Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * ▲ | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
01 Jul 2024
Contextualising samples: Supporting reference genomes of European biodiversity through sample and associated metadata collectionAstrid Böhne, Rosa Fernández, Jennifer A. Leonard, Ann M. McCartney, Seanna McTaggart, José Melo-Ferreira, Rita Monteiro, Rebekah A. Oomen, Olga Vinnere Pettersson, Torsten H. Struck https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.28.546652To avoid biases and to be FAIR, we need to CARE and share biodiversity metadataRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by Julian Osuji and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Julian Osuji and 1 anonymous reviewer
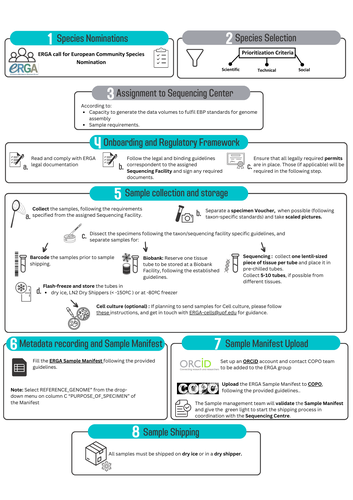
Böhne et al. (2024) do not present a classical scientific paper per se but a report on how the European Reference Genome Atlas (ERGA) aims to deal with sampling and sample information, i.e. metadata. As the goal of ERGA is to provide an almost fully representative set of reference genomes representative of European biodiversity to serve many research areas in biology, they have to be really exhaustive. In this regard, in addition to providing sample metadata recording guidelines, they also discuss the biases existing in sampling and sequencing projects. The first task for such a project is to be sure that the data they generate will be usable and available in the future (“[in] perpetuity", Böhne et al. 2024). The authors deployed a very efficient pipeline for conserving information on sampling: location, physical information, copies of tissues and of DNA, shipping, legal/ethical aspects regarding the Nagoya Protocol, etc., alongside a best-practice manual. This effort is linked to practical guides for the DNA extraction of specific taxa. More generally, these details enable “Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable” (FAIR) principles (Wilkinson et al. 2016) to be followed. An important aspect of this paper, in addition to practical points, is the reflection upon the different biases inherent to the choice of sequenced samples. Acknowledging their own biases with regards to DNA extraction protocol efficiency, small genome size choice, as well as the availability of material (Nagoya Protocol aspects) and material transfer efficiency, the authors recommend in the future to not survey biodiversity by selecting one’s favorite samples or species, but also considering "orphan" taxa. Some of these "orphan" taxonomic groups belong to non-arthropod invertebrates but internal disparities are also prominent within other taxa. Finally, the implementation of the "Collective benefit, Authority to control, Responsibility, and Ethics" (CARE) principles (Carroll et al. 2021) will allow Indigenous rights to be considered when prioritizing samples, and to enable their "knowledge systems to permeate throughout the process of reference genome production and beyond" (Böhne et al. 2024). Last, but not least, as ERGA, including its Sampling and Sample Processing committee, is a large collective effort, it is very refreshing to read a paper starting with the acknowledgements and the roles of each member.
References Böhne A, Fernández R, Leonard JA, McCartney AM, McTaggart S, Melo-Ferreira J, Monteiro R, Oomen RA, Pettersson OV, Struck TH (2024) Contextualising samples: Supporting reference genomes of European biodiversity through sample and associated metadata collection. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.28.546652 Carroll SR, Herczog E, Hudson M, Russell K, Stall S (2021) Operationalizing the CARE and FAIR Principles for Indigenous data futures. Scientific Data, 8, 108. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-021-00892-0 Wilkinson MD, Dumontier M, Aalbersberg IjJ, Appleton G, Axton M, Baak A, Blomberg N, Boiten J-W, da Silva Santos LB, Bourne PE, Bouwman J, Brookes AJ, Clark T, Crosas M, Dillo I, Dumon O, Edmunds S, Evelo CT, Finkers R, Gonzalez-Beltran A, Gray AJG, Groth P, Goble C, Grethe JS, Heringa J, ’t Hoen PAC, Hooft R, Kuhn T, Kok R, Kok J, Lusher SJ, Martone ME, Mons A, Packer AL, Persson B, Rocca-Serra P, Roos M, van Schaik R, Sansone S-A, Schultes E, Sengstag T, Slater T, Strawn G, Swertz MA, Thompson M, van der Lei J, van Mulligen E, Velterop J, Waagmeester A, Wittenburg P, Wolstencroft K, Zhao J, Mons B (2016) The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data, 3, 160018. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.18 | Contextualising samples: Supporting reference genomes of European biodiversity through sample and associated metadata collection | Astrid Böhne, Rosa Fernández, Jennifer A. Leonard, Ann M. McCartney, Seanna McTaggart, José Melo-Ferreira, Rita Monteiro, Rebekah A. Oomen, Olga Vinnere Pettersson, Torsten H. Struck | <p>The European Reference Genome Atlas (ERGA) consortium aims to generate a reference genome catalogue for all of Europe's eukaryotic biodiversity. The biological material underlying this mission, the specimens and their derived samples, are provi... |  | ERGA, ERGA BGE, ERGA Pilot, Evolutionary genomics | Francois Sabot | Julian Osuji, Francois Sabot, Anonymous | 2023-07-03 10:39:36 | View |
