Latest recommendations

| Id | Title▼ | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
02 Apr 2021

Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detectionLucie Tamisier, Annelies Haegeman, Yoika Foucart, Nicolas Fouillien, Maher Al Rwahnih, Nihal Buzkan, Thierry Candresse, Michela Chiumenti, Kris De Jonghe, Marie Lefebvre, Paolo Margaria, Jean Sébastien Reynard, Kristian Stevens, Denis Kutnjak, Sébastien Massart https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4584718Toward a critical assessment of virus detection in plantsRecommended by Hadi Quesneville based on reviews by Alexander Suh and 1 anonymous reviewerThe advent of High Throughput Sequencing (HTS) since the last decade has revealed previously unsuspected diversity of viruses as well as their (sometimes) unexpected presence in some healthy individuals. These results demonstrate that genomics offers a powerful tool for studying viruses at the individual level, allowing an in-depth inventory of those that are infecting an organism. Such approaches make it possible to study viromes with an unprecedented level of detail, both qualitative and quantitative, which opens new venues for analyses of viruses of humans, animals and plants. Consequently, the diagnostic field is using more and more HTS, fueling the need for efficient and reliable bioinformatics tools. Many such tools have already been developed, but in plant disease diagnostics, validation of the bioinformatics pipelines used for the detection of viruses in HTS datasets is still in its infancy. There is an urgent need for benchmarking the different tools and algorithms using well-designed reference datasets generated for this purpose. This is a crucial step to move forward and to improve existing solutions toward well-standardized bioinformatics protocols. This context has led to the creation of the Plant Health Bioinformatics Network (PHBN), a Euphresco network project aiming to build a bioinformatics community working on plant health. One of their objectives is to provide researchers with open-access reference datasets allowing to compare and validate virus detection pipelines. In this framework, Tamisier et al. [1] present real, semi-artificial, and completely artificial datasets, each aimed at addressing challenges that could affect virus detection. These datasets comprise real RNA-seq reads from virus-infected plants as well as simulated virus reads. Such a work, providing open-access datasets for benchmarking bioinformatics tools, should be encouraged as they are key to software improvement as demonstrated by the well-known success story of the protein structure prediction community: their pioneer community-wide effort, called Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction (CASP)[2], has been providing research groups since 1994 with an invaluable way to objectively test their structure prediction methods, thereby delivering an independent assessment of state-of-art protein-structure modelling tools. Following this success, many other bioinformatic community developed similar “competitions”, such as RNA-puzzles [3] to predict RNA structures, Critical Assessment of Function Annotation [4] to predict gene functions, Critical Assessment of Prediction of Interactions [5] to predict protein-protein interactions, Assemblathon [6] for genome assembly, etc. These are just a few examples from a long list of successful initiatives. Such efforts enable rigorous assessments of tools, stimulate the developers’ creativity, but also provide user communities with a state-of-art evaluation of available tools. Inspired by these success stories, the authors propose a “VIROMOCK challenge” [7], asking researchers in the field to test their tools and to provide feedback on each dataset through a repository. This initiative, if well followed, will undoubtedly improve the field of virus detection in plants, but also probably in many other organisms. This will be a major contribution to the field of viruses, leading to better diagnostics and, consequently, a better understanding of viral diseases, thus participating in promoting human, animal and plant health. References [1] Tamisier, L., Haegeman, A., Foucart, Y., Fouillien, N., Al Rwahnih, M., Buzkan, N., Candresse, T., Chiumenti, M., De Jonghe, K., Lefebvre, M., Margaria, P., Reynard, J.-S., Stevens, K., Kutnjak, D. and Massart, S. (2021) Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detection. Zenodo, 4273791, version 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Genomics. doi: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4273791 [2] Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction” (CASP) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CASP [3] RNA-puzzles - https://www.rnapuzzles.org [4] Critical Assessment of Function Annotation (CAFA) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_Assessment_of_Function_Annotation [5] Critical Assessment of Prediction of Interactions (CAPI) - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_Assessment_of_Prediction_of_Interactions [6] Assemblathon - https://assemblathon.org [7] VIROMOCK challenge - https://gitlab.com/ilvo/VIROMOCKchallenge | Semi-artificial datasets as a resource for validation of bioinformatics pipelines for plant virus detection | Lucie Tamisier, Annelies Haegeman, Yoika Foucart, Nicolas Fouillien, Maher Al Rwahnih, Nihal Buzkan, Thierry Candresse, Michela Chiumenti, Kris De Jonghe, Marie Lefebvre, Paolo Margaria, Jean Sébastien Reynard, Kristian Stevens, Denis Kutnjak, Séb... | <p>The widespread use of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) for detection of plant viruses and sequencing of plant virus genomes has led to the generation of large amounts of data and of bioinformatics challenges to process them. Many bioinformatics... |  | Bioinformatics, Plants, Viruses and transposable elements | Hadi Quesneville | 2020-11-27 14:31:47 | View | |
07 Feb 2023
RAREFAN: A webservice to identify REPINs and RAYTs in bacterial genomesFrederic Bertels, Julia von Irmer, Carsten Fortmann-Grote https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.22.493013A workflow for studying enigmatic non-autonomous transposable elements across bacteriaRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by Sophie Abby and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Sophie Abby and 1 anonymous reviewer
Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences (REPs) are common repetitive elements in bacterial genomes (Gilson et al., 1984; Stern et al., 1984). In 2011, Bertels and Rainey identified that REPs are overrepresented in pairs of inverted repeats, which likely form hairpin structures, that they referred to as “REP doublets forming hairpins” (REPINs). Based on bioinformatics analyses, they argued that REPINs are likely selfish elements that evolved from REPs flanking particular transposes (Bertels and Rainey, 2011). These transposases, so-called REP-associated tyrosine transposases (RAYTs), were known to be highly associated with the REP content in a genome and to have characteristic upstream and downstream flanking REPs (Nunvar et al., 2010). The flanking REPs likely enable RAYT transposition, and their horizontal replication is physically linked to this process. In contrast, Bertels and Rainey hypothesized that REPINs are selfish elements that are highly replicated due to the similarity in arrangement to these RAYT-flanking REPs, but independent of RAYT transposition and generally with no impact on bacterial fitness (Bertels and Rainey, 2011). This last point was especially contentious, as REPINs are highly conserved within species (Bertels and Rainey, 2023), which is unusual for non-beneficial bacterial DNA (Mira et al., 2001). Bertels and Rainey have since refined their argument to be that REPINs must provide benefits to host cells, but that there are nonetheless signatures of intragenomic conflict in genomes associated with these elements (Bertels and Rainey, 2023). These signatures reflect the divergent levels of selections driving REPIN distribution: selection at the level of each DNA element and selection on each individual bacterium. I found this observation particularly interesting as I and my colleague recently argued that these divergent levels of selection, and the interaction between them, is key to understanding bacterial pangenome diversity (Douglas and Shapiro, 2021). REPINs could be an excellent system for investigating these levels of selection across bacteria more generally. The problem is that REPINs have not been widely characterized in bacterial genomes, partially because no bioinformatic workflow has been available for this purpose. To address this problem, Fortmann-Grote et al. (2023) developed RAREFAN, which is a web server for identifying RAYTs and associated REPINs in a set of input genomes. The authors showcase their tool by applying it to 49 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia genomes and providing examples of how to identify and assess RAYT-REPIN hits. The workflow requires several manual steps, but nonetheless represents a straightforward and standardized approach. Overall, this workflow should enable RAYTs and REPINs to be identified across diverse bacterial species, which will facilitate further investigation into the mechanisms driving their maintenance and spread. References Bertels F, Rainey PB (2023) Ancient Darwinian replicators nested within eubacterial genomes. BioEssays, 45, 2200085. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.202200085 Bertels F, Rainey PB (2011) Within-Genome Evolution of REPINs: a New Family of Miniature Mobile DNA in Bacteria. PLOS Genetics, 7, e1002132. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002132 Douglas GM, Shapiro BJ (2021) Genic Selection Within Prokaryotic Pangenomes. Genome Biology and Evolution, 13, evab234. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evab234 Fortmann-Grote C, Irmer J von, Bertels F (2023) RAREFAN: A webservice to identify REPINs and RAYTs in bacterial genomes. bioRxiv, 2022.05.22.493013, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.22.493013 Gilson E, Clément J m., Brutlag D, Hofnung M (1984) A family of dispersed repetitive extragenic palindromic DNA sequences in E. coli. The EMBO Journal, 3, 1417–1421. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01986.x Mira A, Ochman H, Moran NA (2001) Deletional bias and the evolution of bacterial genomes. Trends in Genetics, 17, 589–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(01)02447-7 Nunvar J, Huckova T, Licha I (2010) Identification and characterization of repetitive extragenic palindromes (REP)-associated tyrosine transposases: implications for REP evolution and dynamics in bacterial genomes. BMC Genomics, 11, 44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-44 Stern MJ, Ames GF-L, Smith NH, Clare Robinson E, Higgins CF (1984) Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: A major component of the bacterial genome. Cell, 37, 1015–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7 | RAREFAN: A webservice to identify REPINs and RAYTs in bacterial genomes | Frederic Bertels, Julia von Irmer, Carsten Fortmann-Grote | <p style="text-align: justify;">Compared to eukaryotes, repetitive sequences are rare in bacterial genomes and usually do not persist for long. Yet, there is at least one class of persistent prokaryotic mobile genetic elements: REPINs. REPINs are ... | Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Gavin Douglas | 2022-06-07 08:21:34 | View | ||
08 Apr 2022

POSTPRINT
Phylogenetics in the Genomic EraCéline Scornavacca, Frédéric Delsuc, Nicolas Galtier https://hal.inria.fr/PGE/“Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era” brings together experts in the field to present a comprehensive synthesisRecommended by Robert Waterhouse and Karen MeusemannE-book: Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era (Scornavacca et al. 2021) This book was not peer-reviewed by PCI Genomics. It has undergone an internal review by the editors. Accurate reconstructions of the relationships amongst species and the genes encoded in their genomes are an essential foundation for almost all evolutionary inferences emerging from downstream analyses. Molecular phylogenetics has developed as a field over many decades to build suites of models and methods to reconstruct reliable trees that explain, support, or refute such inferences. The genomic era has brought new challenges and opportunities to the field, opening up new areas of research and algorithm development to take advantage of the accumulating large-scale data. Such ‘big-data’ phylogenetics has come to be known as phylogenomics, which broadly aims to connect molecular and evolutionary biology research to address questions centred on relationships amongst taxa, mechanisms of molecular evolution, and the biological functions of genes and other genomic elements. This book brings together experts in the field to present a comprehensive synthesis of Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era, covering key conceptual and methodological aspects of how to build accurate phylogenies and how to apply them in molecular and evolutionary research. The paragraphs below briefly summarise the five constituent parts of the book, highlighting the key concepts, methods, and applications that each part addresses. Being organised in an accessible style, while presenting details to provide depth where necessary, and including guides describing real-world examples of major phylogenomic tools, this collection represents an invaluable resource, particularly for students and newcomers to the field of phylogenomics. Part 1: Phylogenetic analyses in the genomic era Modelling how sequences evolve is a fundamental cornerstone of phylogenetic reconstructions. This part of the book introduces the reader to phylogenetic inference methods and