Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * ▲ | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
08 Apr 2022

POSTPRINT
Phylogenetics in the Genomic EraCéline Scornavacca, Frédéric Delsuc, Nicolas Galtier https://hal.inria.fr/PGE/“Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era” brings together experts in the field to present a comprehensive synthesisRecommended by Robert Waterhouse and Karen MeusemannE-book: Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era (Scornavacca et al. 2021) This book was not peer-reviewed by PCI Genomics. It has undergone an internal review by the editors. Accurate reconstructions of the relationships amongst species and the genes encoded in their genomes are an essential foundation for almost all evolutionary inferences emerging from downstream analyses. Molecular phylogenetics has developed as a field over many decades to build suites of models and methods to reconstruct reliable trees that explain, support, or refute such inferences. The genomic era has brought new challenges and opportunities to the field, opening up new areas of research and algorithm development to take advantage of the accumulating large-scale data. Such ‘big-data’ phylogenetics has come to be known as phylogenomics, which broadly aims to connect molecular and evolutionary biology research to address questions centred on relationships amongst taxa, mechanisms of molecular evolution, and the biological functions of genes and other genomic elements. This book brings together experts in the field to present a comprehensive synthesis of Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era, covering key conceptual and methodological aspects of how to build accurate phylogenies and how to apply them in molecular and evolutionary research. The paragraphs below briefly summarise the five constituent parts of the book, highlighting the key concepts, methods, and applications that each part addresses. Being organised in an accessible style, while presenting details to provide depth where necessary, and including guides describing real-world examples of major phylogenomic tools, this collection represents an invaluable resource, particularly for students and newcomers to the field of phylogenomics. Part 1: Phylogenetic analyses in the genomic era Modelling how sequences evolve is a fundamental cornerstone of phylogenetic reconstructions. This part of the book introduces the reader to phylogenetic inference methods and algorithmic optimisations in the contexts of Markov, Maximum Likelihood, and Bayesian models of sequence evolution. The main concepts and theoretical considerations are mapped out for probabilistic Markov models, efficient tree building with Maximum Likelihood methods, and the flexibility and robustness of Bayesian approaches. These are supported with practical examples of phylogenomic applications using the popular tools RAxML and PhyloBayes. By considering theoretical, algorithmic, and practical aspects, these chapters provide readers with a holistic overview of the challenges and recent advances in developing scalable phylogenetic analyses in the genomic era. Part 2: Data quality, model adequacy This part focuses on the importance of considering the appropriateness of the evolutionary models used and the accuracy of the underlying molecular and genomic data. Both these aspects can profoundly affect the results when applying current phylogenomic methods to make inferences about complex biological and evolutionary processes. A clear example is presented for methods for building multiple sequence alignments and subsequent filtering approaches that can greatly impact phylogeny inference. The importance of error detection in (meta)barcode sequencing data is also highlighted, with solutions offered by the MACSE_BARCODE pipeline for accurate taxonomic assignments. Orthology datasets are essential markers for phylogenomic inferences, but the overview of concepts and methods presented shows that they too face challenges with respect to model selection and data quality. Finally, an innovative approach using ancestral gene order reconstructions provides new perspectives on how to assess gene tree accuracy for phylogenomic analyses. By emphasising through examples the importance of using appropriate evolutionary models and assessing input data quality, these chapters alert readers to key limitations that the field as a whole strives to address. Part 3: Resolving phylogenomic conflicts Conflicting phylogenetic signals are commonplace and may derive from statistical or systematic bias. This part of the book addresses possible causes of conflict, discordance between gene trees and species trees and how processes that lead to such conflicts can be described by phylogenetic models. Furthermore, it provides an overview of various models and methods with examples in phylogenomics including their pros and cons. Outlined in detail is the multispecies coalescent model (MSC) and its applications in phylogenomics. An interesting aspect is that different phylogenetic signals leading to conflict are in fact a key source of information rather than a problem that can – and should – be used to point to events like introgression or hybridisation, highlighting possible future trends in this research area. Last but not least, this part of the book also addresses inferring species trees by concatenating single multiple sequence alignments (gene alignments) versus inferring the species tree based on ensembles of single gene trees pointing out advantages and disadvantages of both approaches. As an important take home message from these chapters, it is recommended to be flexible and identify the most appropriate approach for each dataset to be analysed since this may tremendously differ depending on the dataset, setting, taxa, and phylogenetic level addressed by the researcher. Part 4: Functional evolutionary genomics In this part of the book the focus shifts to functional considerations of phylogenomics approaches both in terms of molecular evolution and adaptation and with respect to gene expression. The utility of multi-species analysis is clearly presented in the context of annotating functional genomic elements through quantifying evolutionary constraint and protein-coding potential. An historical perspective on characterising rates of change highlights how phylogenomic datasets help to understand the modes of molecular evolution across the genome, over time, and between lineages. These are contextualised with respect to the specific aim of detecting signatures of adaptation from protein-coding DNA alignments using the example of the MutSelDP-ω∗ model. This is extended with the presentation of the generally rare case of adaptive sequence convergence, where consideration of appropriate models and knowledge of gene functions and phenotypic effects are needed. Constrained or relaxed, selection pressures on sequence or copy-number affect genomic elements in different ways, making the very concept of function difficult to pin down despite it being fundamental to relate the genome to the phenotype and organismal fitness. Here gene expression provides a measurable intermediate, for which the Expression Comparison tool from the Bgee suite allows exploration of expression patterns across multiple animal species taking into account anatomical homology. Overall, phylogenomics applications in functional evolutionary genomics build on a rich theoretical history from molecular analyses where integration with knowledge of gene functions is challenging but critical. Part 5: Phylogenomic applications Rather than attempting to review the full extent of applications linked to phylogenomics, this part of the book focuses on providing detailed specific insights into selected examples and methods concerning