15 Mar 2024
Convergent origin and accelerated evolution of vesicle-associated RhoGAP proteins in two unrelated parasitoid waspsDominique Colinet, Fanny Cavigliasso, Matthieu Leobold, Appoline Pichon, Serge Urbach, Dominique Cazes, Marine Poullet, Maya Belghazi, Anne-Nathalie Volkoff, Jean-Michel Drezen, Jean-Luc Gatti, and Marylène Poirié https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.05.543686Using transcriptomics and proteomics to understand the expansion of a secreted poisonous armoury in parasitoid wasps genomesRecommended by Ignacio Bravo based on reviews by Inacio Azevedo and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Inacio Azevedo and 2 anonymous reviewers
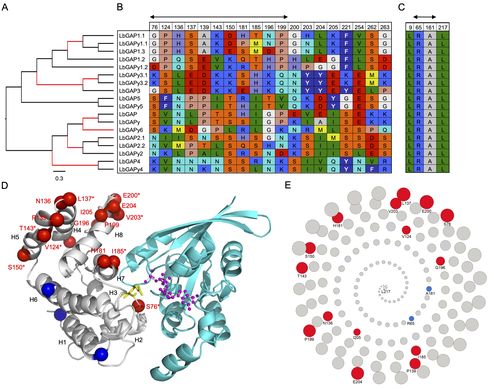
Parasitoid wasps lay their eggs inside another arthropod, whose body is physically consumed by the parasitoid larvae. Phylogenetic inference suggests that Parasitoida are monophyletic, and that this clade underwent a strong radiation shortly after branching off from the Apocrita stem, some 236 million years ago (Peters et al. 2017). The increase in taxonomic diversity during evolutionary radiations is usually concurrent with an increase in genetic/genomic diversity, and is often associated with an increase in phenotypic diversity. Gene (or genome) duplication provides the evolutionary potential for such increase of genomic diversity by neo/subfunctionalisation of one of the gene paralogs, and is often proposed to be related to evolutionary radiations (Ohno 1970; Francino 2005).
References
| Convergent origin and accelerated evolution of vesicle-associated RhoGAP proteins in two unrelated parasitoid wasps | Dominique Colinet, Fanny Cavigliasso, Matthieu Leobold, Appoline Pichon, Serge Urbach, Dominique Cazes, Marine Poullet, Maya Belghazi, Anne-Nathalie Volkoff, Jean-Michel Drezen, Jean-Luc Gatti, and Marylène Poirié | <p>Animal venoms and other protein-based secretions that perform a variety of functions, from predation to defense, are highly complex cocktails of bioactive compounds. Gene duplication, accompanied by modification of the expression and/or functio... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Ignacio Bravo | 2023-06-12 11:08:31 | View | |
11 Sep 2023
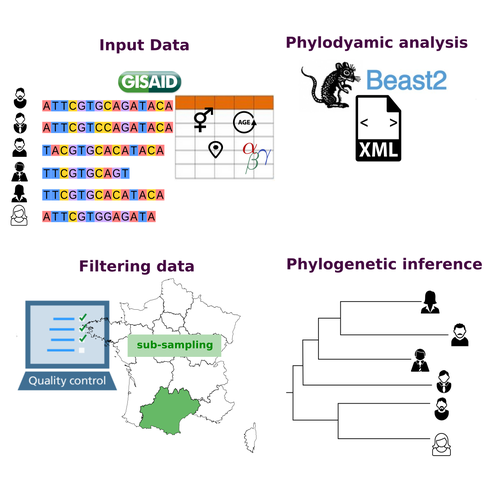
COVFlow: phylodynamics analyses of viruses from selected SARS-CoV-2 genome sequencesGonché Danesh, Corentin Boennec, Laura Verdurme, Mathilde Roussel, Sabine Trombert-Paolantoni, Benoit Visseaux, Stephanie Haim-Boukobza, Samuel Alizon https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.17.496544A pipeline to select SARS-CoV-2 sequences for reliable phylodynamic analysesRecommended by Emmanuelle Lerat based on reviews by Gabriel Wallau and Bastien BoussauPhylodynamic approaches enable viral genetic variation to be tracked over time, providing insight into pathogen phylogenetic relationships and epidemiological dynamics. These are important methods for monitoring viral spread, and identifying important parameters such as transmission rate, geographic origin and duration of infection [1]. This knowledge makes it possible to adjust public health measures in real-time and was important in the case of the COVID-19 pandemic [2]. However, these approaches can be complicated to use when combining a very large number of sequences. This was particularly true during the COVID-19 pandemic, when sequencing data representing millions of entire viral genomes was generated, with associated metadata enabling their precise identification. Danesh et al. [3] present a bioinformatics pipeline, CovFlow, for selecting relevant sequences according to user-defined criteria to produce files that can be used directly for phylodynamic analyses. The selection of sequences first involves a quality filter on the size of the sequences and the absence of unresolved bases before being able to make choices based on the associated metadata. Once the sequences are selected, they are aligned and a time-scaled phylogenetic tree is inferred. An output file in a format directly usable by BEAST 2 [4] is finally generated. To illustrate the use of the pipeline, Danesh et al. [3] present an analysis of the Delta variant in two regions of France. They observed a delay in the start of the epidemic depending on the region. In addition, they identified genetic variation linked to the start of the school year and the extension of vaccination, as well as the arrival of a new variant. This tool will be of major interest to researchers analysing SARS-CoV-2 sequencing data, and a number of future developments are planned by the authors. References [1] Baele G, Dellicour S, Suchard MA, Lemey P, Vrancken B. 2018. Recent advances in computational phylodynamics. Curr Opin Virol. 