Galperin et al., 2021). This approach is valuable but is primarily used for global summaries of functional annotations within a genome: for example, it could be useful to know that a genome is particularly enriched for genes involved in lipid metabolism. However, knowing that a particular gene is involved in the general process of lipid metabolism is less likely to be actionable. In other words, the desired specificity of a gene’s functional annotation will depend on the exact question being investigated. There is no shortage of functional ontologies in genomics that can be applied for this purpose (Douglas and Langille, 2021), and researchers are often overwhelmed by the choice of which functional ontology to use. In this context, giving researchers the ability to precisely specify the gene families and operon structures they are interested in identifying across genomes provides useful control over what precise functions they are profiling. Of course, most researchers will lack the information and/or expertise to fully take advantage of MacSyFinder’s customizable features, but having this option for specialized purposes is valuable. The other MacSyFinder feature that I find especially noteworthy is that it can incorporate genomic organization (e.g., of genes ordered in operons) when calling systems. This is a rare feature among commonly used tools for functional annotation and likely results in much higher specificity. As the authors note, this capability makes the co-occurrence of paralogs, and other divergent genes that share sequence similarity, to contribute less noise (i.e., they result in fewer false positive calls). It is important to emphasize that these features are not new additions in MacSyFinder v2, but there are many other valuable changes. Most practically, this release is written in Python 3, rather than the obsolete Python 2.7, and was made more computationally efficient, which will enable MacSyFinder to be more widely used and more easily maintained moving forward. In addition, the search algorithm for analyzing individual proteins was fundamentally updated as well. The authors show that their improvements to the search algorithm result in an 8% and 20% increase in the number of identified calls for single and multi-locus secretion systems, respectively. Taken together, MacSyFinder v2 represents both practical and scientific improvements over the previous version, which will be of great value to the field. References Abby SS, Néron B, Ménager H, Touchon M, Rocha EPC (2014) MacSyFinder: A Program to Mine Genomes for Molecular Systems with an Application to CRISPR-Cas Systems. PLOS ONE, 9, e110726. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110726 Altermann E, Tegetmeyer HE, Chanyi RM (2022) The evolution of bacterial genome assemblies - where do we need to go next? Microbiome Research Reports, 1, 15. https://doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2022.02 Douglas GM, Langille MGI (2021) A primer and discussion on DNA-based microbiome data and related bioinformatics analyses. Peer Community Journal, 1. https://doi.org/10.24072/pcjournal.2 Galperin MY, Wolf YI, Makarova KS, Vera Alvarez R, Landsman D, Koonin EV (2021) COG database update: focus on microbial diversity, model organisms, and widespread pathogens. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, D274–D281. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1018 Néron B, Denise R, Coluzzi C, Touchon M, Rocha EPC, Abby SS (2023) MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomes. bioRxiv, 2022.09.02.506364, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.02.506364 | MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomes | Bertrand Néron, Rémi Denise, Charles Coluzzi, Marie Touchon, Eduardo P. C. Rocha, Sophie S. Abby | <p style="text-align: justify;">Complex cellular functions are usually encoded by a set of genes in one or a few organized genetic loci in microbial genomes. Macromolecular System Finder (MacSyFinder) is a program that uses these properties to mod... |  | Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Functional genomics | Gavin Douglas | Kwee Boon Brandon Seah, Max Emil Schön | 2022-09-09 10:30:31 | View |
11 May 2024