algorithmic optimisations in the contexts of Markov, Maximum Likelihood, and Bayesian models of sequence evolution. The main concepts and theoretical considerations are mapped out for probabilistic Markov models, efficient tree building with Maximum Likelihood methods, and the flexibility and robustness of Bayesian approaches. These are supported with practical examples of phylogenomic applications using the popular tools RAxML and PhyloBayes. By considering theoretical, algorithmic, and practical aspects, these chapters provide readers with a holistic overview of the challenges and recent advances in developing scalable phylogenetic analyses in the genomic era. Part 2: Data quality, model adequacy This part focuses on the importance of considering the appropriateness of the evolutionary models used and the accuracy of the underlying molecular and genomic data. Both these aspects can profoundly affect the results when applying current phylogenomic methods to make inferences about complex biological and evolutionary processes. A clear example is presented for methods for building multiple sequence alignments and subsequent filtering approaches that can greatly impact phylogeny inference. The importance of error detection in (meta)barcode sequencing data is also highlighted, with solutions offered by the MACSE_BARCODE pipeline for accurate taxonomic assignments. Orthology datasets are essential markers for phylogenomic inferences, but the overview of concepts and methods presented shows that they too face challenges with respect to model selection and data quality. Finally, an innovative approach using ancestral gene order reconstructions provides new perspectives on how to assess gene tree accuracy for phylogenomic analyses. By emphasising through examples the importance of using appropriate evolutionary models and assessing input data quality, these chapters alert readers to key limitations that the field as a whole strives to address. Part 3: Resolving phylogenomic conflicts Conflicting phylogenetic signals are commonplace and may derive from statistical or systematic bias. This part of the book addresses possible causes of conflict, discordance between gene trees and species trees and how processes that lead to such conflicts can be described by phylogenetic models. Furthermore, it provides an overview of various models and methods with examples in phylogenomics including their pros and cons. Outlined in detail is the multispecies coalescent model (MSC) and its applications in phylogenomics. An interesting aspect is that different phylogenetic signals leading to conflict are in fact a key source of information rather than a problem that can – and should – be used to point to events like introgression or hybridisation, highlighting possible future trends in this research area. Last but not least, this part of the book also addresses inferring species trees by concatenating single multiple sequence alignments (gene alignments) versus inferring the species tree based on ensembles of single gene trees pointing out advantages and disadvantages of both approaches. As an important take home message from these chapters, it is recommended to be flexible and identify the most appropriate approach for each dataset to be analysed since this may tremendously differ depending on the dataset, setting, taxa, and phylogenetic level addressed by the researcher. Part 4: Functional evolutionary genomics In this part of the book the focus shifts to functional considerations of phylogenomics approaches both in terms of molecular evolution and adaptation and with respect to gene expression. The utility of multi-species analysis is clearly presented in the context of annotating functional genomic elements through quantifying evolutionary constraint and protein-coding potential. An historical perspective on characterising rates of change highlights how phylogenomic datasets help to understand the modes of molecular evolution across the genome, over time, and between lineages. These are contextualised with respect to the specific aim of detecting signatures of adaptation from protein-coding DNA alignments using the example of the MutSelDP-ω∗ model. This is extended with the presentation of the generally rare case of adaptive sequence convergence, where consideration of appropriate models and knowledge of gene functions and phenotypic effects are needed. Constrained or relaxed, selection pressures on sequence or copy-number affect genomic elements in different ways, making the very concept of function difficult to pin down despite it being fundamental to relate the genome to the phenotype and organismal fitness. Here gene expression provides a measurable intermediate, for which the Expression Comparison tool from the Bgee suite allows exploration of expression patterns across multiple animal species taking into account anatomical homology. Overall, phylogenomics applications in functional evolutionary genomics build on a rich theoretical history from molecular analyses where integration with knowledge of gene functions is challenging but critical. Part 5: Phylogenomic applications Rather than attempting to review the full extent of applications linked to phylogenomics, this part of the book focuses on providing detailed specific insights into selected examples and methods concerning i) estimating divergence times, and ii) species delimitation in the era of ‘omics’ data. With respect to estimating divergence times, an exemplary overview is provided for fossil data recovered from geological records, either using fossil data as calibration points with an extant-species-inferred phylogeny, or using a fossilised birth-death process as a mechanistic model that accounts for lineage diversification. Included is a tutorial for a joint approach to infer phylogenies and estimate divergence times using the RevBayes software with various models implemented for different applications and datasets incorporating molecular and morphological data. An interesting excursion is outlined focusing on timescale estimates with respect to viral evolution introducing BEAGLE, a high-performance likelihood-calculation platform that can be used on multi-core systems. As a second major subject, species delimitation is addressed since currently the increasing amount of available genomic data enables extensive inferences, for instance about the degree of genetic isolation among species and ancient and recent introgression events. Describing the history of molecular species delimitation up to the current genomic era and presenting widely used computational methods incorporating single- and multi-locus genomic data, pros and cons are addressed. Finally, a proposal for a new method for delimiting species based on empirical criteria is outlined. In the closing chapter of this part of the book, BPP (Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo program) for analysing multi-locus sequence data under the multispecies coalescent (MSC) model with and without introgression is introduced, including a tutorial. These examples together provide accessible details on key conceptual and methodological aspects related to the application of phylogenetics in the genomic era. References Scornavacca C, Delsuc F, Galtier N (2021) Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era. https://hal.inria.fr/PGE/ | Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era | Céline Scornavacca, Frédéric Delsuc, Nicolas Galtier | <p style="text-align: justify;">Molecular phylogenetics was born in the middle of the 20th century, when the advent of protein and DNA sequencing offered a novel way to study the evolutionary relationships between living organisms. The first 50 ye... |  | Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics, Fungi, Plants, Population genomics, Vertebrates, Viruses and transposable elements | Robert Waterhouse | 2022-03-15 17:43:52 | View | |