31:24-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2018.08.009 [2] Attwood SW, Hill SC, Aanensen DM, Connor TR, Pybus OG. 2022. Phylogenetic and phylodynamic approaches to understanding and combating the early SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Nat Rev Genet. 23:547-562. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-022-00483-8 [3] Danesh G, Boennec C, Verdurme L, Roussel M, Trombert-Paolantoni S, Visseaux B, Haim-Boukobza S, Alizon S. 2023. COVFlow: phylodynamics analyses of viruses from selected SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences. bioRxiv, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.17.496544 [4] Bouckaert R, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu C-H et al. 2014. BEAST 2: a software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput Biol 10: e1003537. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003537 | COVFlow: phylodynamics analyses of viruses from selected SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences | Gonché Danesh, Corentin Boennec, Laura Verdurme, Mathilde Roussel, Sabine Trombert-Paolantoni, Benoit Visseaux, Stephanie Haim-Boukobza, Samuel Alizon | <p style="text-align: justify;">Phylodynamic analyses generate important and timely data to optimise public health response to SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks and epidemics. However, their implementation is hampered by the massive amount of sequence data and... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics | Emmanuelle Lerat | 2022-12-12 09:04:01 | View | |
18 Jul 2022
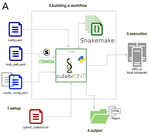
CulebrONT: a streamlined long reads multi-assembler pipeline for prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomesJulie Orjuela, Aurore Comte, Sébastien Ravel, Florian Charriat, Tram Vi, Francois Sabot, Sébastien Cunnac https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.19.452922A flexible and reproducible pipeline for long-read assembly and evaluationRecommended by Raúl Castanera based on reviews by Benjamin Istace and Valentine MurigneuxThird-generation sequencing has revolutionised de novo genome assembly. Thanks to this technology, genome reference sequences have evolved from fragmented drafts to gapless, telomere-to-telomere genome assemblies. Long reads produced by Oxford Nanopore and PacBio technologies can span structural variants and resolve complex repetitive regions such as centromeres, unlocking previously inaccessible genomic information. Nowadays, many research groups can afford to sequence the genome of their working model using long reads. Nevertheless, genome assembly poses a significant computational challenge. Read length, quality, coverage and genomic features such as repeat content can affect assembly contiguity, accuracy, and completeness in almost unpredictable ways. Consequently, there is no best universal software or protocol for this task. Producing a high-quality assembly requires chaining several tools into pipelines and performing extensive comparisons between the assemblies obtained by different tool combinations to decide which one is the best. This task can be extremely challenging, as the number of tools available rises very rapidly, and thorough benchmarks cannot be updated and published at such a fast pace. In their paper, Orjuela and collaborators present CulebrONT [1], a universal pipeline that greatly contributes to overcoming these challenges and facilitates long-read genome assembly for all taxonomic groups. CulebrONT incorporates six commonly used assemblers and allows to perform assembly, circularization (if needed), polishing, and evaluation in a simple framework. One important aspect of CulebrONT is its modularity, which allows the activation or deactivation of specific tools, giving great flexibility to the user. Nevertheless, possibly the best feature of CulebrONT is the opportunity to benchmark the selected tool combinations based on the excellent report generated by the pipeline. This HTML report aggregates the output of several tools for quality evaluation of the assemblies (e.g. BUSCO [2] or QUAST [3]) generated by the different assemblers, in addition to the running time and configuration parameters. Such information is of great help to identify the best-suited pipeline, as exemplified by the authors using four datasets of different taxonomic origins. Finally, CulebrONT can handle multiple samples in parallel, which makes it a good solution for laboratories looking for multiple assemblies on a large scale. References 1. Orjuela J, Comte A, Ravel S, Charriat F, Vi T, Sabot F, Cunnac S (2022) CulebrONT: a streamlined long reads multi-assembler pipeline for prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. bioRxiv, 2021.07.19.452922, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.19.452922 2. Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics, 31, 3210–3212. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351 3. Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics, 29, 1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086 | CulebrONT: a streamlined long reads multi-assembler pipeline for prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes | Julie Orjuela, Aurore Comte, Sébastien Ravel, Florian Charriat, Tram Vi, Francois Sabot, Sébastien Cunnac | <p style="text-align: justify;">Using long reads provides higher contiguity and better genome assemblies. However, producing such high quality sequences from raw reads requires to chain a growing set of tools, and determining the best workflow is ... |  | Bioinformatics | Raúl Castanera | Valentine Murigneux | 2022-02-22 16:21:25 | View |