The European Reference Genome Atlas: piloting a decentralised approach to equitable biodiversity genomicsAnn M Mc Cartney, Giulio Formenti, Alice Mouton, Claudio Ciofi, Robert M Waterhouse, Camila J Mazzoni, Diego De Panis, Luisa S Schlude Marins, Henrique G Leitao, Genevieve Diedericks, Joseph Kirangwa, Marco Morselli, Judit Salces, Nuria Escudero, Alessio Iannucci, Chiara Natali, Hannes Svardal, Rosa Fernandez, Tim De Pooter, Geert Joris, Mojca Strazisar, Jo Wood, Katie E Herron, Ole Seehausen, Phillip C Watts, Felix Shaw, Robert P Davey, Alice Minotto, Jose Maria Fernandez Gonzalez, Astrid Bohne... https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.09.25.559365Informed Choices, Cohesive Future: Decisions and Recommendations for ERGARecommended by Jitendra Narayan based on reviews by Justin Ideozu and Eric Crandall based on reviews by Justin Ideozu and Eric Crandall
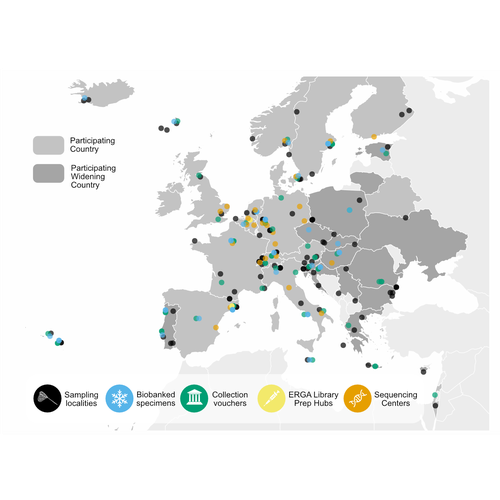
The European Reference Genome Atlas (ERGA) (Mc Cartney et al, 2024, Mazzoni et al, 2023) demonstrates the collaborative spirit and intellectual abilities of researchers from 33 European countries. This ambitious project, which is part of the Earth BioGenome Project (Lewin et al., 2018) Phase II, has embarked on an unprecedented mission: to decipher the genetic makeup of 150,000 species over a span of four years. At the heart of ERGA is a decentralized pilot infrastructure specifically built to assist the production of high-quality reference genomes. This structure acts as a scaffold for the massive task of genome sequencing, giving the necessary framework to manage the complexity of genomic research. The research paper under consideration offers a comprehensive narrative of ERGA's evolution, outlining both successes and challenges encountered along the road. One of the most significant issues addressed in the manuscript is the equitable distribution of resources and expertise among participating laboratories and countries. In a project of this magnitude, it is critical to leverage the pooled talents and capacities of researchers from across Europe. ERGA's pan-European network promotes communications and collaboration, creating an environment in which knowledge flows freely and barriers are overcome. This adoption of strong coordination and communication tactics will be essential to ERGA's success. Scientific collaboration depends on efficient communication channels because they allow researchers to share resources, collaborate on new initiatives, and exchange ideas. Through a diverse range of gatherings, courses, and virtual discussion boards, ERGA fosters an environment of transparency and cooperation among members, enabling scientists to overcome challenges and make significant discoveries. The importance ERGA places on training and information transfer programmes is a pillar of its strategy. Understanding the importance of capacity development, ERGA invests in providing researchers with the knowledge and abilities necessary for effectively navigating the complicated terrain of genomic research. A wide range of subjects are covered in training programmes (Larivière et al. 2023), from sample preparation and collection to data processing methods and sequencing technology. Through the development of a group of highly qualified experts, ERGA creates the foundation for continued advancement and creativity in the genomics sector. This manuscript also covers in detail the technological workflows and sequencing techniques used in ERGA's pilot infrastructure. With the aid of cutting-edge sequencing technologies based on both long-read and short-read sequencing, they are working to unravel the complex structure of the genetic code with a level of accuracy and precision never before possible. To guarantee the accuracy of genetic data and prevent mistakes and flaws that can jeopardize the findings' integrity, quality control methods are put in place. Despite having a focus on genome sequencing due to its technological complexities, ERGA also remains firm in its dedication to metadata collection and sample validation. Metadata serves as a critical link between raw genetic data and useful scientific insights, giving necessary context and allowing researchers to draw practical findings from their investigations. Sample validation approaches improve the reliability and reproducibility of the results, providing users confidence in the quality of the genetic data provided by ERGA. Looking ahead, ERGA envisions its decentralized infrastructure serving as a model for global collaborative research efforts. By embracing diversity, encouraging cooperation, and pushing for open access to data and resources, ERGA hopes to catalyze scientific discovery and generate positive change in the field of biodiversity genomics. ERGA aims to promote a more equitable and sustainable future for all by ongoing interaction with