Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors▲ | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
02 Apr 2021

Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detectionLucie Tamisier, Annelies Haegeman, Yoika Foucart, Nicolas Fouillien, Maher Al Rwahnih, Nihal Buzkan, Thierry Candresse, Michela Chiumenti, Kris De Jonghe, Marie Lefebvre, Paolo Margaria, Jean Sébastien Reynard, Kristian Stevens, Denis Kutnjak, Sébastien Massart https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4584718Toward a critical assessment of virus detection in plantsRecommended by Hadi Quesneville based on reviews by Alexander Suh and 1 anonymous reviewerThe advent of High Throughput Sequencing (HTS) since the last decade has revealed previously unsuspected diversity of viruses as well as their (sometimes) unexpected presence in some healthy individuals. These results demonstrate that genomics offers a powerful tool for studying viruses at the individual level, allowing an in-depth inventory of those that are infecting an organism. Such approaches make it possible to study viromes with an unprecedented level of detail, both qualitative and quantitative, which opens new venues for analyses of viruses of humans, animals and plants. Consequently, the diagnostic field is using more and more HTS, fueling the need for efficient and reliable bioinformatics tools. Many such tools have already been developed, but in plant disease diagnostics, validation of the bioinformatics pipelines used for the detection of viruses in HTS datasets is still in its infancy. There is an urgent need for benchmarking the different tools and algorithms using well-designed reference datasets generated for this purpose. This is a crucial step to move forward and to improve existing solutions toward well-standardized bioinformatics protocols. This context has led to the creation of the Plant Health Bioinformatics Network (PHBN), a Euphresco network project aiming to build a bioinformatics community working on plant health. One of their objectives is to provide researchers with open-access reference datasets allowing to compare and validate virus detection pipelines. In this framework, Tamisier et al. [1] present real, semi-artificial, and completely artificial datasets, each aimed at addressing challenges that could affect virus detection. These datasets comprise real RNA-seq reads from virus-infected plants as well as simulated virus reads. Such a work, providing open-access datasets for benchmarking bioinformatics tools, should be encouraged as they are key to software improvement as demonstrated by the well-known success story of the protein structure prediction community: their pioneer community-wide effort, called Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction (CASP)[2], has been providing research groups since 1994 with an invaluable way to objectively test their structure prediction methods, thereby delivering an independent assessment of state-of-art protein-structure modelling tools. Following this success, many other bioinformatic community developed similar “competitions”, such as RNA-puzzles [3] to predict RNA structures, Critical Assessment of Function Annotation [4] to predict gene functions, Critical Assessment of Prediction of Interactions [5] to predict protein-protein interactions, Assemblathon [6] for genome assembly, etc. These are just a few examples from a long list of successful initiatives. Such efforts enable rigorous assessments of tools, stimulate the developers’ creativity, but also provide user communities with a state-of-art evaluation of available tools. Inspired by these success stories, the authors propose a “VIROMOCK challenge” [7], asking researchers in the field to test their tools and to provide feedback on each dataset through a repository. This initiative, if well followed, will undoubtedly improve the field of virus detection in plants, but also probably in many other organisms. This will be a major contribution to the field of viruses, leading to better diagnostics and, consequently, a better understanding of viral diseases, thus participating in promoting human, animal and plant health. References [1] Tamisier, L., Haegeman, A., Foucart, Y., Fouillien, N., Al Rwahnih, M., Buzkan, N., Candresse, T., Chiumenti, M., De Jonghe, K., Lefebvre, M., Margaria, P., Reynard, J.-S., Stevens, K., Kutnjak, D. and Massart, S. (2021) Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detection. Zenodo, 4273791, version 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Genomics. doi: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4273791 [2] Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction” (CASP) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CASP [3] RNA-puzzles - https://www.rnapuzzles.org [4] Critical Assessment of Function Annotation (CAFA) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_Assessment_of_Function_Annotation [5] Critical Assessment of Prediction of Interactions (CAPI) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_Assessment_of_Prediction_of_Interactions [6] Assemblathon - https://assemblathon.org [7] VIROMOCK challenge - https://gitlab.com/ilvo/VIROMOCKchallenge | Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detection | Lucie Tamisier, Annelies Haegeman, Yoika Foucart, Nicolas Fouillien, Maher Al Rwahnih, Nihal Buzkan, Thierry Candresse, Michela Chiumenti, Kris De Jonghe, Marie Lefebvre, Paolo Margaria, Jean Sébastien Reynard, Kristian Stevens, Denis Kutnjak, Séb... | <p>The widespread use of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) for detection of plant viruses and sequencing of plant virus genomes has led to the generation of large amounts of data and of bioinformatics challenges to process them. Many bioinformatics... |  | Bioinformatics, Plants, Viruses and transposable elements | Hadi Quesneville | 2020-11-27 14:31:47 | View | |
24 Feb 2023
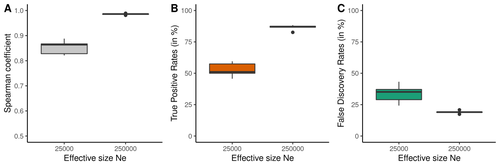
Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation studyMarie Raynaud, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Nicolas Galtier https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.30.486352How to interpret the inference of recombination landscapes on methods based on linkage disequilibrium?Recommended by Sebastian E. Ramos-Onsins based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersData interpretation depends on previously established and validated tools, designed for a specific type of data. These methods, however, are usually based on simple models with validity subject to a set of theoretical parameterized conditions and data types. Accordingly, the tool developers provide the potential users with guidelines for data interpretations within the tools’ limitation. Nevertheless, once the methodology is accepted by the community, it is employed in a large variety of empirical studies outside of the method’s original scope or that typically depart from the standard models used for its design, thus potentially leading to the wrong interpretation of the results. Numerous empirical studies inferred recombination rates across genomes, detecting hotspots of recombination and comparing related species (e.g., Shanfelter et al. 2019, Spence and Song 2019). These studies used indirect methodologies based on the signals that recombination left in the genome, such as linkage disequilibrium and the patterns of haplotype segregation (e.g.,Chan et al. 2012). The conclusions from these analyses have been used, for example, to interpret the evolution of the chromosomal structure or the evolution of recombination among closely related species. Indirect methods have the advantage of collecting a large quantity of recombination events, and thus have a better resolution than direct methods (which only detect the few recombination events occurring at that time). On the other hand, indirect methods are affected by many different evolutionary events, such as demographic changes and selection. Indeed, the inference of recombination levels across the genome has not been studied accurately in non-standard conditions. Linkage disequilibrium is affected by several factors that can modify the recombination inference, such as demographic history, events of selection, population size, and mutation rate, but is also related to the size of the studied sample, and other technical parameters defined for each specific methodology. Raynaud et al (2023) analyzed the reliability of the recombination rate inference when considering the violation of several standard assumptions (evolutionary and methodological) in one of the most popular families of methods based on LDhat (McVean et al. 2004), specifically its improved version, LDhelmet (Chan et al. 2012). These methods cover around 70 % of the studies that infer recombination rates. The authors used recombination maps, obtained from empirical studies on humans, and included hotspots, to perform a detailed simulation study of the capacity of this methodology to correctly infer the pattern of recombination and the location of these hotspots. Correlations between the real, and inferred values from simulations were obtained, as well as several rates, such as the true positive and false discovery rate to detect hotspots. The authors of this work send a message of caution to researchers that are applying this methodology to interpret data from the inference of recombination landscapes and the location of hotspots. The inference of recombination landscapes and hotspots can differ considerably even in standard model conditions. In addition, demographic processes, like bottleneck or admixture, but also the level of population size and mutation rates, can substantially affect the estimation accuracy of the level of recombination and the location of hotspots. Indeed, the inference of the location of hotspots in simulated data with the same landscape, can be very imprecise when standard assumptions are violated or not considered. These effects may lead to incorrect interpretations, for example about the conservation of recombination maps between closely related species. Finally, Raynaud et al (2023) included a useful guide with advice on how to obtain accurate recombination estimations with methods based on linkage disequilibrium, also emphasizing the limitations of such approaches. REFERENCES Chan AH, Jenkins PA, Song YS (2012) Genome-Wide Fine-Scale Recombination Rate Variation in Drosophila melanogaster. PLOS Genetics, 8, e1003090. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003090 McVean GAT, Myers SR, Hunt S, Deloukas P, Bentley DR, Donnelly P (2004) The Fine-Scale Structure of Recombination Rate Variation in the Human Genome. Science, 304, 581–584. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1092500 Raynaud M, Gagnaire P-A, Galtier N (2023) Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation study. bioRxiv, 2022.03.30.486352, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.30.486352 Spence JP, Song YS (2019) Inference and analysis of population-specific fine-scale recombination maps across 26 diverse human populations. Science Advances, 5, eaaw9206. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw9206 | Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation study | Marie Raynaud, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Nicolas Galtier | <p style="text-align: justify;">Knowledge of recombination rate variation along the genome provides important insights into genome and phenotypic evolution. Population genomic approaches offer an attractive way to infer the population-scaled recom... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Population genomics | Sebastian E. Ramos-Onsins | 2022-04-05 14:59:14 | View | |
06 Apr 2021