09 Aug 2023
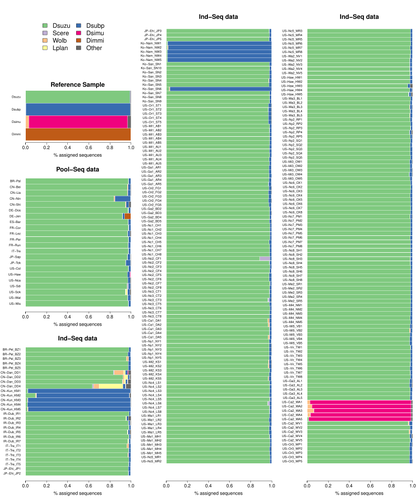
Efficient k-mer based curation of raw sequence data: application in Drosophila suzukiiGautier Mathieu https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.18.537389Decontaminating reads, not contigsRecommended by Nicolas Galtier based on reviews by Marie Cariou and Denis BaurainContamination, the presence of foreign DNA sequences in a sample of interest, is currently a major problem in genomics. Because contamination is often unavoidable at the experimental stage, it is increasingly recognized that the processing of high-throughput sequencing data must include a decontamination step. This is usually performed after the many sequence reads have been assembled into a relatively small number of contigs. Dubious contigs are then discarded based on their composition (e.g. GC-content) or because they are highly similar to a known piece of DNA from a foreign species. Here [1], Mathieu Gautier explores a novel strategy consisting in decontaminating reads, not contigs. Why is this promising? Assembly programs and algorithms are complex, and it is not easy to predict, or monitor, how they handle contaminant reads. Ideally, contaminant reads will be assembled into obvious contaminant contigs. However, there might be more complex situations, such as chimeric contigs with alternating genuine and contaminant segments. Decontaminating at the read level, if possible, should eliminate such unfavorable situations where sequence information from contaminant and target samples are intimately intertwined by an assembler. To achieve this aim, Gautier proposes to use methods initially designed for the analysis of metagenomic data. This is pertinent since the decontamination process involves considering a sample as a mixture of different sources of DNA. The programs used here, CLARK and CLARK-L, are based on so-called k-mer analysis, meaning that the similarity between a read to annotate and a reference sequence is measured by how many sub-sequences (of length 31 base pairs for CLARK and 27 base pairs for CLARK-L) they share. This is notoriously more efficient than traditional sequence alignment algorithms when it comes to comparing a very large number of (most often unrelated) sequences. This is, therefore, a reference-based approach, in which the reads from a sample are assigned to previously sequenced genomes based on k-mer content. This original approach is here specifically applied to the case of Drosophila suzukii, an invasive pest damaging fruit production in Europe and America. Fortunately, Drosophila is a genus of insects with abundant genomic resources, including high-quality reference genomes in dozens of species. Having calibrated and validated his pipeline using data sets of known origins, Gautier quantifies in each of 258 presumed D. suzukii samples the proportion of reads that likely belong to other species of fruit flies, or to fruit fly-associated microbes. This proportion is close to one in 16 samples, which clearly correspond to mis-labelled individuals. It is non-negligible in another ~10 samples, which really correspond to D. suzukii individuals. Most of these reads of unexpected origin are contaminants and should be filtered out. Interestingly, one D. suzukii sample contains a substantial proportion of reads from the closely related D. subpulchera, which might instead reflect a recent episode of gene flow between these two species. The approach, therefore, not only serves as a crucial technical step, but also has the potential to reveal biological processes. Gautier's thorough, well-documented work will clearly benefit the ongoing and future research on D. suzuki, and Drosophila genomics in general. The author and reviewers rightfully note that, like any reference-based approach, this method is heavily dependent on the availability and quality of reference genomes - Drosophila being a favorable case. Building the reference database is a key step, and the interpretation of the output can only be made in the light of its content and gaps, as illustrated by Gautier's careful and detailed discussion of his numerous results. This pioneering study is a striking demonstration of the potential of metagenomic methods for the decontamination of high-throughput sequence data at the read level. The pipeline requires remarkably few computing resources, ensuring low carbon emission. I am looking forward to seeing it applied to a wide range of taxa and samples.