25 Nov 2022
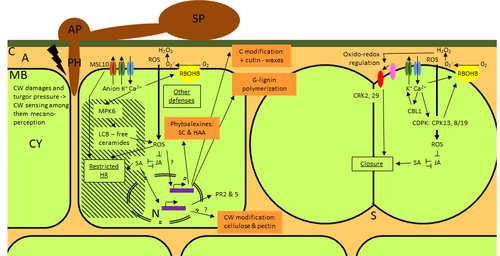
Phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses reveal major differences between apple and pear scab nonhost resistanceE. Vergne, E. Chevreau, E. Ravon, S. Gaillard, S. Pelletier, M. Bahut, L. Perchepied https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.01.446506Apples and pears: two closely related species with differences in scab nonhost resistanceRecommended by Wirulda Pootakham based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersNonhost resistance is a common form of disease resistance exhibited by plants against microorganisms that are pathogenic to other plant species [1]. Apples and pears are two closely related species belonging to Rosaceae family, both affected by scab disease caused by fungal pathogens in the Venturia genus. These pathogens appear to be highly host-specific. While apples are nonhosts for Venturia pyrina, pears are nonhosts for Venturia inaequalis. To date, the molecular bases of scab nonhost resistance in apple and pear have not been elucidated. This preprint by Vergne, et al (2022) [2] analyzed nonhost resistance symptoms in apple/V. pyrina and pear/V. inaequalis interactions as well as their transcriptomic responses. Interestingly, the author demonstrated that the nonhost apple/V. pyrina interaction was almost symptomless while hypersensitive reactions were observed for pear/V. inaequalis interaction. The transcriptomic analyses also revealed a number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that corresponded to the severity of the interactions, with very few DEGs observed during the apple/V. pyrina interaction and a much higher number of DEGs during the pear/V. inaequalis interaction. This type of reciprocal host-pathogen interaction study is valuable in gaining new insights into how plants interact with microorganisms that are potential pathogens in related species. A few processes appeared to be involved in the pear resistance against the nonhost pathogen V. inaequalis at the transcriptomic level, such as stomata closure, modification of cell wall and production of secondary metabolites as well as phenylpropanoids. Based on the transcriptomics changes during the nonhost interaction, the author compared the responses to those of host-pathogen interactions and revealed some interesting findings. They proposed a series of cascading effects in pear induced by the presence of V. inaequalis, which I believe helps shed some light on the basic mechanism for nonhost resistance. I am recommending this study because it provides valuable information that will strengthen our understanding of nonhost resistance in the Rosaceae family and other plant species. The knowledge gained here may be applied to genetically engineer plants for a broader resistance against a number of pathogens in the future. References 1. Senthil-Kumar M, Mysore KS (2013) Nonhost Resistance Against Bacterial Pathogens: Retrospectives and Prospects. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 51, 407–427. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102319 2. Vergne E, Chevreau E, Ravon E, Gaillard S, Pelletier S, Bahut M, Perchepied L (2022) Phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses reveal major differences between apple and pear scab nonhost resistance. bioRxiv, 2021.06.01.446506, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.01.446506 | Phenotypic and transcriptomic analyses reveal major differences between apple and pear scab nonhost resistance | E. Vergne, E. Chevreau, E. Ravon, S. Gaillard, S. Pelletier, M. Bahut, L. Perchepied | <p style="text-align: justify;"><strong>Background. </strong>Nonhost resistance is the outcome of most plant/pathogen interactions, but it has rarely been described in Rosaceous fruit species. Apple (<em>Malus x domestica</em> Borkh.) have a nonho... |  | Functional genomics, Plants | Wirulda Pootakham | Jessica Soyer, Anonymous | 2022-05-13 15:06:08 | View |
24 Feb 2023
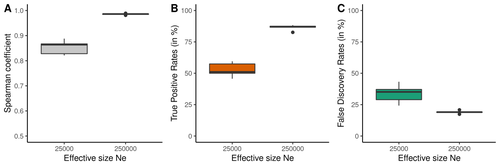
Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation studyMarie Raynaud, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Nicolas Galtier https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.30.486352How to interpret the inference of recombination landscapes on methods based on linkage disequilibrium?Recommended by Sebastian E. Ramos-Onsins based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersData interpretation depends on previously established and validated tools, designed for a specific type of data. These methods, however, are usually based on simple models with validity subject to a set of theoretical parameterized conditions and data types. Accordingly, the tool developers provide the potential users with guidelines for data interpretations within the tools’ limitation. Nevertheless, once the methodology is accepted by the community, it is employed in a large variety of empirical studies outside of the method’s original scope or that typically depart from the standard models used for its design, thus potentially leading to the wrong interpretation of the results. Numerous empirical studies inferred recombination rates across genomes, detecting hotspots of recombination and comparing related species (e.g., Shanfelter et al. 2019, Spence and Song 2019). These studies used indirect methodologies based on the signals that recombination left in the genome, such as linkage disequilibrium and the patterns of haplotype segregation (e.g.,Chan et al. 2012). The conclusions from these analyses have been used, for example, to interpret the evolution of the chromosomal structure or the evolution of recombination among closely related species. Indirect methods have the advantage of collecting a large quantity of recombination events, and thus have a better resolution than direct methods (which only detect the few recombination events occurring at that time). On the other hand, indirect methods are affected by many different evolutionary events, such