stakeholders, intensive outreach and education activities, and policy change advocacy. In addition to its immediate goals, ERGA considers the long-term implications of its work. As genomic technology progresses, the potential application of high-quality reference genomes will continue to grow. From informing conservation efforts and illuminating evolutionary histories to revolutionizing healthcare and agriculture, it is likely that ERGA's contributions will have far-reaching consequences for people and the planet as a whole. Furthermore, ERGA understands the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in addressing the difficult challenges of the twenty-first century. ERGA aims to integrate genetic research into larger initiatives to promote sustainability and biodiversity conservation by forming relationships with stakeholders from other areas, such as policymakers, conservationists, and indigenous groups. Through shared knowledge and community action, ERGA seeks to create a future in which mankind coexists peacefully with the natural world, guided by a thorough grasp of its genetic legacy and ecological interconnectivity. Finally, the manuscript exemplifies ERGA's collaborative ambitions and achievements, capturing the spirit of creativity and collaboration that defines this ground-breaking effort. As ERGA continues to push the boundaries of genetic research, it remains dedicated to scientific excellence, inclusivity, and the quest of knowledge for the benefit of society. I wholeheartedly recommend the publication of this groundbreaking initiative, offering my enthusiastic endorsement for its valuable contribution to the scientific community. References Lewin, H. A., Robinson, G. E., Kress, W. J., Baker, W. J., Coddington, J., Crandall, K. A., Durbin, R., Edwards, S. V., Forest, F., Gilbert, M. T. P., Goldstein, M. M., Grigoriev, I. V., Hackett, K. J., Haussler, D., Jarvis, E. D., Johnson, W. E., Patrinos, A., Richards, S., Castilla-Rubio, J. C., … Zhang, G. (2018). Earth BioGenome Project: Sequencing life for the future of life. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(17), 4325–4333. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1720115115 Mazzoni, C. J., Claudio, C.i, Waterhouse, R. M. (2023). Biodiversity: an atlas of European reference genomes. Nature 619 : 252-252. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-02229-w Mc Cartney, A. M., Formenti, G., Mouton, A., Panis, D. de, Marins, L. S., Leitão, H. G., Diedericks, G., Kirangwa, J., Morselli, M., Salces-Ortiz, J., Escudero, N., Iannucci, A., Natali, C., Svardal, H., Fernández, R., Pooter, T. de, Joris, G., Strazisar, M., Wood, J., … Mazzoni, C. J. (2024). The European Reference Genome Atlas: piloting a decentralised approach to equitable biodiversity genomics. bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.09.25.559365 | The European Reference Genome Atlas: piloting a decentralised approach to equitable biodiversity genomics | Ann M Mc Cartney, Giulio Formenti, Alice Mouton, Claudio Ciofi, Robert M Waterhouse, Camila J Mazzoni, Diego De Panis, Luisa S Schlude Marins, Henrique G Leitao, Genevieve Diedericks, Joseph Kirangwa, Marco Morselli, Judit Salces, Nuria Escudero, ... | <p>English: A global genome database of all of Earth's species diversity could be a treasure trove of scientific discoveries. However, regardless of the major advances in genome sequencing technologies, only a tiny fraction of species have genomic... |  | Bioinformatics, ERGA Pilot | Jitendra Narayan | Justin Ideozu, Eric Crandall | 2023-10-01 01:03:58 | View |
25 Nov 2022
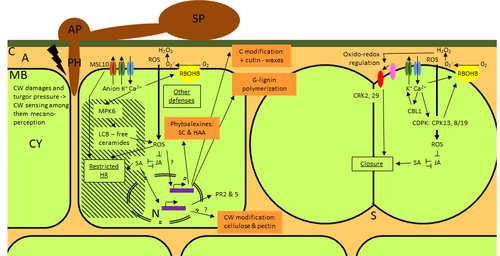
Phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses reveal major differences between apple and pear scab nonhost resistanceE. Vergne, E. Chevreau, E. Ravon, S. Gaillard, S. Pelletier, M. Bahut, L. Perchepied https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.01.446506Apples and pears: two closely related species with differences in scab nonhost resistanceRecommended by Wirulda Pootakham based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersNonhost resistance is a common form of disease resistance exhibited by plants against microorganisms that are pathogenic to other plant species [1]. Apples and pears are two closely related species belonging to Rosaceae family, both affected by scab disease caused by fungal pathogens in the Venturia genus. These pathogens appear to be highly host-specific. While apples are nonhosts for Venturia pyrina, pears are nonhosts for Venturia inaequalis. To