Reference [1] Gautier Mathieu. Efficient k-mer based curation of raw sequence data: application in Drosophila suzukii. bioRxiv, 2023.04.18.537389, ver. 2, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.18.537389 | Efficient k-mer based curation of raw sequence data: application in *Drosophila suzukii* | Gautier Mathieu | <p>Several studies have highlighted the presence of contaminated entries in public sequence repositories, calling for special attention to the associated metadata. Here, we propose and evaluate a fast and efficient kmer-based approach to assess th... |  | Bioinformatics, Population genomics | Nicolas Galtier | 2023-04-20 22:05:13 | View | |
15 Sep 2022
EukProt: A database of genome-scale predicted proteins across the diversity of eukaryotesDaniel J. Richter, Cédric Berney, Jürgen F. H. Strassert, Yu-Ping Poh, Emily K. Herman, Sergio A. Muñoz-Gómez, Jeremy G. Wideman, Fabien Burki, Colomban de Vargas https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.30.180687EukProt enables reproducible Eukaryota-wide protein sequence analysesRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Comparative genomics is a general approach for understanding how genomes differ, which can be considered from many angles. For instance, this approach can delineate how gene content varies across organisms, which can lead to novel hypotheses regarding what those organisms do. It also enables investigations into the sequence-level divergence of orthologous DNA, which can provide insight into how evolutionary forces differentially shape genome content and structure across lineages. Burki F, Roger AJ, Brown MW, Simpson AGB (2020) The New Tree of Eukaryotes. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35, 43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2019.08.008 Richter DJ, Berney C, Strassert JFH, Poh Y-P, Herman EK, Muñoz-Gómez SA, Wideman JG, Burki F, Vargas C de (2022) EukProt: A database of genome-scale predicted proteins across the diversity of eukaryotes. bioRxiv, 2020.06.30.180687, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.30.180687 Wilkinson MD, Dumontier M, Aalbersberg IjJ, Appleton G, Axton M, Baak A, Blomberg N, Boiten J-W, da Silva Santos LB, Bourne PE, Bouwman J, Brookes AJ, Clark T, Crosas M, Dillo I, Dumon O, Edmunds S, Evelo CT, Finkers R, Gonzalez-Beltran A, Gray AJG, Groth P, Goble C, Grethe JS, Heringa J, ’t Hoen PAC, Hooft R, Kuhn T, Kok R, Kok J, Lusher SJ, Martone ME, Mons A, Packer AL, Persson B, Rocca-Serra P, Roos M, van Schaik R, Sansone S-A, Schultes E, Sengstag T, Slater T, Strawn G, Swertz MA, Thompson M, van der Lei J, van Mulligen E, Velterop J, Waagmeester A, Wittenburg P, Wolstencroft K, Zhao J, Mons B (2016) The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data, 3, 160018. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.18 | EukProt: A database of genome-scale predicted proteins across the diversity of eukaryotes | Daniel J. Richter, Cédric Berney, Jürgen F. H. Strassert, Yu-Ping Poh, Emily K. Herman, Sergio A. Muñoz-Gómez, Jeremy G. Wideman, Fabien Burki, Colomban de Vargas | <p style="text-align: justify;">EukProt is a database of published and publicly available predicted protein sets selected to represent the breadth of eukaryotic diversity, currently including 993 species from all major supergroups as well as orpha... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics | Gavin Douglas | 2022-06-08 14:19:28 | View | |
06 Apr 2021
Evidence for shared ancestry between Actinobacteria and Firmicutes bacteriophagesMatthew Koert, Júlia López-Pérez, Courtney Mattson, Steven M. Caruso, Ivan Erill https://doi.org/10.1101/842583Viruses of bacteria: phages evolution across phylum boundariesRecommended by Denis Tagu based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersBacteria and phages have coexisted and coevolved for a long time. Phages are bacteria-infecting viruses, with a symbiotic status sensu lato, meaning they can be pathogenic, commensal or mutualistic. Thus, the association between bacteria phages has probably played a key role in the high adaptability of bacteria to most - if not all – of Earth’s ecosystems, including other living organisms (such as eukaryotes), and also regulate bacterial community size (for instance during bacterial blooms). As genetic entities, phages are submitted to mutations and natural selection, which