i) estimating divergence times, and ii) species delimitation in the era of ‘omics’ data. With respect to estimating divergence times, an exemplary overview is provided for fossil data recovered from geological records, either using fossil data as calibration points with an extant-species-inferred phylogeny, or using a fossilised birth-death process as a mechanistic model that accounts for lineage diversification. Included is a tutorial for a joint approach to infer phylogenies and estimate divergence times using the RevBayes software with various models implemented for different applications and datasets incorporating molecular and morphological data. An interesting excursion is outlined focusing on timescale estimates with respect to viral evolution introducing BEAGLE, a high-performance likelihood-calculation platform that can be used on multi-core systems. As a second major subject, species delimitation is addressed since currently the increasing amount of available genomic data enables extensive inferences, for instance about the degree of genetic isolation among species and ancient and recent introgression events. Describing the history of molecular species delimitation up to the current genomic era and presenting widely used computational methods incorporating single- and multi-locus genomic data, pros and cons are addressed. Finally, a proposal for a new method for delimiting species based on empirical criteria is outlined. In the closing chapter of this part of the book, BPP (Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo program) for analysing multi-locus sequence data under the multispecies coalescent (MSC) model with and without introgression is introduced, including a tutorial. These examples together provide accessible details on key conceptual and methodological aspects related to the application of phylogenetics in the genomic era. References Scornavacca C, Delsuc F, Galtier N (2021) Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era. https://hal.inria.fr/PGE/ | Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era | Céline Scornavacca, Frédéric Delsuc, Nicolas Galtier | <p style="text-align: justify;">Molecular phylogenetics was born in the middle of the 20th century, when the advent of protein and DNA sequencing offered a novel way to study the evolutionary relationships between living organisms. The first 50 ye... |  | Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics, Fungi, Plants, Population genomics, Vertebrates, Viruses and transposable elements | Robert Waterhouse | 2022-03-15 17:43:52 | View | |
15 Mar 2024
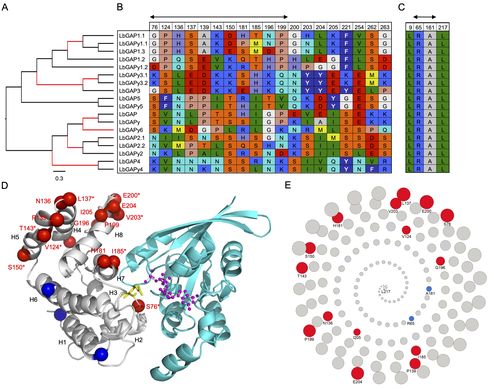
Convergent origin and accelerated evolution of vesicle-associated RhoGAP proteins in two unrelated parasitoid waspsDominique Colinet, Fanny Cavigliasso, Matthieu Leobold, Appoline Pichon, Serge Urbach, Dominique Cazes, Marine Poullet, Maya Belghazi, Anne-Nathalie Volkoff, Jean-Michel Drezen, Jean-Luc Gatti, and Marylène Poirié https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.05.543686Using transcriptomics and proteomics to understand the expansion of a secreted poisonous armoury in parasitoid wasps genomesRecommended by Ignacio Bravo based on reviews by Inacio Azevedo and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Inacio Azevedo and 2 anonymous reviewers
Parasitoid wasps lay their eggs inside another arthropod, whose body is physically consumed by the parasitoid larvae. Phylogenetic inference suggests that Parasitoida are monophyletic, and that this clade underwent a strong radiation shortly after branching off from the Apocrita stem, some 236 million years ago (Peters et al. 2017). The increase in taxonomic diversity during evolutionary radiations is usually concurrent with an increase in genetic/genomic diversity, and is often associated with an increase in phenotypic diversity. Gene (or genome) duplication provides the evolutionary potential for such increase of genomic diversity by neo/subfunctionalisation of one of the gene paralogs, and is often proposed to be related to evolutionary radiations (Ohno 1970; Francino 2005).
References
| Convergent origin and accelerated evolution of vesicle-associated RhoGAP proteins in two unrelated parasitoid wasps | Dominique Colinet, Fanny Cavigliasso, Matthieu Leobold, Appoline Pichon, Serge Urbach, Dominique Cazes, Marine Poullet, Maya Belghazi, Anne-Nathalie Volkoff, Jean-Michel Drezen, Jean-Luc Gatti, and Marylène Poirié | <p>Animal venoms and other protein-based secretions that perform a variety of functions, from predation to defense, are highly complex cocktails of bioactive compounds. Gene duplication, accompanied by modification of the expression and/or functio... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Ignacio Bravo | 2023-06-12 11:08:31 | View | |
12 Jul 2022

Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: steppingstones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert antsHugo Darras, Natalia de Souza Araujo, Lyam Baudry, Nadège Guiglielmoni, Pedro Lorite, Martial Marbouty, Fernando Rodriguez, Irina Arkhipova, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot, Serge Aron https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.07.475286A genomic resource for ants, and moreRecommended by Nadia Ponts based on reviews by Isabel Almudi and Nicolas NègreThe ant species Cataglyphis hispanica is remarkably well adapted to arid habitats of the Iberian Peninsula where two hybridogenetic lineages co-occur, i.e., queens mating with males from the other lineage produce only non-reproductive hybrid workers whereas reproductive males and females are produced by parthenogenesis (Lavanchy and Schwander, 2019). For these two reasons, the genomes of these lineages, Chis1 and Chis2, are potential gold mines to explore the genetic bases of thermal adaptation and the evolution of alternative reproductive modes. Nowadays, sequencing technology enables assembling all kinds of genomes provided genomic DNA can be extracted. More difficult to achieve is high-quality assemblies with just as high-quality annotations that are readily available to the community to be used and re-used at will (Byrne et al., 2019; Salzberg, 2019). The challenge was successfully completed by Darras and colleagues, the generated resource being fully available to the community, including scripts and command lines used to obtain the proposed results. The authors particularly describe that lineage Chis2 has 27 chromosomes, against 26 or 27 for lineage Chis1, with a Robertsonian translocation identified by chromosome conformation capture (Duan et al., 2010, 2012) in the two Queens sequenced. Transcript-supported gene annotation provided 11,290 high-quality gene models. In addition, an ant-tailored annotation pipeline identified 56 different families of repetitive elements in both Chis1 and Chis2 lineages of C. hispanica spread in a little over 15 % of the genome. Altogether, the genomes of Chis1 and Chis2 are highly similar and syntenic, with some level of polymorphism raising questions about their evolutionary story timeline. In particular, the uniform distribution of polymorphisms along the genomes shakes up a previous hypothesis of hybridogenetic lineage pairs determined by ancient non-recombining regions (Linksvayer, Busch and Smith, 2013). I recommend this paper because the science behind is both solid and well-explained. The provided resource is of high quality, and accompanied by a critical exploration of the perspectives brought by the results. These genomes are excellent resources to now go further in exploring the possible events at the genome level that accompanied the remarkable thermal adaptation of the ants Cataglyphis, as well as insights into the genetics of hybridogenetic lineages. Beyond the scientific value of the resources and insights provided by the work performed, I also recommend this article because it is an excellent example of Open Science (Allen and Mehler, 2019; Sarabipour et al., 2019), all data methods and tools being fully and easily accessible to whoever wants/needs it. References Allen C, Mehler DMA (2019) Open science challenges, benefits and tips in early career and beyond. PLOS Biology, 17, e3000246. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000246 Byrne A, Cole C, Volden R, Vollmers C (2019) Realizing the potential of full-length transcriptome sequencing. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 374, 20190097. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2019.0097 Darras H, de Souza Araujo N, Baudry L, Guiglielmoni N, Lorite P, Marbouty M, Rodriguez F, Arkhipova I, Koszul R, Flot J-F, Aron S (2022) Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: stepping stones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert ants. bioRxiv, 2022.01.07.475286, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.07.475286 Duan Z, Andronescu M, Schutz K, Lee C, Shendure J, Fields S, Noble WS, Anthony Blau C (2012) A genome-wide 3C-method for characterizing the three-dimensional architectures of genomes. Methods, 58, 277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.06.018 Duan Z, Andronescu M, Schutz K, McIlwain S, Kim YJ, Lee C, Shendure J, Fields S, Blau CA, Noble WS (2010) A three-dimensional model of the yeast genome. Nature, 465, 363–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08973 Lavanchy G, Schwander T (2019) Hybridogenesis. Current Biology, 29, R9–R11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.11.046 Linksvayer TA, Busch JW, Smith CR (2013) Social supergenes of superorganisms: Do supergenes play important roles in social evolution? BioEssays, 35, 683–689. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201300038 Salzberg SL (2019) Next-generation genome annotation: we still struggle to get it right. Genome Biology, 20, 92. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1715-2 Sarabipour S, Debat HJ, Emmott E, Burgess SJ, Schwessinger B, Hensel Z (2019) On the value of preprints: An early career researcher perspective. PLOS Biology, 17, e3000151. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000151 | Chromosome-level genome assembly and annotation of two lineages of the ant Cataglyphis hispanica: steppingstones towards genomic studies of hybridogenesis and thermal adaptation in desert ants | Hugo Darras, Natalia de Souza Araujo, Lyam Baudry, Nadège Guiglielmoni, Pedro Lorite, Martial Marbouty, Fernando Rodriguez, Irina Arkhipova, Romain Koszul, Jean-François Flot, Serge Aron | <p style="text-align: justify;"><em>Cataglyphis</em> are thermophilic ants that forage during the day when temperatures are highest and sometimes close to their critical thermal limit. Several Cataglyphis species have evolved unusual reproductive ... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Nadia Ponts | Nicolas Nègre, Isabel Almudi | 2022-01-13 16:47:30 | View |
26 Jun 2024
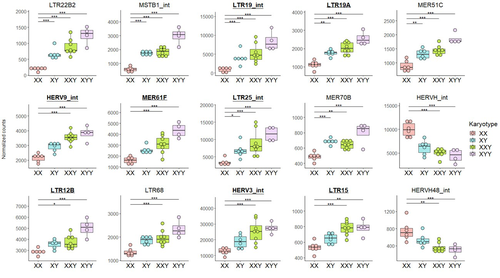
Transposable element expression with variation in sex chromosome number supports a toxic Y effect on human longevityJordan Teoli, Miriam Merenciano, Marie Fablet, Anamaria Necsulea, Daniel Siqueira-de-Oliveira, Alessandro Brandulas-Cammarata, Audrey Labalme, Hervé Lejeune, Jean-François Lemaitre, François Gueyffier, Damien Sanlaville, Claire Bardel, Cristina Vieira, Gabriel AB Marais, Ingrid Plotton https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.03.550779The number of Y chromosomes is positively associated with transposable element expression in humans, in line with the toxic Y hypothesisRecommended by Anna-Sophie Fiston-Lavier based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers
The study of human longevity has long been a source of fascination for scientists, particularly in relation to the genetic factors that contribute to differences in lifespan between the sexes. One particularly intriguing area of research concerns the Y chromosome and its impact on male longevity. The Y chromosome expresses genes that are essential for male development and reproduction. However, it may also influence various physiological processes and health outcomes. It is therefore of great importance to investigate the impact of the Y chromosome on longevity. This may assist in elucidating the biological mechanisms underlying sex-specific differences in aging and disease susceptibility. As longevity research progresses, the Y chromosome's role presents a promising avenue for elucidating the complex interplay between genetics and aging. Transposable elements (TEs), often referred to as "jumping genes", are DNA sequences that can move within the genome, potentially causing mutations and genomic instability. In young, healthy cells, various mechanisms, including DNA methylation and histone modifications, suppress TE activity to maintain genomic integrity. However, as individuals age, these regulatory mechanisms may deteriorate, leading to increased TE activity. This dysregulation could contribute to age-related genomic instability, cellular dysfunction, and the onset of diseases such as cancer. Understanding how TE repression changes with age is crucial for uncovering the molecular underpinnings of aging (De Cecco et al. 2013; Van Meter et al. 2014). The lower recombination rates observed on Y chromosomes result in the accumulation of TE insertions, which in turn leads to an enrichment of TEs and potentially higher TE activity. To ascertain whether the number of Y chromosomes is associated with TE activity in humans, Teoli et al. (2024) studied the TE expression level, as a proxy of the TE activity, in several karyotype compositions (i.e. with differing numbers of Y chromosomes). They used transcriptomic data from blood samples collected in 24 individuals (six females 46,XX, six males 46,XY, eight males 47,XXY and four males 47,XYY). Even though they did not observe a significant correlation between the number of Y chromosomes and TE expression, their results suggest an impact of the presence of the Y chromosome on the overall TE expression. The presence of Y chromosomes also affected the type (family) of TE present/expressed. To ensure that the TE expression level was not biased by the expression of a gene in proximity due to intron retention or pervasive intragenic transcription, the authors also tested whether the TE expression variation observed between the different karyotypes could be explained by gene (i.e. here non-TE gene) expression. As TE repression mechanisms are known to decrease over time, the authors also tested whether TE repression is weaker in older individuals, which would support a compelling link between genomic stability and aging. They investigated the TE expression differently between males and females, hypothesizing that old males should exhibit a stronger TE activity than old females. Using selected 45 males (47,XY) and 35 females (46,XX) blood samples of various ages (from 20 to 70) from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project, the authors studied the effect of age on TE expression using 10-year range to group the study subjects. Based on these data, they fail to find an overall increase of TE expression in old males compared to old females. Notwithstanding the small number of samples, the study is well-designed and innovative, and its findings are highly promising. It marks an initial step towards understanding the impact of Y-chromosome ‘toxicity’ on human longevity. Despite the relatively small sample size, which is a consequence of the difficulty of obtaining samples from individuals with sex chromosome aneuploidies, the results are highly intriguing and will be of interest to a broad range of biologists.