Evidence for shared ancestry between Actinobacteria and Firmicutes bacteriophagesMatthew Koert, Júlia López-Pérez, Courtney Mattson, Steven M. Caruso, Ivan Erill https://doi.org/10.1101/842583Viruses of bacteria: phages evolution across phylum boundariesRecommended by Denis Tagu based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersBacteria and phages have coexisted and coevolved for a long time. Phages are bacteria-infecting viruses, with a symbiotic status sensu lato, meaning they can be pathogenic, commensal or mutualistic. Thus, the association between bacteria phages has probably played a key role in the high adaptability of bacteria to most - if not all – of Earth’s ecosystems, including other living organisms (such as eukaryotes), and also regulate bacterial community size (for instance during bacterial blooms). As genetic entities, phages are submitted to mutations and natural selection, which changes their DNA sequence. Therefore, comparative genomic analyses of contemporary phages can be useful to understand their evolutionary dynamics. International initiatives such as SEA-PHAGES have started to tackle the issue of history of phage-bacteria interactions and to describe the dynamics of the co-evolution between bacterial hosts and their associated viruses. Indeed, the understanding of this cross-talk has many potential implications in terms of health and agriculture, among others. The work of Koert et al. (2021) deals with one of the largest groups of bacteria (Actinobacteria), which are Gram-positive bacteria mainly found in soil and water. Some soil-born Actinobacteria develop filamentous structures reminiscent of the mycelium of eukaryotic fungi. In this study, the authors focused on the Streptomyces clade, a large genus of Actinobacteria colonized by phages known for their high level of genetic diversity. The authors tested the hypothesis that large exchanges of genetic material occurred between Streptomyces and diverse phages associated with bacterial hosts. Using public datasets, their comparative phylogenomic analyses identified a new cluster among Actinobacteria–infecting phages closely related to phages of Firmicutes. Moreover, the GC content and codon-usage biases of this group of phages of Actinobacteria are similar to those of Firmicutes. This work demonstrates for the first time the transfer of a bacteriophage lineage from one bacterial phylum to another one. The results presented here suggest that the age of the described transfer is probably recent since several genomic characteristics of the phage are not fully adapted to their new hosts. However, the frequency of such transfer events remains an open question. If frequent, such exchanges would mean that pools of bacteriophages are regularly fueled by genetic material coming from external sources, which would have important implications for the co-evolutionary dynamics of phages and bacteria. References Koert, M., López-Pérez, J., Courtney Mattson, C., Caruso, S. and Erill, I. (2021) Evidence for shared ancestry between Actinobacteria and Firmicutes bacteriophages. bioRxiv, 842583, version 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Genomics. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/842583 | Evidence for shared ancestry between Actinobacteria and Firmicutes bacteriophages | Matthew Koert, Júlia López-Pérez, Courtney Mattson, Steven M. Caruso, Ivan Erill | <p>Bacteriophages typically infect a small set of related bacterial strains. The transfer of bacteriophages between more distant clades of bacteria has often been postulated, but remains mostly unaddressed. In this work we leverage the sequencing ... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Denis Tagu | 2019-12-10 15:26:31 | View | |
24 Sep 2020

A rapid and simple method for assessing and representing genome sequence relatednessM Briand, M Bouzid, G Hunault, M Legeay, M Fischer-Le Saux, M Barret https://doi.org/10.1101/569640A quick alternative method for resolving bacterial taxonomy using short identical DNA sequences in genomes or metagenomesRecommended by B. Jesse Shapiro based on reviews by Gavin Douglas and 1 anonymous reviewerThe bacterial species problem can be summarized as follows: bacteria recombine too little, and yet too much (Shapiro 2019). References Arevalo P, VanInsberghe D, Elsherbini J, Gore J, Polz MF (2019) A Reverse Ecology Approach Based on a Biological Definition of Microbial Populations. Cell, 178, 820-834.e14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.033 | A rapid and simple method for assessing and representing genome sequence relatedness | M Briand, M Bouzid, G Hunault, M Legeay, M Fischer-Le Saux, M Barret | <p>Coherent genomic groups are frequently used as a proxy for bacterial species delineation through computation of overall genome relatedness indices (OGRI). Average nucleotide identity (ANI) is a widely employed method for estimating relatedness ... |  | Bioinformatics, Metagenomics | B. Jesse Shapiro | Gavin Douglas | 2019-11-07 16:37:56 | View |
06 May 2022
A deep dive into genome assemblies of non-vertebrate animalsNadège Guiglielmoni, Ramón Rivera-Vicéns, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202111.0170.v3Diving, and even digging, into the wild jungle of annotation pathways for non-vertebrate animalsRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by Yann Bourgeois, Cécile Monat, Valentina Peona and Benjamin Istace based on reviews by Yann Bourgeois, Cécile Monat, Valentina Peona and Benjamin Istace
In their paper, Guiglielmoni et al. propose we pick up our snorkels and palms and take "A deep dive into genome assemblies of non-vertebrate animals" (1). Indeed, while numerous assembly-related tools were developed and tested for human genomes (or at least vertebrates such as mice), very few were tested on non-vertebrate animals so far. Moreover, most of the benchmarks are aimed at raw assembly tools, and very few offer a guide from raw reads to an almost finished assembly, including quality control and phasing. This huge and exhaustive review starts with an overview of the current sequencing technologies, followed by the theory of the different approaches for assembly and their implementation. For each approach, the authors present some of the most representative tools, as well as the limits of the approach. The authors additionally present all the steps required to obtain an almost complete assembly at a chromosome-scale, with all the different