changes their DNA sequence. Therefore, comparative genomic analyses of contemporary phages can be useful to understand their evolutionary dynamics. International initiatives such as SEA-PHAGES have started to tackle the issue of history of phage-bacteria interactions and to describe the dynamics of the co-evolution between bacterial hosts and their associated viruses. Indeed, the understanding of this cross-talk has many potential implications in terms of health and agriculture, among others. The work of Koert et al. (2021) deals with one of the largest groups of bacteria (Actinobacteria), which are Gram-positive bacteria mainly found in soil and water. Some soil-born Actinobacteria develop filamentous structures reminiscent of the mycelium of eukaryotic fungi. In this study, the authors focused on the Streptomyces clade, a large genus of Actinobacteria colonized by phages known for their high level of genetic diversity. The authors tested the hypothesis that large exchanges of genetic material occurred between Streptomyces and diverse phages associated with bacterial hosts. Using public datasets, their comparative phylogenomic analyses identified a new cluster among Actinobacteria–infecting phages closely related to phages of Firmicutes. Moreover, the GC content and codon-usage biases of this group of phages of Actinobacteria are similar to those of Firmicutes. This work demonstrates for the first time the transfer of a bacteriophage lineage from one bacterial phylum to another one. The results presented here suggest that the age of the described transfer is probably recent since several genomic characteristics of the phage are not fully adapted to their new hosts. However, the frequency of such transfer events remains an open question. If frequent, such exchanges would mean that pools of bacteriophages are regularly fueled by genetic material coming from external sources, which would have important implications for the co-evolutionary dynamics of phages and bacteria. References Koert, M., López-Pérez, J., Courtney Mattson, C., Caruso, S. and Erill, I. (2021) Evidence for shared ancestry between Actinobacteria and Firmicutes bacteriophages. bioRxiv, 842583, version 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Genomics. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/842583 | Evidence for shared ancestry between Actinobacteria and Firmicutes bacteriophages | Matthew Koert, Júlia López-Pérez, Courtney Mattson, Steven M. Caruso, Ivan Erill | <p>Bacteriophages typically infect a small set of related bacterial strains. The transfer of bacteriophages between more distant clades of bacteria has often been postulated, but remains mostly unaddressed. In this work we leverage the sequencing ... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Denis Tagu | 2019-12-10 15:26:31 | View | |
01 May 2024
Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of lifeCristóbal Uribe, Mariana F. Nery, Kattina Zavala, Gonzalo A. Mardones, Gonzalo Riadi & Juan C. Opazo https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.06.15.545160v8Positive selection acted upon cetacean ion channels during the aquatic transitionRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
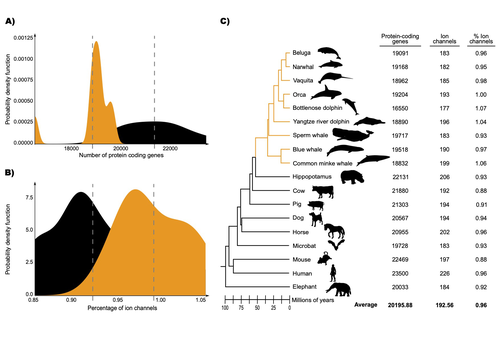
The transition of cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) from terrestrial to aquatic lifestyles is a striking example of natural selection driving major phenotypic changes (Figure 1). For instance, cetaceans have evolved the ability to withstand high pressure and to store oxygen for long periods, among other adaptations (Das et al. 2023). Many phenotypic changes, such as shifts in organ structure, have been well-characterized through fossils (Thewissen et al. 2009). Although such phenotypic transitions are now well understood, we have only a partial understanding of the underlying genetic mechanisms. Scanning for signatures of adaptation in genes related to phenotypes of interest is one approach to better understand these mechanisms. This was the focus of Uribe and colleagues’ (2024) work, who tested for such signatures across cetacean protein-coding genes.
Figure 1: The skeletons of Ambulocetus (an early whale; top) and Pakicetus (the earliest known cetacean, which lived about 50 million years ago; bottom). Copyright: J. G. M. Thewissen. Displayed here with permission from the copyright holder.