date, the molecular bases of scab nonhost resistance in apple and pear have not been elucidated. This preprint by Vergne, et al (2022) [2] analyzed nonhost resistance symptoms in apple/V. pyrina and pear/V. inaequalis interactions as well as their transcriptomic responses. Interestingly, the author demonstrated that the nonhost apple/V. pyrina interaction was almost symptomless while hypersensitive reactions were observed for pear/V. inaequalis interaction. The transcriptomic analyses also revealed a number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that corresponded to the severity of the interactions, with very few DEGs observed during the apple/V. pyrina interaction and a much higher number of DEGs during the pear/V. inaequalis interaction. This type of reciprocal host-pathogen interaction study is valuable in gaining new insights into how plants interact with microorganisms that are potential pathogens in related species. A few processes appeared to be involved in the pear resistance against the nonhost pathogen V. inaequalis at the transcriptomic level, such as stomata closure, modification of cell wall and production of secondary metabolites as well as phenylpropanoids. Based on the transcriptomics changes during the nonhost interaction, the author compared the responses to those of host-pathogen interactions and revealed some interesting findings. They proposed a series of cascading effects in pear induced by the presence of V. inaequalis, which I believe helps shed some light on the basic mechanism for nonhost resistance. I am recommending this study because it provides valuable information that will strengthen our understanding of nonhost resistance in the Rosaceae family and other plant species. The knowledge gained here may be applied to genetically engineer plants for a broader resistance against a number of pathogens in the future. References 1. Senthil-Kumar M, Mysore KS (2013) Nonhost Resistance Against Bacterial Pathogens: Retrospectives and Prospects. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 51, 407–427. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102319 2. Vergne E, Chevreau E, Ravon E, Gaillard S, Pelletier S, Bahut M, Perchepied L (2022) Phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses reveal major differences between apple and pear scab nonhost resistance. bioRxiv, 2021.06.01.446506, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.01.446506 | Phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses reveal major differences between apple and pear scab nonhost resistance | E. Vergne, E. Chevreau, E. Ravon, S. Gaillard, S. Pelletier, M. Bahut, L. Perchepied | <p style="text-align: justify;"><strong>Background. </strong>Nonhost resistance is the outcome of most plant/pathogen interactions, but it has rarely been described in Rosaceous fruit species. Apple (<em>Malus x domestica</em> Borkh.) have a nonho... |  | Functional genomics, Plants | Wirulda Pootakham | Jessica Soyer, Anonymous | 2022-05-13 15:06:08 | View |
24 Sep 2020

A rapid and simple method for assessing and representing genome sequence relatednessM Briand, M Bouzid, G Hunault, M Legeay, M Fischer-Le Saux, M Barret https://doi.org/10.1101/569640A quick alternative method for resolving bacterial taxonomy using short identical DNA sequences in genomes or metagenomesRecommended by B. Jesse Shapiro based on reviews by Gavin Douglas and 1 anonymous reviewerThe bacterial species problem can be summarized as follows: bacteria recombine too little, and yet too much (Shapiro 2019). References Arevalo P, VanInsberghe D, Elsherbini J, Gore J, Polz MF (2019) A Reverse Ecology Approach Based on a Biological Definition of Microbial Populations. Cell, 178, 820-834.e14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.033 | A rapid and simple method for assessing and representing genome sequence relatedness | M Briand, M Bouzid, G Hunault, M Legeay, M Fischer-Le Saux, M Barret | <p>Coherent genomic groups are frequently used as a proxy for bacterial species delineation through computation of overall genome relatedness indices (OGRI). Average nucleotide identity (ANI) is a widely employed method for estimating relatedness ... |  | Bioinformatics, Metagenomics | B. Jesse Shapiro | Gavin Douglas | 2019-11-07 16:37:56 | View |
15 Dec 2022

Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAsAdeline Simon, Alex Mercier, Pierre Gladieux, Benoit Poinssot, Anne-Sophie Walker, Muriel Viaud https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.07.483234Exploring genomic determinants of host specialization in Botrytis cinereaRecommended by Sebastien Duplessis based on reviews by Cecile Lorrain and Thorsten LangnerThe genomics era has pushed forward our understanding of fungal biology. Much progress has been made in unraveling new gene functions and pathways, as well as the evolution or adaptation of fungi to their hosts or environments through population studies (Hartmann et al. 2019; Gladieux et al. 2018). Closing gaps more systematically in draft genomes using the most recent long-read technologies now seems the new standard, even with fungal species presenting complex genome structures (e.g. large and highly repetitive dikaryotic genomes; Duan et al. 2022). Understanding the genomic dynamics underlying host specialization in phytopathogenic fungi is of utmost importance as it may open new avenues to combat diseases. A strong host specialization is commonly observed for biotrophic and hemi-biotrophic fungal species or for necrotrophic fungi with a narrow host range, whereas necrotrophic fungi with broad host range are considered generalists (Liang and Rollins, 2018; Newman and Derbyshire, 2020). However, some degrees of specialization towards given hosts have been reported in generalist fungi and the underlying mechanisms remain to be determined. Botrytis cinerea is a polyphagous necrotrophic phytopathogen with a particularly wide host range and it is notably responsible for grey mould disease on many fruits, such as tomato and grapevine. Because of its importance as a plant pathogen, its relatively small genome size and its taxonomical position, it has been targeted for early genome sequencing and a first reference genome was provided in 2011 (Amselem et al. 2011). Other genomes were subsequently sequenced for other strains, and most importantly a gapless assembled version of the initial reference genome B05.10 was provided to the community (van Kan et al. 2017). This genomic resource has supported advances in various aspects of the biology of B. cinerea such as the production of specialized metabolites, which plays an important role in host-plant colonization, or more recently in the production of small RNAs which interfere with the host immune system, representing a new class of non-proteinaceous virulence effectors (Dalmais et al. 2011; Weiberg et al. 2013). In the present study, Simon et al. (2022) use PacBio long-read sequencing for Sl3 and Vv3 strains, which represent genetic clusters in B. cinerea populations found on tomato and grapevine. The authors combined these complete and high-quality genome assemblies with the B05.10 reference genome and population sequencing data to perform a comparative genomic analysis of specialization towards the two host plants. Transposable elements generate genomic diversity due to their mobile and repetitive nature and they are of utmost importance in the evolution of fungi as they deeply reshape the genomic landscape (Lorrain et al. 2021). Accessory chromosomes are also known drivers of adaptation in fungi (Möller and Stukenbrock, 2017). Here, the authors identify several genomic features such as the presence of different sets of accessory chromosomes, the presence of differentiated repertoires of transposable elements, as well as related small RNAs in the tomato and grapevine populations, all of which may be involved in host specialization. Whereas core chromosomes are highly syntenic between strains, an accessory chromosome validated by pulse-field electrophoresis is specific of the strains isolated from grapevine. Particularly, they show that two particular retrotransposons are discriminant between the strains and that they allow the production of small RNAs that may act as effectors. The discriminant accessory chromosome of the Vv3 strain harbors one of the unraveled retrotransposons as well as new genes of yet unidentified function. I recommend this article because it perfectly illustrates how efforts put into generating reference genomic sequences of higher quality can lead to new discoveries and allow to build strong hypotheses about biology and evolution in fungi. Also, the study combines an up-to-date genomics approach with a classical methodology such as pulse-field electrophoresis to validate the presence of accessory chromosomes. A major input of this investigation of the genomic determinants of B. cinerea is that it provides solid hints for further analysis of host-specialization at the population level in a broad-scale phytopathogenic fungus. References Amselem J, Cuomo CA, Kan JAL van, Viaud M, Benito