technologies currently available for scaffolding, QC, and phasing, and the way these tools can be applied to non-vertebrates animals. Finally, they propose some useful advice on the choice of the different approaches (but not always tools, see below), and advocate for a robust genome database with all information on the way the assembly was obtained. This review is a very complete one for now and is a very good starting point for any student or scientist interested to start working on genome assembly, from either model or non-model organisms. However, the authors do not provide a list of tools or a benchmark of them as a recommendation. Why? Because such a proposal may be obsolete in less than a year.... Indeed, with the explosion of the 3rd generation of sequencing technology, assembly tools (from different steps) are constantly evolving, and their relative performance increases on a monthly basis. In addition, some tools are really efficient at the time of a review or of an article, but are not further developed later on, and thus will not evolve with the technology. We have all seen it with wonderful tools such as Chiron (2) or TopHat (3), which were very promising ones, but cannot be developed further due to the stop of the project, the end of the contract of the post-doc in charge of the development, or the decision of the developer to switch to another paradigm. Such advice would, therefore, need to be constantly updated. Thus, the manuscript from Guiglielmoni et al will be an almost intemporal one (up to the next sequencing revolution at last), and as they advocated for a more informed genome database, I think we should consider a rolling benchmarking system (tools, genome and sequence dataset) allowing to keep the performance of the tools up-to-date, and to propose the best set of assembly tools for a given type of genome. References 1. Guiglielmoni N, Rivera-Vicéns R, Koszul R, Flot J-F (2022) A Deep Dive into Genome Assemblies of Non-vertebrate Animals. Preprints, 2021110170, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202111.0170 2. Teng H, Cao MD, Hall MB, Duarte T, Wang S, Coin LJM (2018) Chiron: translating nanopore raw signal directly into nucleotide sequence using deep learning. GigaScience, 7, giy037. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giy037 3. Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics, 25, 1105–1111. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120 | A deep dive into genome assemblies of non-vertebrate animals | Nadège Guiglielmoni, Ramón Rivera-Vicéns, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot | <p style="text-align: justify;">Non-vertebrate species represent about ∼95% of known metazoan (animal) diversity. They remain to this day relatively unexplored genetically, but understanding their genome structure and function is pivotal for expan... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics | Francois Sabot | Valentina Peona, Benjamin Istace, Cécile Monat, Yann Bourgeois | 2021-11-10 17:47:31 | View |
07 Oct 2021

Fine-scale quantification of GC-biased gene conversion intensity in mammalsNicolas Galtier https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.05.442789A systematic approach to the study of GC-biased gene conversion in mammalsRecommended by Carina Farah Mugal based on reviews by Fanny Pouyet , David Castellano and 1 anonymous reviewerThe role of GC-biased gene conversion (gBGC) in molecular evolution has interested scientists for the last two decades since its discovery in 1999 (Eyre-Walker 1999; Galtier et al. 2001). gBGC is a process that is associated with meiotic recombination, and is characterized by a transmission distortion in favor of G and C over A and T alleles at GC/AT heterozygous sites that occur in the vicinity of recombination-inducing double-strand breaks (Duret and Galtier 2009; Mugal et al. 2015). This transmission distortion results in a fixation bias of G and C alleles, equivalent to directional selection for G and C (Nagylaki 1983). The fixation bias subsequently leads to a correlation between recombination rate and GC content across the genome, which has served as indirect evidence for the prevalence of gBGC in many organisms. The fixation bias also produces shifts in the allele frequency spectrum (AFS) towards higher frequencies of G and C alleles. These molecular signatures of gBGC provide a means to quantify the strength of gBGC and study its variation among species and across the genome. Following this idea, first Lartillot (2013) and Capra et al. (2013) developed phylogenetic methodology to quantify gBGC based on substitutions, and De Maio et al. (2013) combined information on polymorphism into a phylogenetic setting. Complementary to the phylogenetic methods, later Glemin et al. (2015) developed a method that draws information solely from polymorphism data and the shape of the AFS. Application of these methods to primates (Capra et al. 2013; De Maio et al. 2013; Glemin et al. 2015) and mammals (Lartillot 2013) supported the notion that variation in the strength of gBGC across the genome reflects the dynamics of the recombination landscape, while variation among species correlates with proxies of the effective population size. However, application of the polymorphism-based method by Glemin et al. (2015) to distantly related Metazoa did not confirm the correlation with effective population size (Galtier et al. 2018). Here, Galtier (2021) introduces a novel phylogenetic approach applicable to the study of closely related species. Specifically, Galtier introduces a statistical framework that enables the systematic study of variation in the strength of gBGC among species and among genes. In addition, Galtier assesses fine-scale variation of gBGC across the genome by means of spatial autocorrelation analysis. This puts Galtier in a position to study variation in the strength of gBGC at three different scales, i) among species, ii) among genes, and iii) within genes. Galtier applies his method to four families of mammals, Hominidae, Cercopithecidae, Bovidae, and