References De Cecco M, Criscione SW, Peckham EJ, Hillenmeyer S, Hamm EA, Manivannan J, Peterson AL, Kreiling JA, Neretti N, Sedivy JM (2013) Genomes of replicatively senescent cells undergo global epigenetic changes leading to gene silencing and activation of transposable elements. Aging Cell, 12, 247–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12047 Teoli J, Merenciano M, Fablet M, Necsulea A, Siqueira-de-Oliveira D, Brandulas-Cammarata A, Labalme A, Lejeune H, Lemaitre J-F, Gueyffier F, Sanlaville D, Bardel C, Vieira C, Marais GAB, Plotton I (2024) Transposable element expression with variation in sex chromosome number supports a toxic Y effect on human longevity. bioRxiv, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.03.550779 Van Meter M, Kashyap M, Rezazadeh S, Geneva AJ, Morello TD, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V (2014) SIRT6 represses LINE1 retrotransposons by ribosylating KAP1 but this repression fails with stress and age. Nature Communications, 5, 5011. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6011
| Transposable element expression with variation in sex chromosome number supports a toxic Y effect on human longevity | Jordan Teoli, Miriam Merenciano, Marie Fablet, Anamaria Necsulea, Daniel Siqueira-de-Oliveira, Alessandro Brandulas-Cammarata, Audrey Labalme, Hervé Lejeune, Jean-François Lemaitre, François Gueyffier, Damien Sanlaville, Claire Bardel, Cristina Vi... | <p>Why women live longer than men is still an open question in human biology. Sex chromosomes have been proposed to play a role in the observed sex gap in longevity, and the Y male chromosome has been suspected of having a potential toxic genomic ... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Anna-Sophie Fiston-Lavier | Anonymous, Igor Rogozin , Paul Jay , Anonymous | 2023-08-18 15:01:38 | View |
14 Sep 2023
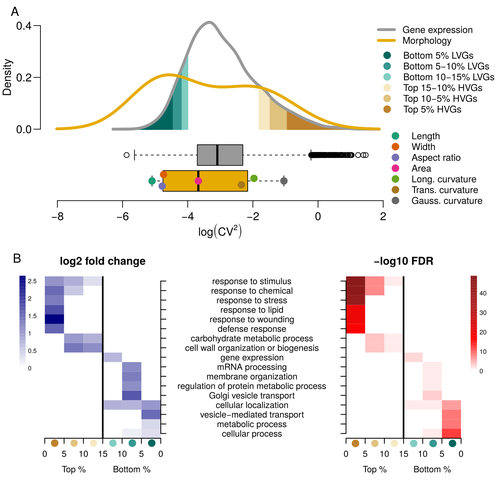
Expression of cell-wall related genes is highly variable and correlates with sepal morphologyDiego A. Hartasánchez, Annamaria Kiss, Virginie Battu, Charline Soraru, Abigail Delgado-Vaquera, Florian Massinon, Marina Brasó-Vives, Corentin Mollier, Marie-Laure Martin-Magniette, Arezki Boudaoud, Françoise Monéger https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.26.489498The same but different: How small scale hidden variations can have large effectsRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by Sandra Corjito and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Sandra Corjito and 1 anonymous reviewer
For ages, we considered only single genes, or just a few, in order to understand the relationship between phenotype and genotype in response to environmental challenges. Recently, the use of meaningful groups of genes, e.g. gene regulatory networks, or modules of co-expression, allowed scientists to have a larger view of gene regulation. However, all these findings were based on contrasted genotypes, e.g. between wild-types and mutants, as the implicit assumption often made is that there is little transcriptomic variability within the same genotype context. Hartasànchez and collaborators (2023) decided to challenge both views: they used a single genotype instead of two, the famous A. thaliana Col0, and numerous plants, and considered whole gene networks related to sepal morphology and its variations. They used a clever approach, combining high-level phenotyping and gene expression to better understand phenomena and regulations underlying sepal morphologies. Using multiple controls, they showed that basic variations in the expression of genes related to the cell wall regulation, as well as the ones involved in chloroplast metabolism, influenced the global transcriptomic pattern observed in sepal while being in near-identical genetic background and controlling for all other experimental conditions. The paper of Hartasànchez et al. is thus a tremendous call for humility in biology, as we saw in their work that we just understand the gross machinery. However, the Devil is in the details: understanding those very small variations that may have a large influence on phenotypes, and thus on local adaptation to environmental challenges, is of great importance in these times of climatic changes. References Hartasánchez DA, Kiss A, Battu V, Soraru C, Delgado-Vaquera A, Massinon F, Brasó-Vives M, Mollier C, Martin-Magniette M-L, Boudaoud A, Monéger F. 2023. Expression of cell-wall related genes is highly variable and correlates with sepal morphology. bioRxiv, ver. 4, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.26.489498 | Expression of cell-wall related genes is highly variable and correlates with sepal morphology | Diego A. Hartasánchez, Annamaria Kiss, Virginie Battu, Charline Soraru, Abigail Delgado-Vaquera, Florian Massinon, Marina Brasó-Vives, Corentin Mollier, Marie-Laure Martin-Magniette, Arezki Boudaoud, Françoise Monéger | <p style="text-align: justify;">Control of organ morphology is a fundamental feature of living organisms. There is, however, observable variation in organ size and shape within a given genotype. Taking the sepal of Arabidopsis as a model, we inves... |  | Bioinformatics, Epigenomics, Plants | Francois Sabot | 2023-03-14 19:10:15 | View | |
15 Dec 2022

Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAsAdeline Simon, Alex Mercier, Pierre Gladieux, Benoit Poinssot, Anne-Sophie Walker, Muriel Viaud https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.07.483234Exploring genomic determinants of host specialization in Botrytis cinereaRecommended by Sebastien Duplessis based on reviews by Cecile Lorrain and Thorsten LangnerThe genomics era has pushed forward our understanding of fungal biology. Much progress has been made in unraveling new gene functions and pathways, as well as the evolution or adaptation of fungi to their hosts or environments through population studies (Hartmann et al. 2019; Gladieux et al. 2018). Closing gaps more systematically in draft genomes using the most recent long-read technologies now seems the new standard, even with fungal species presenting complex genome structures (e.g. large and highly repetitive dikaryotic genomes; Duan et al. 2022). Understanding the genomic dynamics underlying host specialization in phytopathogenic fungi is of utmost importance as it may open new avenues to combat diseases. A strong host specialization is commonly observed for biotrophic and