EP, Couloux A, Coutinho PM, Vries RP de, Dyer PS, Fillinger S, Fournier E, Gout L, Hahn M, Kohn L, Lapalu N, Plummer KM, Pradier J-M, Quévillon E, Sharon A, Simon A, Have A ten, Tudzynski B, Tudzynski P, Wincker P, Andrew M, Anthouard V, Beever RE, Beffa R, Benoit I, Bouzid O, Brault B, Chen Z, Choquer M, Collémare J, Cotton P, Danchin EG, Silva CD, Gautier A, Giraud C, Giraud T, Gonzalez C, Grossetete S, Güldener U, Henrissat B, Howlett BJ, Kodira C, Kretschmer M, Lappartient A, Leroch M, Levis C, Mauceli E, Neuvéglise C, Oeser B, Pearson M, Poulain J, Poussereau N, Quesneville H, Rascle C, Schumacher J, Ségurens B, Sexton A, Silva E, Sirven C, Soanes DM, Talbot NJ, Templeton M, Yandava C, Yarden O, Zeng Q, Rollins JA, Lebrun M-H, Dickman M (2011) Genomic Analysis of the Necrotrophic Fungal Pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLOS Genetics, 7, e1002230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002230 Dalmais B, Schumacher J, Moraga J, Le Pêcheur P, Tudzynski B, Collado IG, Viaud M (2011) The Botrytis cinerea phytotoxin botcinic acid requires two polyketide synthases for production and has a redundant role in virulence with botrydial. Molecular Plant Pathology, 12, 564–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00692.x Duan H, Jones AW, Hewitt T, Mackenzie A, Hu Y, Sharp A, Lewis D, Mago R, Upadhyaya NM, Rathjen JP, Stone EA, Schwessinger B, Figueroa M, Dodds PN, Periyannan S, Sperschneider J (2022) Physical separation of haplotypes in dikaryons allows benchmarking of phasing accuracy in Nanopore and HiFi assemblies with Hi-C data. Genome Biology, 23, 84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-022-02658-2 Gladieux P, Condon B, Ravel S, Soanes D, Maciel JLN, Nhani A, Chen L, Terauchi R, Lebrun M-H, Tharreau D, Mitchell T, Pedley KF, Valent B, Talbot NJ, Farman M, Fournier E (2018) Gene Flow between Divergent Cereal- and Grass-Specific Lineages of the Rice Blast Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. mBio, 9, e01219-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01219-17 Hartmann FE, Rodríguez de la Vega RC, Carpentier F, Gladieux P, Cornille A, Hood ME, Giraud T (2019) Understanding Adaptation, Coevolution, Host Specialization, and Mating System in Castrating Anther-Smut Fungi by Combining Population and Comparative Genomics. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 57, 431–457. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082718-095947 Liang X, Rollins JA (2018) Mechanisms of Broad Host Range Necrotrophic Pathogenesis in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathology®, 108, 1128–1140. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-06-18-0197-RVW Lorrain C, Oggenfuss U, Croll D, Duplessis S, Stukenbrock E (2021) Transposable Elements in Fungi: Coevolution With the Host Genome Shapes, Genome Architecture, Plasticity and Adaptation. In: Encyclopedia of Mycology (eds Zaragoza Ó, Casadevall A), pp. 142–155. Elsevier, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819990-9.00042-1 Möller M, Stukenbrock EH (2017) Evolution and genome architecture in fungal plant pathogens. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 15, 756–771. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.76 Newman TE, Derbyshire MC (2020) The Evolutionary and Molecular Features of Broad Host-Range Necrotrophy in Plant Pathogenic Fungi. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.591733 Simon A, Mercier A, Gladieux P, Poinssot B, Walker A-S, Viaud M (2022) Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAs. bioRxiv, 2022.03.07.483234, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.07.483234 Van Kan JAL, Stassen JHM, Mosbach A, Van Der Lee TAJ, Faino L, Farmer AD, Papasotiriou DG, Zhou S, Seidl MF, Cottam E, Edel D, Hahn M, Schwartz DC, Dietrich RA, Widdison S, Scalliet G (2017) A gapless genome sequence of the fungus Botrytis cinerea. Molecular Plant Pathology, 18, 75–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12384 Weiberg A, Wang M, Lin F-M, Zhao H, Zhang Z, Kaloshian I, Huang H-D, Jin H (2013) Fungal Small RNAs Suppress Plant Immunity by Hijacking Host RNA Interference Pathways. Science, 342, 118–123. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1239705 | Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAs | Adeline Simon, Alex Mercier, Pierre Gladieux, Benoit Poinssot, Anne-Sophie Walker, Muriel Viaud | <p style="text-align: justify;">The fungus <em>Botrytis cinerea</em> is a polyphagous pathogen that encompasses multiple host-specialized lineages. While several secreted proteins, secondary metabolites and retrotransposons-derived small RNAs have... |  | Fungi, Structural genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Sebastien Duplessis | Cecile Lorrain, Thorsten Langner | 2022-03-15 11:15:48 | View |