Muridae and provides a thorough discussion of his findings and methodology. Galtier found that the strength of gBGC correlates with proxies of the effective population size (Ne), but that the slope of the relationship differs among the four families of mammals. Given the relationship between the population-scaled strength of gBGC B = 4Neb, this finding suggests that the conversion bias (b) could vary among mammalian species. Variation in b could either result from differences in the strength of the transmission distortion (Galtier et al. 2018) or evolutionary changes in the rate of recombination (Boman et al. 2021). Alternatively, Galtier suggests that also systematic variation in proxies of Ne could lead to similar observations. Finally, the present study reports intriguing inter-species differences between the extent of variation in the strength of gBGC among and within genes, which are interpreted in consideration of the recombination dynamics in mammals. References Boman J, Mugal CF, Backström N (2021) The Effects of GC-Biased Gene Conversion on Patterns of Genetic Diversity among and across Butterfly Genomes. Genome Biology and Evolution, 13. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evab064 Capra JA, Hubisz MJ, Kostka D, Pollard KS, Siepel A (2013) A Model-Based Analysis of GC-Biased Gene Conversion in the Human and Chimpanzee Genomes. PLOS Genetics, 9, e1003684. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003684 De Maio N, Schlötterer C, Kosiol C (2013) Linking Great Apes Genome Evolution across Time Scales Using Polymorphism-Aware Phylogenetic Models. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2249–2262. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst131 Duret L, Galtier N (2009) Biased Gene Conversion and the Evolution of Mammalian Genomic Landscapes. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics, 10, 285–311. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-082908-150001 Eyre-Walker A (1999) Evidence of Selection on Silent Site Base Composition in Mammals: Potential Implications for the Evolution of Isochores and Junk DNA. Genetics, 152, 675–683. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/152.2.675 Galtier N (2021) Fine-scale quantification of GC-biased gene conversion intensity in mammals. bioRxiv, 2021.05.05.442789, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.05.442789 Galtier N, Piganeau G, Mouchiroud D, Duret L (2001) GC-Content Evolution in Mammalian Genomes: The Biased Gene Conversion Hypothesis. Genetics, 159, 907–911. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/159.2.907 Galtier N, Roux C, Rousselle M, Romiguier J, Figuet E, Glémin S, Bierne N, Duret L (2018) Codon Usage Bias in Animals: Disentangling the Effects of Natural Selection, Effective Population Size, and GC-Biased Gene Conversion. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1092–1103. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy015 Glémin S, Arndt PF, Messer PW, Petrov D, Galtier N, Duret L (2015) Quantification of GC-biased gene conversion in the human genome. Genome Research, 25, 1215–1228. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.185488.114 Lartillot N (2013) Phylogenetic Patterns of GC-Biased Gene Conversion in Placental Mammals and the Evolutionary Dynamics of Recombination Landscapes. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 489–502. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss239 Mugal CF, Weber CC, Ellegren H (2015) GC-biased gene conversion links the recombination landscape and demography to genomic base composition. BioEssays, 37, 1317–1326. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201500058 Nagylaki T (1983) Evolution of a finite population under gene conversion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 80, 6278–6281. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.80.20.6278 | Fine-scale quantification of GC-biased gene conversion intensity in mammals | Nicolas Galtier | <p style="text-align: justify;">GC-biased gene conversion (gBGC) is a molecular evolutionary force that favours GC over AT alleles irrespective of their fitness effect. Quantifying the variation in time and across genomes of its intensity is key t... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Population genomics, Vertebrates | Carina Farah Mugal | 2021-05-25 09:25:52 | View | |
07 Sep 2023
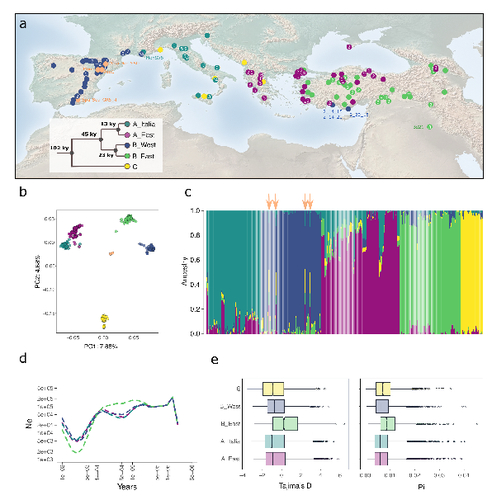
The demographic history of the wild crop relative Brachypodium distachyon is shaped by distinct past and present ecological nichesNikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.01.543285Natural variation and adaptation in Brachypodium distachyonRecommended by Josep Casacuberta based on reviews by Thibault Leroy and 1 anonymous reviewerIdentifying the genetic factors that allow plant adaptation is a major scientific question that is particularly relevant in the face of the climate change that we are already experiencing. To address this, it is essential to have genetic information on a high number of accessions (i.e., plants registered with unique accession numbers) growing under contrasting environmental conditions. There is already an important number of studies addressing these issues in the plant Arabidopsis thaliana, but there is a need to expand these analyses to species that play key roles in wild ecosystems and are close to very relevant crops, as is the case of grasses. The work of Minadakis, Roulin and co-workers (1) presents a Brachypodium distachyon panel of 332 fully sequences accessions that covers the whole species distribution across a wide range of bioclimatic conditions, which will be an invaluable tool to fill this gap. In addition, the authors use this data to start analyzing the population structure and demographic history of this plant, suggesting that the species experienced a shift of its distribution following the Last Glacial Maximum, which may have forced the species into new habitats. The authors also present a modeling of the niches occupied by B. distachyon together with an analysis of the genetic