hemi-biotrophic fungal species or for necrotrophic fungi with a narrow host range, whereas necrotrophic fungi with broad host range are considered generalists (Liang and Rollins, 2018; Newman and Derbyshire, 2020). However, some degrees of specialization towards given hosts have been reported in generalist fungi and the underlying mechanisms remain to be determined. Botrytis cinerea is a polyphagous necrotrophic phytopathogen with a particularly wide host range and it is notably responsible for grey mould disease on many fruits, such as tomato and grapevine. Because of its importance as a plant pathogen, its relatively small genome size and its taxonomical position, it has been targeted for early genome sequencing and a first reference genome was provided in 2011 (Amselem et al. 2011). Other genomes were subsequently sequenced for other strains, and most importantly a gapless assembled version of the initial reference genome B05.10 was provided to the community (van Kan et al. 2017). This genomic resource has supported advances in various aspects of the biology of B. cinerea such as the production of specialized metabolites, which plays an important role in host-plant colonization, or more recently in the production of small RNAs which interfere with the host immune system, representing a new class of non-proteinaceous virulence effectors (Dalmais et al. 2011; Weiberg et al. 2013). In the present study, Simon et al. (2022) use PacBio long-read sequencing for Sl3 and Vv3 strains, which represent genetic clusters in B. cinerea populations found on tomato and grapevine. The authors combined these complete and high-quality genome assemblies with the B05.10 reference genome and population sequencing data to perform a comparative genomic analysis of specialization towards the two host plants. Transposable elements generate genomic diversity due to their mobile and repetitive nature and they are of utmost importance in the evolution of fungi as they deeply reshape the genomic landscape (Lorrain et al. 2021). Accessory chromosomes are also known drivers of adaptation in fungi (Möller and Stukenbrock, 2017). Here, the authors identify several genomic features such as the presence of different sets of accessory chromosomes, the presence of differentiated repertoires of transposable elements, as well as related small RNAs in the tomato and grapevine populations, all of which may be involved in host specialization. Whereas core chromosomes are highly syntenic between strains, an accessory chromosome validated by pulse-field electrophoresis is specific of the strains isolated from grapevine. Particularly, they show that two particular retrotransposons are discriminant between the strains and that they allow the production of small RNAs that may act as effectors. The discriminant accessory chromosome of the Vv3 strain harbors one of the unraveled retrotransposons as well as new genes of yet unidentified function. I recommend this article because it perfectly illustrates how efforts put into generating reference genomic sequences of higher quality can lead to new discoveries and allow to build strong hypotheses about biology and evolution in fungi. Also, the study combines an up-to-date genomics approach with a classical methodology such as pulse-field electrophoresis to validate the presence of accessory chromosomes. A major input of this investigation of the genomic determinants of B. cinerea is that it provides solid hints for further analysis of host-specialization at the population level in a broad-scale phytopathogenic fungus. References Amselem J, Cuomo CA, Kan JAL van, Viaud M, Benito EP, Couloux A, Coutinho PM, Vries RP de, Dyer PS, Fillinger S, Fournier E, Gout L, Hahn M, Kohn L, Lapalu N, Plummer KM, Pradier J-M, Quévillon E, Sharon A, Simon A, Have A ten, Tudzynski B, Tudzynski P, Wincker P, Andrew M, Anthouard V, Beever RE, Beffa R, Benoit I, Bouzid O, Brault B, Chen Z, Choquer M, Collémare J, Cotton P, Danchin EG, Silva CD, Gautier A, Giraud C, Giraud T, Gonzalez C, Grossetete S, Güldener U, Henrissat B, Howlett BJ, Kodira C, Kretschmer M, Lappartient A, Leroch M, Levis C, Mauceli E, Neuvéglise C, Oeser B, Pearson M, Poulain J, Poussereau N, Quesneville H, Rascle C, Schumacher J, Ségurens B, Sexton A, Silva E, Sirven C, Soanes DM, Talbot NJ, Templeton M, Yandava C, Yarden O, Zeng Q, Rollins JA, Lebrun M-H, Dickman M (2011) Genomic Analysis of the Necrotrophic Fungal Pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLOS Genetics, 7, e1002230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002230 Dalmais B, Schumacher J, Moraga J, Le Pêcheur P, Tudzynski B, Collado IG, Viaud M (2011) The Botrytis cinerea phytotoxin botcinic acid requires two polyketide synthases for production and has a redundant role in virulence with botrydial. Molecular Plant Pathology, 12, 564–579. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00692.x Duan H, Jones AW, Hewitt T, Mackenzie A, Hu Y, Sharp A, Lewis D, Mago R, Upadhyaya NM, Rathjen JP, Stone EA, Schwessinger B, Figueroa M, Dodds PN, Periyannan S, Sperschneider J (2022) Physical separation of haplotypes in dikaryons allows benchmarking of phasing accuracy in Nanopore and HiFi assemblies with Hi-C data. Genome Biology, 23, 84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-022-02658-2 Gladieux P, Condon B, Ravel S, Soanes D, Maciel JLN, Nhani A, Chen L, Terauchi R, Lebrun M-H, Tharreau D, Mitchell T, Pedley KF, Valent B, Talbot NJ, Farman M, Fournier E (2018) Gene Flow between Divergent Cereal- and Grass-Specific Lineages of the Rice Blast Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. mBio, 9, e01219-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01219-17 Hartmann FE, Rodríguez de la Vega RC, Carpentier F, Gladieux P, Cornille A, Hood ME, Giraud T (2019) Understanding Adaptation, Coevolution, Host Specialization, and Mating System in Castrating Anther-Smut Fungi by Combining Population and Comparative Genomics. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 57, 431–457. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082718-095947 Liang X, Rollins JA (2018) Mechanisms of Broad Host Range Necrotrophic Pathogenesis in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathology®, 108, 1128–1140. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-06-18-0197-RVW Lorrain C, Oggenfuss U, Croll D, Duplessis S, Stukenbrock E (2021) Transposable Elements in Fungi: Coevolution With the Host Genome Shapes, Genome Architecture, Plasticity and Adaptation. In: Encyclopedia of Mycology (eds Zaragoza Ó, Casadevall A), pp. 142–155. Elsevier, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819990-9.00042-1 Möller M, Stukenbrock EH (2017) Evolution and genome architecture in fungal plant pathogens. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 15, 756–771. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.76 Newman TE, Derbyshire MC (2020) The Evolutionary and Molecular Features of Broad Host-Range Necrotrophy in Plant Pathogenic Fungi. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.591733 Simon A, Mercier A, Gladieux P, Poinssot B, Walker A-S, Viaud M (2022) Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAs. bioRxiv, 2022.03.07.483234, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.07.483234 Van Kan JAL, Stassen JHM, Mosbach A, Van Der Lee TAJ, Faino L, Farmer AD, Papasotiriou DG, Zhou S, Seidl MF, Cottam E, Edel D, Hahn M, Schwartz DC, Dietrich RA, Widdison S, Scalliet G (2017) A gapless genome sequence of the fungus Botrytis cinerea. Molecular Plant Pathology, 18, 75–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12384 Weiberg A, Wang M, Lin F-M, Zhao H, Zhang Z, Kaloshian I, Huang H-D, Jin H (2013) Fungal Small RNAs Suppress Plant Immunity by Hijacking Host RNA Interference Pathways. Science, 342, 118–123. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1239705 | Botrytis cinerea strains infecting grapevine and tomato display contrasted repertoires of accessory chromosomes, transposons and small RNAs | Adeline Simon, Alex Mercier, Pierre Gladieux, Benoit Poinssot, Anne-Sophie Walker, Muriel Viaud | <p style="text-align: justify;">The fungus <em>Botrytis cinerea</em> is a polyphagous pathogen that encompasses multiple host-specialized lineages. While several secreted proteins, secondary metabolites and retrotransposons-derived small RNAs have... |  | Fungi, Structural genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Sebastien Duplessis | Cecile Lorrain, Thorsten Langner | 2022-03-15 11:15:48 | View |
13 Jul 2022
Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structuresColin Clairet, Nicolas Lapalu, Adeline Simon, Jessica L. Soyer, Muriel Viaud, Enric Zehraoui, Berengere Dalmais, Isabelle Fudal, Nadia Ponts https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.16.439968Genome-wide chromatin and expression datasets of various pathogenic ascomycetesRecommended by Sébastien Bloyer and Romain Koszul based on reviews by Ricardo C. Rodríguez de la Vega and 1 anonymous reviewerPlant pathogenic fungi represent serious economic threats. These organisms are rapidly adaptable, with plastic genomes containing many variable regions and evolving rapidly. It is, therefore, useful to characterize their genetic regulation in order to improve their control. One of the steps to do this is to obtain omics data that link their DNA structure and gene expression. Clairet C, Lapalu N, Simon A, Soyer JL, Viaud M, Zehraoui E, Dalmais B, Fudal I, Ponts N (2022) Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structures. bioRxiv, 2021.04.16.439968, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.04.16.439968 | Nucleosome patterns in four plant pathogenic fungi with contrasted genome structures | Colin Clairet, Nicolas Lapalu, Adeline Simon, Jessica L. Soyer, Muriel Viaud, Enric Zehraoui, Berengere Dalmais, Isabelle Fudal, Nadia Ponts | <p style="text-align: justify;">Fungal pathogens represent a serious threat towards agriculture, health, and environment. Control of fungal diseases on crops necessitates a global understanding of fungal pathogenicity determinants and their expres... |  | Epigenomics, Fungi | Sébastien Bloyer | 2021-04-17 10:32:41 | View | |
18 Feb 2021
Traces of transposable element in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networksAgnes Baud, Mariene Wan, Danielle Nouaud, Nicolas Francillonne, Dominique Anxolabehere, Hadi Quesneville https://doi.org/10.1101/547877Using small fragments to discover old TE remnants: the Duster approach empowers the TE detectionRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by Josep Casacuberta and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Josep Casacuberta and 1 anonymous reviewer
Transposable elements are the raw material of the dark matter of the genome, the foundation of the next generation of genes and regulation networks". This sentence could be the essence of the paper of Baud et al. (2021). Transposable elements (TEs) are endogenous mobile genetic elements found in almost all genomes, which were discovered in 1948 by Barbara McClintock (awarded in 1983 the only unshared Medicine Nobel Prize so far). TEs are present everywhere, from a single isolated copy for some elements to more than millions for others, such as Alu. They are founders of major gene lineages (HET-A, TART and telomerases, RAG1/RAG2 proteins from mammals immune system; Diwash et al, 2017), and even of retroviruses (Xiong & Eickbush, 1988). However, most TEs appear as selfish elements that replicate, land in a new genomic region, then start to decay and finally disappear in the midst of the genome, turning into genomic ‘dark matter’ (Vitte et al, 2007). The mutations (single point, deletion, recombination, and so on) that occur during this slow death erase some of their most notable features and signature sequences, rendering them completely unrecognizable after a few million years. Numerous TE detection tools have tried to optimize their detection (Goerner-Potvin & Bourque, 2018), but further improvement is definitely challenging. This is what Baud et al. (2021) accomplished in their paper. They used a simple, elegant and efficient k-mer based approach to find small signatures that, when accumulated, allow identifying very old TEs. Using this method, called Duster, they improved the amount of annotated TEs in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana by 20%, pushing the part of this genome occupied by TEs up from 40 to almost 50%. They further observed that these very old Duster-specific TEs (i.e., TEs that are only detected by Duster) are, among other properties, close to genes (much more than recent TEs), not targeted by small RNA pathways, and highly associated with conserved regions across the rosid family. In addition, they are highly associated with flowering or stress