as demographic changes and selection. Indeed, the inference of recombination levels across the genome has not been studied accurately in non-standard conditions. Linkage disequilibrium is affected by several factors that can modify the recombination inference, such as demographic history, events of selection, population size, and mutation rate, but is also related to the size of the studied sample, and other technical parameters defined for each specific methodology. Raynaud et al (2023) analyzed the reliability of the recombination rate inference when considering the violation of several standard assumptions (evolutionary and methodological) in one of the most popular families of methods based on LDhat (McVean et al. 2004), specifically its improved version, LDhelmet (Chan et al. 2012). These methods cover around 70 % of the studies that infer recombination rates. The authors used recombination maps, obtained from empirical studies on humans, and included hotspots, to perform a detailed simulation study of the capacity of this methodology to correctly infer the pattern of recombination and the location of these hotspots. Correlations between the real, and inferred values from simulations were obtained, as well as several rates, such as the true positive and false discovery rate to detect hotspots. The authors of this work send a message of caution to researchers that are applying this methodology to interpret data from the inference of recombination landscapes and the location of hotspots. The inference of recombination landscapes and hotspots can differ considerably even in standard model conditions. In addition, demographic processes, like bottleneck or admixture, but also the level of population size and mutation rates, can substantially affect the estimation accuracy of the level of recombination and the location of hotspots. Indeed, the inference of the location of hotspots in simulated data with the same landscape, can be very imprecise when standard assumptions are violated or not considered. These effects may lead to incorrect interpretations, for example about the conservation of recombination maps between closely related species. Finally, Raynaud et al (2023) included a useful guide with advice on how to obtain accurate recombination estimations with methods based on linkage disequilibrium, also emphasizing the limitations of such approaches. REFERENCES Chan AH, Jenkins PA, Song YS (2012) Genome-Wide Fine-Scale Recombination Rate Variation in Drosophila melanogaster. PLOS Genetics, 8, e1003090. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003090 McVean GAT, Myers SR, Hunt S, Deloukas P, Bentley DR, Donnelly P (2004) The Fine-Scale Structure of Recombination Rate Variation in the Human Genome. Science, 304, 581–584. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1092500 Raynaud M, Gagnaire P-A, Galtier N (2023) Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation study. bioRxiv, 2022.03.30.486352, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.30.486352 Spence JP, Song YS (2019) Inference and analysis of population-specific fine-scale recombination maps across 26 diverse human populations. Science Advances, 5, eaaw9206. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw9206 | Performance and limitations of linkage-disequilibrium-based methods for inferring the genomic landscape of recombination and detecting hotspots: a simulation study | Marie Raynaud, Pierre-Alexandre Gagnaire, Nicolas Galtier | <p style="text-align: justify;">Knowledge of recombination rate variation along the genome provides important insights into genome and phenotypic evolution. Population genomic approaches offer an attractive way to infer the population-scaled recom... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Population genomics | Sebastian E. Ramos-Onsins | 2022-04-05 14:59:14 | View | |
13 Jul 2022
Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structuresColin Clairet, Nicolas Lapalu, Adeline Simon, Jessica L. Soyer, Muriel Viaud, Enric Zehraoui, Berengere Dalmais, Isabelle Fudal, Nadia Ponts https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.16.439968Genome-wide chromatin and expression datasets of various pathogenic ascomycetesRecommended by Sébastien Bloyer and Romain Koszul based on reviews by Ricardo C. Rodríguez de la Vega and 1 anonymous reviewerPlant pathogenic fungi represent serious economic threats. These organisms are rapidly adaptable, with plastic genomes containing many variable regions and evolving rapidly. It is, therefore, useful to characterize their genetic regulation in order to improve their control. One of the steps to do this is to obtain omics data that link their DNA structure and gene expression. Clairet C, Lapalu N, Simon A, Soyer JL, Viaud M, Zehraoui E, Dalmais B, Fudal I, Ponts N (2022) Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structures. bioRxiv, 2021.04.16.439968, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.16.439968 | Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structures | Colin Clairet, Nicolas Lapalu, Adeline Simon, Jessica L. Soyer, Muriel Viaud, Enric Zehraoui, Berengere Dalmais, Isabelle Fudal, Nadia Ponts | <p style="text-align: justify;">Fungal pathogens represent a serious threat towards agriculture, health, and environment. Control of fungal diseases on crops necessitates a global understanding of fungal pathogenicity determinants and their expres... |  | Epigenomics, Fungi | Sébastien Bloyer | 2021-04-17 10:32:41 | View | |
02 Jun 2023
Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois milesChristos V. Kitsoulis, Vasileios Papadogiannis, Jon B. Kristoffersen, Elisavet Kaitetzidou, Aspasia Sterioti, Costas S. Tsigenopoulos, Tereza Manousaki https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.10.523469The genome of a dangerous invader (fish) beautyRecommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Maria Recuerda and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Maria Recuerda and 1 anonymous reviewer
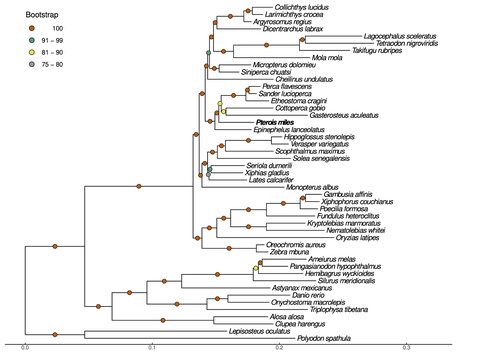