clades found in each of them, and start analyzing the different adaptive loci that may have allowed the species’ expansion into different bioclimatic areas. In addition to the importance of the resources made available by the authors for the scientific community, the analyses presented are well done and carefully discussed, and they highlight the potential of these new resources to investigate the genetic bases of plant adaptation. References 1. Nikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin. The demographic history of the wild crop relative Brachypodium distachyon is shaped by distinct past and present ecological niches. bioRxiv, 2023.06.01.543285, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.01.543285 | The demographic history of the wild crop relative *Brachypodium distachyon* is shaped by distinct past and present ecological niches | Nikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin | <p style="text-align: justify;">Closely related to economically important crops, the grass <em>Brachypodium distachyon</em> has been originally established as a pivotal species for grass genomics but more recently flourished as a model for develop... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics, Plants, Population genomics | Josep Casacuberta | 2023-06-14 15:28:30 | View | |
22 Nov 2023
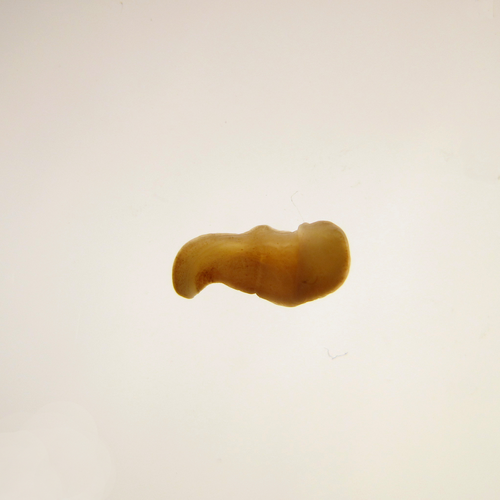
The slow evolving genome of the xenacoelomorph worm Xenoturbella bockiPhilipp H. Schiffer, Paschalis Natsidis, Daniel J. Leite, Helen Robertson, François Lapraz, Ferdinand Marlétaz, Bastian Fromm, Liam Baudry, Fraser Simpson, Eirik Høye, Anne-C. Zakrzewski, Paschalia Kapli, Katharina J. Hoff, Steven Mueller, Martial Marbouty, Heather Marlow, Richard R. Copley, Romain Koszul, Peter Sarkies, Maximilian J. Telford https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.24.497508Genomic idiosyncrasies of Xenoturbella bocki: morphologically simple yet genetically complexRecommended by Rosa Fernández based on reviews by Christopher Laumer and 1 anonymous reviewerXenoturbella is a genus of morphologically simple bilaterians inhabiting benthic environments. Until very recently, only one species was known from the genus, Xenoturbella bocki Westblad 1949 [1]. Less than a decade ago, five more species were discovered (X. churro, X. monstrosa, X. profunda, X. hollandorum [2] and X. japonica [3]). These enigmatic animals lack an anus, a coelom, reproductive organs, nephrocytes and a centralized nervous system [1]. The systematic classification of the genus has substantially changed in the last decades, with first being considered as its own phylum (Xenoturbellida) and then being clustered together with acoels and nemertodermatids into the phylum Xenacoelomorpha [4,5]. The phylogenetic position of the xenacoelomorphs has been recalcitrant to resolution, with its position ranging from being the sister group to Nephrozoa (ie, protostomes and deuterostomes [6]) to the sister group to Ambulacraria (ie, Hemichordata and Echinodermata) in a clade called Xenambulacraria [4]. Recent studies based on expanded datasets and more refined analyses support either topology [7,8]. Either way, it is clear that additional studies on Xenoturbella could provide important insights into the origins of bilaterian traits such as the anus, the nephrons and the evolution of a centralized nervous system.
In any case, we are approaching a qualitative jump in how we understand phylogenomics thanks to efforts derived from the availability of chromosome-level genome assemblies for a growing number of species. Exciting times are ahead for us, evolutionary biologists, to explore what high-quality genomes - in combination with multiomics datasets - will reveal about animal evolution. I am personally really looking forward to it. References 1. Westblad E. (1949). Xenoturbella bocki n.g., n.sp., a peculiar, primitive Turbellarian type. Arkiv för Zoologi 1, 3-29 (1949). 2. Rouse, G. W., Wilson, N. G., Carvajal, J. I. & Vrijenhoek, R. C. New deep-sea species of Xenoturbella and the position of Xenacoelomorpha. Nature 530, 94–97 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16545 3. Nakano, H. et al. Correction to: A new species of Xenoturbella from the western Pacific Ocean and the evolution of Xenoturbella. BMC Evol. Biol. 18, 1–2 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-018-1190-5https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-018-1190-5 4. Philippe, H. et al. Acoelomorph flatworms are deuterostomes related to Xenoturbella. Nature 470, 255–258 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09676 5. Hejnol, A. et al. Assessing the root of bilaterian animals with scalable phylogenomic methods. Proc. Biol. Sci. 276, 4261–4270 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2009.0896 6. Cannon, J. T. et al. Xenacoelomorpha is the sister group to Nephrozoa. Nature 530, 89–93 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16520 7. Laumer, C. E. et al. Revisiting metazoan phylogeny with genomic sampling of all phyla. Proc. Biol. Sci. 286, 20190831 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2019.0831 8. Philippe, H. et al. Mitigating anticipated effects of systematic errors supports sister-group relationship between Xenacoelomorpha and Ambulacraria. Curr. Biol. 29, 1818–1826.e6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.04.009 9. Schiffer, P. H., Natsidis, P., Leite D. J., Robertson, H., Lapraz, F., Marlétaz, F., Fromm, B., Baudry, L., Simpson, F., Høye, E., Zakrzewski, A-C., Kapli, P., Hoff, K. J., Mueller, S., Marbouty, M., Marlow, H., Copley, R. R., Koszul, R., Sarkies, P. & Telford, M .J. The slow evolving genome of the xenacoelomorph worm Xenoturbella bocki. bioRxiv (2023), ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.24.497508 10. Suga, H. et al. The Capsaspora genome reveals a complex unicellular prehistory of animals. Nat. Commun. 4, 2325 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3325 11. Fernández, R. & Gabaldón, T. Gene gain and loss across the metazoan tree of life. Nat Ecol Evol 4, 524–533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-019-1069-x | The slow evolving genome of the xenacoelomorph worm *Xenoturbella bocki* | Philipp H. Schiffer, Paschalis Natsidis, Daniel J. Leite, Helen Robertson, François Lapraz, Ferdinand Marlétaz, Bastian Fromm, Liam Baudry, Fraser Simpson, Eirik Høye, Anne-C. Zakrzewski, Paschalia Kapli, Katharina J. Hoff, Steven Mueller, Martial... | <p style="text-align: justify;">The evolutionary origins of Bilateria remain enigmatic. One of the more enduring proposals highlights similarities between a cnidarian-like planula larva and simple acoel-like flatworms. This idea is based in part o... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Rosa Fernández | 2022-11-01 12:31:53 | View | |