response genes, and may be involved through exaptation in the evolution of responses to environmental changes. TEs are not just selfish elements: more and more studies have shown their key role in the evolution of their hosts, and tools such as Duster will help us better understand their impact. References Baud, A., Wan, M., Nouaud, D., Francillonne, N., Anxolabéhère, D. and Quesneville, H. (2021). Traces of transposable elements in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networks. bioRxiv, 547877, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics.doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/547877 | Traces of transposable element in genome dark matter co-opted by flowering gene regulation networks | Agnes Baud, Mariene Wan, Danielle Nouaud, Nicolas Francillonne, Dominique Anxolabehere, Hadi Quesneville | <p>Transposable elements (TEs) are mobile, repetitive DNA sequences that make the largest contribution to genome bulk. They thus contribute to the so-called 'dark matter of the genome', the part of the genome in which nothing is immediately recogn... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics, Plants, Structural genomics, Viruses and transposable elements | Francois Sabot | Anonymous, Josep Casacuberta | 2020-04-07 17:12:12 | View |
23 Sep 2022
MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studiesRosa Fernandez, Vanina Tonzo, Carolina Simon Guerrero, Jesus Lozano-Fernandez, Gemma I Martinez-Redondo, Pau Balart-Garcia, Leandro Aristide, Klara Eleftheriadi, Carlos Vargas-Chavez https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500182MATEdb: a new phylogenomic-driven database for MetazoaRecommended by Samuel Abalde based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The development (and standardization) of high-throughput sequencing techniques has revolutionized evolutionary biology, to the point that we almost see as normal fine-detail studies of genome architecture evolution (Robert et al., 2022), adaptation to new habitats (Rahi et al., 2019), or the development of key evolutionary novelties (Hilgers et al., 2018), to name three examples. One of the fields that has benefited the most is phylogenomics, i.e. the use of genome-wide data for inferring the evolutionary relationships among organisms. Dealing with such amount of data, however, has come with important analytical and computational challenges. Likewise, although the steady generation of genomic data from virtually any organism opens exciting opportunities for comparative analyses, it also creates a sort of “information fog”, where it is hard to find the most appropriate and/or the higher quality data. I have personally experienced this not so long ago, when I had to spend several weeks selecting the most complete transcriptomes from several phyla, moving back and forth between the NCBI SRA repository and the relevant literature. In an attempt to deal with this issue, some research labs have committed their time and resources to the generation of taxa- and topic-specific databases (Lathe et al., 2008), such as MolluscDB (Liu et al., 2021), focused on mollusk genomics, or EukProt (Richter et al., 2022), a protein repository representing the diversity of eukaryotes. A new database that promises to become an important resource in the near future is MATEdb (Fernández et al., 2022), a repository of high-quality genomic data from Metazoa. MATEdb has been developed from publicly available and newly generated transcriptomes and genomes, prioritizing quality over quantity. Upon download, the user has access to both raw data and the related datasets: assemblies, several quality metrics, the set of inferred protein-coding genes, and their annotation. Although it is clear to me that this repository has been created with phylogenomic analyses in mind, I see how it could be generalized to other related problems such as analyses of gene content or evolution of specific gene families. In my opinion, the main strengths of MATEdb are threefold:
On a negative note, I see two main drawbacks. First, as of today (September 16th, 2022) this database is in an early stage and it still needs to incorporate a lot of animal groups. This has been discussed during the revision process and the authors are already working on it, so it is only a matter of time until all major taxa are represented. Second, there is a scalability issue. In its current format it is not possible to select the taxa of interest and the full database has to be downloaded, which will become more and more difficult as it grows. Nonetheless, with the appropriate resources it would be easy to find a better solution. There are plenty of examples that could serve as inspiration, so I hope this does not become a big problem in the future. Altogether, I and the researchers that participated in the revision process believe that MATEdb has the potential to become an important and valuable addition to the metazoan phylogenomics community. Personally, I wish it was available just a few months ago, it would have saved me so much time. References Fernández R, Tonzo V, Guerrero CS, Lozano-Fernandez J, Martínez-Redondo GI, Balart-García P, Aristide L, Eleftheriadi K, Vargas-Chávez C (2022) MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studies. bioRxiv, 2022.07.18.500182, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500182 Hilgers L, Hartmann S, Hofreiter M, von Rintelen T (2018) Novel Genes, Ancient Genes, and Gene Co-Option Contributed to the Genetic Basis of the Radula, a Molluscan Innovation. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1638–1652. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy052 Lathe W, Williams J, Mangan M, Karolchik, D (2008). Genomic data resources: challenges and promises. Nature Education, 1(3), 2. Liu F, Li Y, Yu H, Zhang L, Hu J, Bao Z, Wang S (2021) MolluscDB: an integrated functional and evolutionary genomics database for the hyper-diverse animal phylum Mollusca. Nucleic Acids Research, 49, D988–D997. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa918 Rahi ML, Mather PB, Ezaz T, Hurwood DA (2019) The Molecular Basis of Freshwater Adaptation in Prawns: Insights from Comparative Transcriptomics of Three Macrobrachium Species. Genome Biology and Evolution, 11, 1002–1018. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evz045 Richter DJ, Berney C, Strassert JFH, Poh Y-P, Herman EK, Muñoz-Gómez SA, Wideman JG, Burki F, Vargas C de (2022) EukProt: A database of genome-scale predicted proteins across the diversity of eukaryotes. bioRxiv, 2020.06.30.180687, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.30.180687 Robert NSM, Sarigol F, Zimmermann B, Meyer A, Voolstra CR, Simakov O (2022) Emergence of distinct syntenic density regimes is associated with early metazoan genomic transitions. BMC Genomics, 23, 143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08304-2 | MATEdb, a data repository of high-quality metazoan transcriptome assemblies to accelerate phylogenomic studies | Rosa Fernandez, Vanina Tonzo, Carolina Simon Guerrero, Jesus Lozano-Fernandez, Gemma I Martinez-Redondo, Pau Balart-Garcia, Leandro Aristide, Klara Eleftheriadi, Carlos Vargas-Chavez | <p style="text-align: justify;">With the advent of high throughput sequencing, the amount of genomic data available for animals (Metazoa) species has bloomed over the last decade, especially from transcriptomes due to lower sequencing costs and ea... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics | Samuel Abalde | 2022-07-20 07:30:39 | View | |
22 May 2023

Genetic bases of resistance to the rice hoja blanca disease deciphered by a QTL approachAlexander Silva, Maria Elker Montoya, Constanza Quintero, Juan Cuasquer, Joe Tohme, Eduardo Graterol, Maribel Cruz, Mathias Lorieux https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.07.515427Scoring symptoms of a plant viral diseaseRecommended by Olivier Panaud based on reviews by Grégoire Aubert and Valérie GeffroyThe paper from Silva et al. (2023) provides new insights into the genetic bases of natural resistance of rice to the Rice Hoja Blanca (RHB) disease, one of its most serious diseases in tropical countries of the American continent and the Caribbean. This disease is caused by the Rice Hoja Blanca Virus, or RHBV, the vector of which is the planthopper insect Tagosodes orizicolus Müir. It is responsible for serious damage to the rice crop (Morales and Jennings 2010). The authors take a Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) detection approach to find genomic regions statistically associated with the resistant phenotype. To this aim, they use four resistant x susceptible crosses (the susceptible parent being the same in all four crosses) to maximize the chances to find new QTLs. The F2 populations derived from the crosses are genotyped using Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) extracted from whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data of the resistant parents, and the F3 families derived from the F2 individuals are scored for disease symptoms. For this, they use a computer-aided image analysis protocol that they designed so they can estimate the severity of the damages in the plant. They find several new QTLs, some being apparently more associated with disease severity, others with disease incidence. They also find that a previously identified QTL of Oryza sativa ssp. japonica origin is also present in the indica cluster (Romero et al. 2014). Finally, they discuss the candidate genes that could underlie the QTLs and provide a simple model for resistance. It has to be noted that scoring symptoms of a viral disease such as RHB is very challenging. It requires maintaining populations of viruliferous insect vectors, mastering times and conditions for infestation by nymphs, and precise symptom scoring. It also requires the preparation of segregating populations, their genotyping with enough genetic markers, and mastering QTL detection methods. All these aspects are present in this work. In particular, the phenotyping of symptom severity implemented using computer-aided image processing represents an impressive, enormous amount of work. From the genomics side, the fine-scale genotyping is based on the WGS of the parental lines (resistant and susceptible), followed by the application of suitable bioinformatic tools for SNP extraction and primers prediction that can be used on their Fluidigm platform. It also required implementing data correction algorithms to achieve precise genetic maps in the four crosses. The QTL detection itself required careful statistical pre-processing of phenotypic data. The authors then used a combination of several QTL detection methods, including an original meta-QTL method they developed in the software MapDisto. The authors then perform a very complete and convincing analysis of candidate genes, which includes genes already identified for a similar disease (RSV) on chromosome 11 of rice. What remains to elucidate is whether the candidate genes are actually involved or not in the disease resistance process. The team has already started implementing gene knockout strategies to study some of them in more detail. It will be interesting to see whether those genes act against the virus itself, or against the insect vector. Overall the work is of high quality and represents an important advance in the knowledge of disease resistance. In addition, it has many implications for crop breeding, allowing the setup of large-scale, marker-assisted strategies, for new resistant elite varieties of rice. References Morales F and Jennings P (2010) Rice hoja blanca: a complex plant-virus-vector pathosystem. CAB Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1079/PAVSNNR20105043 Romero LE, Lozano I, Garavito A, et al (2014) Major QTLs control resistance to Rice hoja blanca virus and its vector Tagosodes orizicolus. G3 | Genes, Genomes, Genetics 4:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.113.009373 Silva A, Montoya ME, Quintero C, Cuasquer J, Tohme J, Graterol E, Cruz M, Lorieux M (2023) Genetic bases of resistance to the rice hoja blanca disease deciphered by a QTL approach. bioRxiv, 2022.11.07.515427, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.07.515427 | Genetic bases of resistance to the rice hoja blanca disease deciphered by a QTL approach | Alexander Silva, Maria Elker Montoya, Constanza Quintero, Juan Cuasquer, Joe Tohme, Eduardo Graterol, Maribel Cruz, Mathias Lorieux | <p style="text-align: justify;">Rice hoja blanca (RHB) is one of the most serious diseases in rice growing areas in tropical Americas. Its causal agent is Rice hoja blanca virus (RHBV), transmitted by the planthopper <em>Tagosodes orizicolus </em>... |  | Functional genomics, Plants | Olivier Panaud | 2022-11-09 09:13:30 | View |