High-quality genomes are currently being generated at an unprecedented speed powered by long-read sequencing technologies. However, sequencing effort is concentrated unequally across the tree of life and several key evolutionary and ecological groups remain largely unexplored. So is the case for fish species of the family Scorpaenidae (Perciformes). Kitsoulis et al. present the genome of the devil firefish, Pterois miles (1). Following current best practices, the assembly relies largely on Oxford Nanopore long reads, aided by Illumina short reads for polishing to increase the per-base accuracy. PacBio’s IsoSeq was used to sequence RNA from a variety of tissues as direct evidence for annotating genes. The reconstructed genome is 902 Mb in size and has high contiguity (N50=14.5 Mb; 660 scaffolds, 90% of the genome covered by the 83 longest scaffolds) and completeness (98% BUSCO completeness). The new genome is used to assess the phylogenetic position of P. miles, explore gene synteny against zebrafish, look at orthogroup expansion and contraction patterns in Perciformes, as well as to investigate the evolution of toxins in scorpaenid fish (2). In addition to its value for better understanding the evolution of scorpaenid and teleost fishes, this new genome is also an important resource for monitoring its invasiveness through the Mediterranean Sea (3) and the Atlantic Ocean, in the latter case forming the invasive lionfish complex with P. volitans (4). REFERENCES 1. Kitsoulis CV, Papadogiannis V, Kristoffersen JB, Kaitetzidou E, Sterioti E, Tsigenopoulos CS, Manousaki T. (2023) Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, Pterois miles. BioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.10.523469 2. Kiriake A, Shiomi K. (2011) Some properties and cDNA cloning of proteinaceous toxins from two species of lionfish (Pterois antennata and Pterois volitans). Toxicon, 58(6-7):494–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.08.010 3. Katsanevakis S, et al. (2020) Un- published Mediterranean records of marine alien and cryptogenic species. BioInvasions Records, 9:165–182. https://doi.org/10.3391/bir.2020.9.2.01 4. Lyons TJ, Tuckett QM, Hill JE. (2019) Data quality and quantity for invasive species: A case study of the lionfishes. Fish and Fisheries, 20:748–759. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12374 | Near-chromosome level genome assembly of devil firefish, *Pterois miles* | Christos V. Kitsoulis, Vasileios Papadogiannis, Jon B. Kristoffersen, Elisavet Kaitetzidou, Aspasia Sterioti, Costas S. Tsigenopoulos, Tereza Manousaki | <p style="text-align: justify;">Devil firefish (<em>Pterois miles</em>), a member of Scorpaenidae family, is one of the most successful marine non-native species, dominating around the world, that was rapidly spread into the Mediterranean Sea, thr... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Iker Irisarri | 2023-01-17 12:37:20 | View | |
23 Sep 2022
MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studiesRosa Fernandez, Vanina Tonzo, Carolina Simon Guerrero, Jesus Lozano-Fernandez, Gemma I Martinez-Redondo, Pau Balart-Garcia, Leandro Aristide, Klara Eleftheriadi, Carlos Vargas-Chavez https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500182MATEdb: a new phylogenomic-driven database for MetazoaRecommended by Samuel Abalde based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The development (and standardization) of high-throughput sequencing techniques has revolutionized evolutionary biology, to the point that we almost see as normal fine-detail studies of genome architecture evolution (Robert et al., 2022), adaptation to new habitats (Rahi et al., 2019), or the development of key evolutionary novelties (Hilgers et al., 2018), to name three examples. One of the fields that has benefited the most is phylogenomics, i.e. the use of genome-wide data for inferring the evolutionary relationships among organisms. Dealing with such amount of data, however, has come with important analytical and computational challenges. Likewise, although the steady generation of genomic data from virtually any organism opens exciting opportunities for comparative analyses, it also creates a sort of “information fog”, where it is hard to find the most appropriate and/or the higher quality data. I have personally experienced this not so long ago, when I had to spend several weeks selecting the most complete transcriptomes from several phyla, moving back and forth between the NCBI SRA repository and the relevant literature. In an attempt to deal with this issue, some research labs have committed their time and resources to the generation of taxa- and topic-specific databases (Lathe et al., 2008), such as MolluscDB (Liu et al., 2021), focused on mollusk genomics, or EukProt (Richter et al., 2022), a protein repository representing the diversity of eukaryotes. A new database that promises to become an important resource in the near future is MATEdb (Fernández et al., 2022), a repository of high-quality genomic data from Metazoa. MATEdb has been developed from publicly available and newly generated transcriptomes and genomes, prioritizing quality over quantity. Upon download, the user has access to both raw data and the related datasets: assemblies, several quality metrics, the set of inferred protein-coding genes, and their annotation. Although it is clear to me that this repository has been created with phylogenomic analyses in mind, I see how it could be generalized to other related problems such as analyses of gene content or evolution of specific gene families. In my opinion, the main strengths of MATEdb are threefold:
On a negative note, I see two main drawbacks. First, as of today (September 16th, 2022) this database is in an early stage and it still needs to incorporate a lot of animal groups. This has been discussed during the revision process and the authors are already working on it, so it is only a matter of time until all major taxa are represented. Second, there is a scalability issue. In its current format it is not possible to select the taxa of interest and the full database has to be downloaded, which will become more and more difficult as it grows. Nonetheless, with the appropriate resources it would be easy to find a better solution. There are plenty of examples that could serve as inspiration, so I hope this does not become a big problem in the future. Altogether, I and the researchers that participated in the revision process believe that MATEdb has the potential to become an important and valuable addition to the metazoan phylogenomics community. Personally, I wish it was available just a few months ago, it would have saved me so much time. References Fernández R, Tonzo V, Guerrero CS, Lozano-Fernandez J, Martínez-Redondo GI, Balart-García P, Aristide L, Eleftheriadi K, Vargas-Chávez C (2022) MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studies. bioRxiv, 2022.07.18.500182, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500182 Hilgers L, Hartmann S, Hofreiter M, von Rintelen T (2018) Novel Genes, Ancient Genes, and Gene Co-Option Contributed to the Genetic Basis of the Radula, a Molluscan Innovation. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1638–1652. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy052 Lathe W, Williams J, Mangan M, Karolchik, D (2008). Genomic data resources: challenges and promises. Nature Education, 1(3), 2. Liu F, Li Y, Yu H, Zhang L, Hu J, Bao Z, Wang S (2021) MolluscDB: an integrated functional and evolutionary genomics database for the hyper-diverse animal phylum Mollusca. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, D988–D997. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa918 Rahi ML, Mather PB, Ezaz T, Hurwood DA (2019) The Molecular Basis of Freshwater Adaptation in Prawns: Insights from Comparative Transcriptomics of Three Macrobrachium Species. Genome Biology and Evolution, 11, 1002–1018. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evz045 Richter DJ, Berney C, Strassert JFH, Poh Y-P, Herman EK, Muñoz-Gómez SA, Wideman JG, Burki F, Vargas C de (2022) EukProt: A database of genome-scale predicted proteins across the diversity of eukaryotes. bioRxiv, 2020.06.30.180687, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.30.180687 Robert NSM, Sarigol F, Zimmermann B, Meyer A, Voolstra CR, Simakov O (2022) Emergence of distinct syntenic density regimes is associated with early metazoan genomic transitions. BMC Genomics, 23, 143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08304-2 | MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studies | Rosa Fernandez, Vanina Tonzo, Carolina Simon Guerrero, Jesus Lozano-Fernandez, Gemma I Martinez-Redondo, Pau Balart-Garcia, Leandro Aristide, Klara Eleftheriadi, Carlos Vargas-Chavez | <p style="text-align: justify;">With the advent of high throughput sequencing, the amount of genomic data available for animals (Metazoa) species has bloomed over the last decade, especially from transcriptomes due to lower sequencing costs and ea... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics | Samuel Abalde | 2022-07-20 07:30:39 | View | |
24 Feb 2023

MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomesBertrand Néron, Rémi Denise, Charles Coluzzi, Marie Touchon, Eduardo P. C. Rocha, Sophie S. Abby https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.02.506364A unique and customizable approach for functionally annotating prokaryotic genomesRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by Kwee Boon Brandon Seah and Max Emil Schön based on reviews by Kwee Boon Brandon Seah and Max Emil Schön
Macromolecular System Finder (MacSyFinder) v2 (Néron et al., 2023) is a newly updated approach for performing functional annotation of prokaryotic genomes (Abby et al., 2014). This tool parses an input file of protein sequences from a single genome (either ordered by genome location or unordered) and identifies the presence of specific cellular functions (referred to as “systems”). These systems are called based on two criteria: (1) that the "quorum" of a minimum set of core proteins involved is reached the “quorum” of a minimum set of core proteins being involved that are present, and (2) that the genes encoding these proteins are in the expected genomic organization (e.g., within the same order in an operon), when ordered data is provided. I believe the MacSyFinder approach represents an improvement over more commonly used methods exactly because it can incorporate such information on genomic organization, and also because it is more customizable. Before properly appreciating these points, it is worth noting the norms and key challenges surrounding high-throughput functional annotation of prokaryotic genomes. Genome sequences are being added to online repositories at increasing rates, which has led to an enormous amount of bacterial genome diversity available to investigate (Altermann et al., 2022). A key aspect of understanding this diversity is the functional annotation step, which enables genes to be grouped into more biologically interpretable categories. For instance, gene calls can be mapped against existing Clusters of Orthologous Genes, which are themselves grouped into general categories such as ‘Transcription’ and ‘Lipid metabolism’ (Galperin et al., 2021). This approach is valuable but is primarily used for global summaries of functional annotations within a genome: for example, it could be useful to know that a genome is particularly enriched for genes involved in lipid metabolism. However, knowing that a particular gene is involved in the general process of lipid metabolism is less likely to be actionable. In other words, the desired specificity of a gene’s functional annotation will depend on the exact question being investigated. There is no shortage of functional ontologies in genomics that can be applied for this purpose (Douglas and Langille, 2021), and researchers are often overwhelmed by the choice of which functional ontology to use. In this context, giving researchers the ability to precisely specify the gene families and operon structures they are interested in identifying across genomes provides useful control over what precise functions they are profiling. Of course, most researchers will lack the information and/or expertise to fully take advantage of MacSyFinder’s customizable features, but having this option for specialized purposes is valuable. The other MacSyFinder feature that I find especially noteworthy is that it can incorporate genomic organization (e.g., of genes ordered in operons) when calling systems. This is a rare feature among commonly used tools for functional annotation and likely results in much higher specificity. As the authors note, this capability makes the co-occurrence of paralogs, and other divergent genes that share sequence similarity, to contribute less noise (i.e., they result in fewer false positive calls). It is important to emphasize that these features are not new additions in MacSyFinder v2, but there are many other valuable changes. Most practically, this release is written in Python 3, rather than the obsolete Python 2.7, and was made more computationally efficient, which will enable MacSyFinder to be more widely used and more easily maintained moving forward. In addition, the search algorithm for analyzing individual proteins was fundamentally updated as well. The authors show that their improvements to the search algorithm result in an 8% and 20% increase in the number of identified calls for single and multi-locus secretion systems, respectively. Taken together, MacSyFinder v2 represents both practical and scientific improvements over the previous version, which will be of great value to the field. References Abby SS, Néron B, Ménager H, Touchon M, Rocha EPC (2014) MacSyFinder: A Program to Mine Genomes for Molecular Systems with an Application to CRISPR-Cas Systems. PLOS ONE, 9, e110726. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110726 Altermann E, Tegetmeyer HE, Chanyi RM (2022) The evolution of bacterial genome assemblies - where do we need to go next? Microbiome Research Reports, 1, 15. https://doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2022.02 Douglas GM, Langille MGI (2021) A primer and discussion on DNA-based microbiome data and related bioinformatics analyses. Peer Community Journal, 1. https://doi.org/10.24072/pcjournal.2 Galperin MY, Wolf YI, Makarova KS, Vera Alvarez R, Landsman D, Koonin EV (2021) COG database update: focus on microbial diversity, model organisms, and widespread pathogens. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, D274–D281. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1018 Néron B, Denise R, Coluzzi C, Touchon M, Rocha EPC, Abby SS (2023) MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomes. bioRxiv, 2022.09.02.506364, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.02.506364 | MacSyFinder v2: Improved modelling and search engine to identify molecular systems in genomes | Bertrand Néron, Rémi Denise, Charles Coluzzi, Marie Touchon, Eduardo P. C. Rocha, Sophie S. Abby | <p style="text-align: justify;">Complex cellular functions are usually encoded by a set of genes in one or a few organized genetic loci in microbial genomes. Macromolecular System Finder (MacSyFinder) is a program that uses these properties to mod... |  | Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Functional genomics | Gavin Douglas | Kwee Boon Brandon Seah, Max Emil Schön | 2022-09-09 10:30:31 | View |