18 Feb 2021
Traces of transposable element in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networksAgnes Baud, Mariene Wan, Danielle Nouaud, Nicolas Francillonne, Dominique Anxolabehere, Hadi Quesneville https://doi.org/10.1101/547877Using small fragments to discover old TE remnants: the Duster approach empowers the TE detectionRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by Josep Casacuberta and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Josep Casacuberta and 1 anonymous reviewer
Transposable elements are the raw material of the dark matter of the genome, the foundation of the next generation of genes and regulation networks". This sentence could be the essence of the paper of Baud et al. (2021). Transposable elements (TEs) are endogenous mobile genetic elements found in almost all genomes, which were discovered in 1948 by Barbara McClintock (awarded in 1983 the only unshared Medicine Nobel Prize so far). TEs are present everywhere, from a single isolated copy for some elements to more than millions for others, such as Alu. They are founders of major gene lineages (HET-A, TART and telomerases, RAG1/RAG2 proteins from mammals immune system; Diwash et al, 2017), and even of retroviruses (Xiong & Eickbush, 1988). However, most TEs appear as selfish elements that replicate, land in a new genomic region, then start to decay and finally disappear in the midst of the genome, turning into genomic ‘dark matter’ (Vitte et al, 2007). The mutations (single point, deletion, recombination, and so on) that occur during this slow death erase some of their most notable features and signature sequences, rendering them completely unrecognizable after a few million years. Numerous TE detection tools have tried to optimize their detection (Goerner-Potvin & Bourque, 2018), but further improvement is definitely challenging. This is what Baud et al. (2021) accomplished in their paper. They used a simple, elegant and efficient k-mer based approach to find small signatures that, when accumulated, allow identifying very old TEs. Using this method, called Duster, they improved the amount of annotated TEs in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana by 20%, pushing the part of this genome occupied by TEs up from 40 to almost 50%. They further observed that these very old Duster-specific TEs (i.e., TEs that are only detected by Duster) are, among other properties, close to genes (much more than recent TEs), not targeted by small RNA pathways, and highly associated with conserved regions across the rosid family. In addition, they are highly associated with flowering or stress response genes, and may be involved through exaptation in the evolution of responses to environmental changes. TEs are not just selfish elements: more and more studies have shown their key role in the evolution of their hosts, and tools such as Duster will help us better understand their impact. References Baud, A., Wan, M., Nouaud, D., Francillonne, N., Anxolabéhère, D. and Quesneville, H. (2021). Traces of transposable elements in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networks. bioRxiv, 547877, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics.doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/547877 | Traces of transposable element in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networks | Agnes Baud, Mariene Wan, Danielle Nouaud, Nicolas Francillonne, Dominique Anxolabehere, Hadi Quesneville | <p>Transposable elements (TEs) are mobile, repetitive DNA sequences that make the largest contribution to genome bulk. They thus contribute to the so-called 'dark matter of the genome', the part of the genome in which nothing is immediately recogn... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics, Plants, Structural genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Francois Sabot | Anonymous, Josep Casacuberta | 2020-04-07 17:12:12 | View |
08 Nov 2022