19 Jul 2021
TransPi - a comprehensive TRanscriptome ANalysiS PIpeline for de novo transcriptome assemblyRamon E Rivera-Vicens, Catalina Garcia-Escudero, Nicola Conci, Michael Eitel, Gert Wörheide https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.18.431773TransPI: A balancing act between transcriptome assemblersRecommended by Oleg Simakov based on reviews by Gustavo Sanchez and Juan Daniel Montenegro CabreraEver since the introduction of the first widely usable assemblers for transcriptomic reads (Huang and Madan 1999; Schulz et al. 2012; Simpson et al. 2009; Trapnell et al. 2010, and many more), it has been a technical challenge to compare different methods and to choose the “right” or “best” assembly. It took years until the first widely accepted set of benchmarks beyond raw statistical evaluation became available (e.g., Parra, Bradnam, and Korf 2007; Simão et al. 2015). However, an approach to find the right balance between the number of transcripts or isoforms vs. evolutionary completeness measures has been lacking. This has been particularly pronounced in the field of non-model organisms (i.e., wild species that lack a genomic reference). Often, studies in this area employed only one set of assembly tools (the most often used to this day being Trinity, Haas et al. 2013; Grabherr et al. 2011). While it was relatively straightforward to obtain an initial assembly, its validation, annotation, as well its application to the particular purpose that the study was designed for (phylogenetics, differential gene expression, etc) lacked a clear workflow. This led to many studies using a custom set of tools with ensuing various degrees of reproducibility. TransPi (Rivera-Vicéns et al. 2021) fills this gap by first employing a meta approach using several available transcriptome assemblers and algorithms to produce a combined and reduced transcriptome assembly, then validating and annotating the resulting transcriptome. Notably, TransPI performs an extensive analysis/detection of chimeric transcripts, the results of which show that this new tool often produces fewer misassemblies compared to Trinity. TransPI not only generates a final report that includes the most important plots (in clickable/zoomable format) but also stores all relevant intermediate files, allowing advanced users to take a deeper look and/or experiment with different settings. As running TransPi is largely automated (including its installation via several popular package managers), it is very user-friendly and is likely to become the new "gold standard" for transcriptome analyses, especially of non-model organisms. References Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, di Palma F, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nature Biotechnology, 29, 644–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1883 Haas BJ, Papanicolaou A, Yassour M, Grabherr M, Blood PD, Bowden J, Couger MB, Eccles D, Li B, Lieber M, MacManes MD, Ott M, Orvis J, Pochet N, Strozzi F, Weeks N, Westerman R, William T, Dewey CN, Henschel R, LeDuc RD, Friedman N, Regev A (2013) De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nature Protocols, 8, 1494–1512. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.084 Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: A DNA Sequence Assembly Program. Genome Research, 9, 868–877. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.9.9.868 Parra G, Bradnam K, Korf I (2007) CEGMA: a pipeline to accurately annotate core genes in eukaryotic genomes. Bioinformatics, 23, 1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm071 Rivera-Vicéns RE, Garcia-Escudero CA, Conci N, Eitel M, Wörheide G (2021) TransPi – a comprehensive TRanscriptome ANalysiS PIpeline for de novo transcriptome assembly. bioRxiv, 2021.02.18.431773, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.18.431773 Schulz MH, Zerbino DR, Vingron M, Birney E (2012) Oases: robust de novo RNA-seq assembly across the dynamic range of expression levels. Bioinformatics, 28, 1086–1092. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts094 Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics, 31, 3210–3212. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351 Simpson JT, Wong K, Jackman SD, Schein JE, Jones SJM, Birol İ (2009) ABySS: A parallel assembler for short read sequence data. Genome Research, 19, 1117–1123. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.089532.108 Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L (2010) Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nature Biotechnology, 28, 511–515. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1621 | TransPi - a comprehensive TRanscriptome ANalysiS PIpeline for de novo transcriptome assembly | Ramon E Rivera-Vicens, Catalina Garcia-Escudero, Nicola Conci, Michael Eitel, Gert Wörheide | <p style="text-align: justify;">The use of RNA-Seq data and the generation of de novo transcriptome assemblies have been pivotal for studies in ecology and evolution. This is distinctly true for non-model organisms, where no genome information is ... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics | Oleg Simakov | 2021-02-18 20:56:08 | View | |
23 Sep 2022
MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studiesRosa Fernandez, Vanina Tonzo, Carolina Simon Guerrero, Jesus Lozano-Fernandez, Gemma I Martinez-Redondo, Pau Balart-Garcia, Leandro Aristide, Klara Eleftheriadi, Carlos Vargas-Chavez https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500182MATEdb: a new phylogenomic-driven database for MetazoaRecommended by Samuel Abalde based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The development (and standardization) of high-throughput sequencing techniques has revolutionized evolutionary biology, to the point that we almost see as normal fine-detail studies of genome architecture evolution (Robert et al., 2022), adaptation to new habitats (Rahi et al., 2019), or the development of key evolutionary novelties (Hilgers et al., 2018), to name three examples. One of the fields that has benefited the most is phylogenomics, i.e. the use of genome-wide data for inferring the evolutionary relationships among organisms. Dealing with such amount of data, however, has come with important analytical and computational challenges. Likewise, although the steady generation of genomic data from virtually any organism opens exciting opportunities for comparative analyses, it also creates a sort of “information fog”, where it is hard to find the most appropriate and/or the higher quality data. I have personally experienced this not so long ago, when I had to spend several weeks selecting the most complete transcriptomes from several phyla, moving back and forth between the NCBI SRA repository and the relevant literature. In an attempt to deal with this issue, some research labs have committed their time and resources to the generation of taxa- and topic-specific databases (Lathe et al., 2008), such as MolluscDB (Liu et al., 2021), focused on mollusk genomics, or EukProt (Richter et al., 2022), a protein repository representing the diversity of eukaryotes. A new database that promises to become an important resource in the near future is MATEdb (Fernández et al., 2022), a repository of high-quality genomic data from Metazoa. MATEdb has been developed from publicly available and newly generated transcriptomes and genomes, prioritizing quality over quantity. Upon download, the user has access to both raw data and the related datasets: assemblies, several quality metrics, the set of inferred protein-coding genes, and their annotation. Although it is clear to me that this repository has been created with phylogenomic analyses in mind, I see how it could be generalized to other related problems such as analyses of gene content or evolution of specific gene families. In my opinion, the main strengths of MATEdb are threefold:
On a negative note, I see two main drawbacks. First, as of today (September 16th, 2022) this database is in an early stage and it still needs to incorporate a lot of animal groups. This has been discussed during the revision process and the authors are already working on it, so it is only a matter of time until all major taxa are represented. Second, there is a scalability issue. In its current format it is not possible to select the taxa of interest and the full database has to be downloaded, which will become more and more difficult as it grows. Nonetheless, with the appropriate resources it would be easy to find a better solution. There are plenty of examples that could serve as inspiration, so I hope this does not become a big problem in the future. Altogether, I and the researchers that participated in the revision process believe that MATEdb has the potential to become an important and valuable addition to the metazoan phylogenomics community. Personally, I wish it was available just a few months ago, it would have saved me so much time. References Fernández R, Tonzo V, Guerrero CS, Lozano-Fernandez J, Martínez-Redondo GI, Balart-García P, Aristide L, Eleftheriadi K, Vargas-Chávez C (2022) MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studies. bioRxiv, 2022.07.18.500182, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500182 Hilgers L, Hartmann S, Hofreiter M, von Rintelen T (2018) Novel Genes, Ancient Genes, and Gene Co-Option Contributed to the Genetic Basis of the Radula, a Molluscan Innovation. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1638–1652. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy052 Lathe W, Williams J, Mangan M, Karolchik, D (2008). Genomic data resources: challenges and promises. Nature Education, 1(3), 2. Liu F, Li Y, Yu H, Zhang L, Hu J, Bao Z, Wang S (2021) MolluscDB: an integrated functional and evolutionary genomics database for the hyper-diverse animal phylum Mollusca. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, D988–D997. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa918 Rahi ML, Mather PB, Ezaz T, Hurwood DA (2019) The Molecular Basis of Freshwater Adaptation in Prawns: Insights from Comparative Transcriptomics of Three Macrobrachium Species. Genome Biology and Evolution, 11, 1002–1018. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evz045 Richter DJ, Berney C, Strassert JFH, Poh Y-P, Herman EK, Muñoz-Gómez SA, Wideman JG, Burki F, Vargas C de (2022) EukProt: A database of genome-scale predicted proteins across the diversity of eukaryotes. bioRxiv, 2020.06.30.180687, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.30.180687 Robert NSM, Sarigol F, Zimmermann B, Meyer A, Voolstra CR, Simakov O (2022) Emergence of distinct syntenic density regimes is associated with early metazoan genomic transitions. BMC Genomics, 23, 143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08304-2 | MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studies | Rosa Fernandez, Vanina Tonzo, Carolina Simon Guerrero, Jesus Lozano-Fernandez, Gemma I Martinez-Redondo, Pau Balart-Garcia, Leandro Aristide, Klara Eleftheriadi, Carlos Vargas-Chavez | <p style="text-align: justify;">With the advent of high throughput sequencing, the amount of genomic data available for animals (Metazoa) species has bloomed over the last decade, especially from transcriptomes due to lower sequencing costs and ea... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics | Samuel Abalde | 2022-07-20 07:30:39 | View |