13 Jul 2022
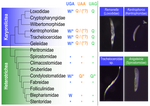
Karyorelict ciliates use an ambiguous genetic code with context-dependent stop/sense codonsBrandon Kwee Boon Seah, Aditi Singh, Estienne Carl Swart https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.12.488043An accident frozen in time: the ambiguous stop/sense genetic code of karyorelict ciliatesRecommended by Iker Irisarri based on reviews by Vittorio Boscaro and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Vittorio Boscaro and 2 anonymous reviewers
Several variations of the “universal” genetic code are known. Among the most striking are those where a codon can either encode for an amino acid or a stop signal depending on the context. Such ambiguous codes are known to have evolved in eukaryotes multiple times independently, particularly in ciliates – eight different codes have so far been discovered (1). We generally view such genetic codes are rare ‘variants’ of the standard code restricted to single species or strains, but this might as well reflect a lack of study of closely related species. In this study, Seah and co-authors (2) explore the possibility of codon reassignment in karyorelict ciliates closely related to Parduczia sp., which has been shown to contain an ambiguous genetic code (1). Here, single-cell transcriptomics are used, along with similar available data, to explore the possibility of codon reassignment across the diversity of Karyorelictea (four out of the six recognized families). Codon reassignments were inferred from their frequencies within conserved Pfam (3) protein domains, whereas stop codons were inferred from full-length transcripts with intact 3’-UTRs. Results show the reassignment of UAA and UAG stop codons to code for glutamine (Q) and the reassignment of the UGA stop codon into tryptophan (W). This occurs only within the coding sequences, whereas the end of transcription is marked by UGA as the main stop codon, and to a lesser extent by UAA. In agreement with a previous model proposed that explains the functioning of ambiguous codes (1,4), the authors observe a depletion of in-frame UGAs before the UGA codon that indicates the stop, thus avoiding premature termination of transcription. The inferred codon reassignments occur in all studied karyorelicts, including the previously studied Parduczia sp. Despite the overall clear picture, some questions remain. Data for two out of six main karyorelict lineages are so far absent and the available data for Cryptopharyngidae was inconclusive; the phylogenetic affinities of Cryptopharyngidae have also been questioned (5). This indicates the need for further study of this interesting group of organisms. As nicely discussed by the authors, experimental evidence could further strengthen the conclusions of this paper, including ribosome profiling, mass spectrometry – as done for Condylostoma (1) – or even direct genetic manipulation. The uniformity of the ambiguous genetic code across karyorelicts might at first seem dull, but when viewed in a phylogenetic context character distribution strongly suggest that this genetic code has an ancient origin in the karyorelict ancestor ~455 Ma in the Proterozoic (6). This ambiguous code is also not a rarity of some obscure species, but it is shared by ciliates that are very diverse and ecologically important. The origin of the karyorelict code is also intriguing. Adaptive arguments suggest that it could confer robustness to mutations causing premature stop codons. However, we lack evidence for ambiguous codes being linked to specific habitats of lifestyles that could account for it. Instead, the authors favor the neutral view of an ancient “frozen accident”, fixed stochastically simply because it did not pose a significant selective disadvantage. Once a stop codon is reassigned to an amino acid, it is increasingly difficult to revert this without the deleterious effect of prematurely terminating translation. At the end, the origin of the genetic code itself is thought to be a frozen accident too (7). References 1. Swart EC, Serra V, Petroni G, Nowacki M. Genetic codes with no dedicated stop codon: Context-dependent translation termination. Cell 2016;166: 691–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.020 2. Seah BKB, Singh A, Swart EC (2022) Karyorelict ciliates use an ambiguous genetic code with context-dependent stop/sense codons. bioRxiv, 2022.04.12.488043. ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.12.488043 3. Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, Qureshi M, Salazar GA, Sonnhammer ELL, Tosatto SCE, Paladin L, Raj S, Richardson LJ, Finn RD, Bateman A. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021, Nuc Acids Res 2020;49: D412-D419. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa913 4. Alkalaeva E, Mikhailova T. Reassigning stop codons via translation termination: How a few eukaryotes broke the dogma. Bioessays. 2017;39. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201600213 5. Xu Y, Li J, Song W, Warren A. Phylogeny and establishment of a new ciliate family, Wilbertomorphidae fam. nov. (Ciliophora, Karyorelictea), a highly specialized taxon represented by Wilbertomorpha colpoda gen. nov., spec. nov. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2013;60: 480–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12055 6. Fernandes NM, Schrago CG. A multigene timescale and diversification dynamics of Ciliophora evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2019;139: 106521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.106521 7. Crick FH. The origin of the genetic code. J Mol Biol. 1968;38: 367–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(68)90392-6 | Karyorelict ciliates use an ambiguous genetic code with context-dependent stop/sense codons | Brandon Kwee Boon Seah, Aditi Singh, Estienne Carl Swart | <p style="text-align: justify;">In ambiguous stop/sense genetic codes, the stop codon(s) not only terminate translation but can also encode amino acids. Such codes have evolved at least four times in eukaryotes, twice among ciliates (<em>Condylost... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics | Iker Irisarri | 2022-05-02 11:06:10 | View |