Somatic mutation detection: a critical evaluation through simulations and reanalyses in oaksSylvain Schmitt, Thibault Leroy, Myriam Heuertz, Niklas Tysklind https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.11.462798How to best call the somatic mosaic tree?Recommended by Nicolas Bierne based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersAny multicellular organism is a molecular mosaic with some somatic mutations accumulated between cell lineages. Big long-lived trees have nourished this imaginary of a somatic mosaic tree, from the observation of spectacular phenotypic mosaics and also because somatic mutations are expected to potentially be passed on to gametes in plants (review in Schoen and Schultz 2019). The lower cost of genome sequencing now offers the opportunity to tackle the issue and identify somatic mutations in trees. However, when it comes to characterizing this somatic mosaic from genome sequences, things become much more difficult than one would think in the first place. What separates cell lineages ontogenetically, in cell division number, or in time? How to sample clonal cell populations? How do somatic mutations distribute in a population of cells in an organ or an organ sample? Should they be fixed heterozygotes in the sample of cells sequenced or be polymorphic? Do we indeed expect somatic mutations to be fixed? How should we identify and count somatic mutations? To date, the detection of somatic mutations has mostly been done with a single variant caller in a given study, and we have little perspective on how different callers provide similar or different results. Some studies have used standard SNP callers that assumed a somatic mutation is fixed at the heterozygous state in the sample of cells, with an expected allele coverage ratio of 0.5, and less have used cancer callers, designed to detect mutations in a fraction of the cells in the sample. However, standard SNP callers detect mutations that deviate from a balanced allelic coverage, and different cancer callers can have different characteristics that should affect their outcomes. In order to tackle these issues, Schmitt et al. (2022) conducted an extensive simulation analysis to compare different variant callers. Then, they reanalyzed two large published datasets on pedunculate oak, Quercus robur. The analysis of in silico somatic mutations allowed the authors to evaluate the performance of different variant callers as a function of the allelic fraction of somatic mutations and the sequencing depth. They found one of the seven callers to provide better and more robust calls for a broad set of allelic fractions and sequencing depths. The reanalysis of published datasets in oaks with the most effective cancer caller of the in silico analysis allowed them to identify numerous low-frequency mutations that were missed in the original studies. I recommend the study of Schmitt et al. (2022) first because it shows the benefit of using cancer callers in the study of somatic mutations, whatever the allelic fraction you are interested in at the end. You can select fixed heterozygotes if this is your ultimate target, but cancer callers allow you to have in addition a valuable overview of the allelic fractions of somatic mutations in your sample, and most do as well as SNP callers for fixed heterozygous mutations. In addition, Schmitt et al. (2022) provide the pipelines that allow investigating in silico data that should correspond to a given study design, encouraging to compare different variant callers rather than arbitrarily going with only one. We can anticipate that the study of somatic mutations in non-model species will increasingly attract attention now that multiple tissues of the same individual can be sequenced at low cost, and the study of Schmitt et al. (2022) paves the way for questioning and choosing the best variant caller for the question one wants to address. References Schoen DJ, Schultz ST (2019) Somatic Mutation and Evolution in Plants. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 50, 49–73. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110218-024955 Schmitt S, Leroy T, Heuertz M, Tysklind N (2022) Somatic mutation detection: a critical evaluation through simulations and reanalyses in oaks. bioRxiv, 2021.10.11.462798. ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.11.462798 | Somatic mutation detection: a critical evaluation through simulations and reanalyses in oaks | Sylvain Schmitt, Thibault Leroy, Myriam Heuertz, Niklas Tysklind | <p style="text-align: justify;">1. Mutation, the source of genetic diversity, is the raw material of evolution; however, the mutation process remains understudied, especially in plants. Using both a simulation and reanalysis framework, we set out ... |  | Bioinformatics, Plants | Nicolas Bierne | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-04-28 13:24:19 | View |