The authors were specifically interested in investigating the evolution of ion channels, as these proteins play fundamental roles in physiological processes. An important aspect of their work was to develop a bioinformatic pipeline to identify orthologous ion channel genes across a set of genomes. After applying their bioinformatic workflow to 18 mammalian species (including nine cetaceans), they conducted tests to find out whether these genes showed signatures of positive selection in the cetacean lineage. For many ion channel genes, elevated ratios of non-synonymous to synonymous substitution rates were detected (for at least a subset of sites, and not necessarily the entire coding region of the genes). The genes concerned were enriched for several functions, including heart and nervous system-related phenotypes. One top gene hit among the putatively selected genes was SCN5A, which encodes a sodium channel expressed in the heart. Interestingly, the authors noted a specific amino acid replacement, which is associated with sensitivity to the toxin tetrodotoxin in other lineages. This substitution appears to have occurred in the common ancestor of toothed whales, and then was reversed in the ancestor of bottlenose dolphins. The authors describe known bottlenose dolphin interactions with toxin-producing pufferfish that could result in high tetrodotoxin exposure, and thus perhaps higher selection for tetrodotoxin resistance. Although this observation is intriguing, the authors emphasize it requires experimental confirmation. The authors also recapitulated the previously described observation (Yim et al. 2014; Huelsmann et al. 2019) that cetaceans have fewer protein-coding genes compared to terrestrial mammals, on average. This signal has previously been hypothesized to partially reflect adaptive gene loss. For example, specific gene loss events likely decreased the risk of developing blood clots while diving (Huelsmann et al. 2019). Uribe and colleagues also considered overall gene turnover rate, which encompasses gene copy number variation across lineages, and found the cetacean gene turnover rate to be three times higher than that of terrestrial mammals. Finally, they found that cetaceans have a higher proportion of ion channel genes (relative to all protein-coding genes in a genome) compared to terrestrial mammals. Similar investigations of the relative non-synonymous to synonymous substitution rates across cetacean and terrestrial mammal orthologs have been conducted previously, but these have primarily focused on dolphins as the sole cetacean representative (McGowen et al. 2012; Nery et al. 2013; Sun et al. 2013). These projects have also been conducted across a large proportion of orthologous genes, rather than a subset with a particular function. Performing proteome-wide investigations can be valuable in that they summarize the genome-wide signal, but can suffer from a high multiple testing burden. More generally, investigating a more targeted question, such as the extent of positive selection acting on ion channels in this case, or on genes potentially linked to cetaceans’ increased brain sizes (McGowen et al. 2011) or hypoxia tolerance (Tian et al. 2016), can be easier to interpret, as opposed to summarizing broader signals. However, these smaller-scale studies can also experience a high multiple testing burden, especially as similar tests are conducted across numerous studies, which often is not accounted for (Ioannidis 2005). In addition, integrating signals across the entire genome will ultimately be needed given that many genetic changes undoubtedly underlie cetaceans’ phenotypic diversification. As highlighted by the fact that past genome-wide analyses have produced some differing biological interpretations (McGowen et al. 2012; Nery et al. 2013; Sun et al. 2013), this is not a trivial undertaking. Nonetheless, the work performed in this preprint, and in related research, is valuable for (at least) three reasons. First, although it is a challenging task, a better understanding of the genetic basis of cetacean phenotypes could have benefits for many aspects of cetacean biology, including conservation efforts. In addition, the remarkable phenotypic shifts in cetaceans make the question of what genetic mechanisms underlie these changes intrinsically interesting to a wide audience. Last, since the cetacean fossil record is especially well-documented (Thewissen et al. 2009), cetaceans represent an appealing system to validate and further develop statistical methods for inferring adaptation from genetic data. Uribe and colleagues’ (2024) analyses provide useful insights relevant to each of these points, and have generated intriguing hypotheses for further investigation.
Das K, Sköld H, Lorenz A, Parmentier E (2023) Who are the marine mammals? In: “Marine Mammals: A Deep Dive into the World of Science”. Brennecke D, Knickmeier K, Pawliczka I, Siebert U, Wahlberg, M (editors). Springer, Cham. p. 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06836-2_1 Huelsmann M, Hecker N, Springer MS, Gatesy J, Sharma V, Hiller M (2019) Genes lost during the transition from land to water in cetaceans highlight genomic changes associated with aquatic adaptations. Science Advances, 5, eaaw6671. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw6671 Ioannidis JPA (2005) Why most published research findings are false. PLOS Medicine, 2, e124. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020124 McGowen MR, Montgomery SH, Clark C, Gatesy J (2011) Phylogeny and adaptive evolution of the brain-development gene microcephalin (MCPH1) in cetaceans. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 11, 98. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-98 McGowen MR, Grossman LI, Wildman DE (2012) Dolphin genome provides evidence for adaptive evolution of nervous system genes and a molecular rate slowdown. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279, 3643–3651. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.0869 Nery MF, González DJ, Opazo JC (2013) How to make a dolphin: molecular signature of positive selection in cetacean genome. PLOS ONE, 8, e65491. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065491 Sun YB, Zhou WP, Liu HQ, Irwin DM, Shen YY, Zhang YP (2013) Genome-wide scans for candidate genes involved in the aquatic adaptation of dolphins. Genome Biology and Evolution, 5, 130–139. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evs123 Tian R, Wang Z, Niu X, Zhou K, Xu S, Yang G (2016) Evolutionary genetics of hypoxia tolerance in cetaceans during diving. Genome Biology and Evolution, 8, 827–839. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evw037 Thewissen JGM, Cooper LN, George JC, Bajpai (2009) From land to water: the origin of whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Evolution: Education and Outreach, 2, 272–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12052-009-0135-2 Uribe C, Nery M, Zavala K, Mardones G, Riadi G, Opazo J (2024) Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of life. bioRxiv, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.15.545160 Yim HS, Cho YS, Guang X, Kang SG, Jeong JY, Cha SS, Oh HM, Lee JH, Yang EC, Kwon KK, et al. (2014) Minke whale genome and aquatic adaptation in cetaceans. Nature Genetics, 46, 88–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2835
| Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of life | Cristóbal Uribe, Mariana F. Nery, Kattina Zavala, Gonzalo A. Mardones, Gonzalo Riadi & Juan C. Opazo | <p>Cetaceans could be seen as a natural experiment within the tree of life in which a mammalian lineage changed from terrestrial to aquatic habitats. This shift involved extensive phenotypic modifications, which represent an opportunity to explore... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Gavin Douglas | 2023-07-04 20:53:46 | View | |
14 Sep 2023
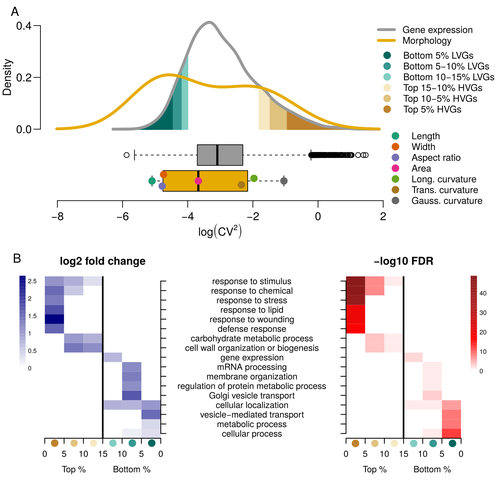
Expression of cell-wall related genes is highly variable and correlates with sepal morphologyDiego A. Hartasánchez, Annamaria Kiss, Virginie Battu, Charline Soraru, Abigail Delgado-Vaquera, Florian Massinon, Marina Brasó-Vives, Corentin Mollier, Marie-Laure Martin-Magniette, Arezki Boudaoud, Françoise Monéger https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.26.489498The same but different: How small scale hidden variations can have large effectsRecommended by Francois Sabot based on reviews by Sandra Corjito and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Sandra Corjito and 1 anonymous reviewer
For ages, we considered only single genes, or just a few, in order to understand the relationship between phenotype and genotype in response to environmental challenges. Recently, the use of meaningful groups of genes, e.g. gene regulatory networks, or modules of co-expression, allowed scientists to have a larger view of gene regulation. However, all these findings were based on contrasted genotypes, e.g. between wild-types and mutants, as the implicit assumption often made is that there is little transcriptomic variability within the same genotype context. Hartasànchez and collaborators (2023) decided to challenge both views: they used a single genotype instead of two, the famous A. thaliana Col0, and numerous plants, and considered whole gene networks related to sepal morphology and its variations. They used a clever approach, combining high-level phenotyping and gene expression to better understand phenomena and regulations underlying sepal morphologies. Using multiple controls, they showed that basic variations in the expression of genes related to the cell wall regulation, as well as the ones involved in chloroplast metabolism, influenced the global transcriptomic pattern observed in sepal while being in near-identical genetic background and controlling for all other experimental conditions. The paper of Hartasànchez et al. is thus a tremendous call for humility in biology, as we saw in their work that we just understand the gross machinery. However, the Devil is in the details: understanding those very small variations that may have a large influence on phenotypes, and thus on local adaptation to environmental challenges, is of great importance in these times of climatic changes. References Hartasánchez DA, Kiss A, Battu V, Soraru C, Delgado-Vaquera A, Massinon F, Brasó-Vives M, Mollier C, Martin-Magniette M-L, Boudaoud A, Monéger F. 2023. Expression of cell-wall related genes is highly variable and correlates with sepal morphology. bioRxiv, ver. 4, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.26.489498 | Expression of cell-wall related genes is highly variable and correlates with sepal morphology | Diego A. Hartasánchez, Annamaria Kiss, Virginie Battu, Charline Soraru, Abigail Delgado-Vaquera, Florian Massinon, Marina Brasó-Vives, Corentin Mollier, Marie-Laure Martin-Magniette, Arezki Boudaoud, Françoise Monéger | <p style="text-align: justify;">Control of organ morphology is a fundamental feature of living organisms. There is, however, observable variation in organ size and shape within a given genotype. Taking the sepal of Arabidopsis as a model, we inves... |  | Bioinformatics, Epigenomics, Plants | Francois Sabot | 2023-03-14 19:10:15 | View | |
07 Oct 2021

Fine-scale quantification of GC-biased gene conversion intensity in mammalsNicolas Galtier https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.05.442789A systematic approach to the study of GC-biased gene conversion in mammalsRecommended by Carina Farah Mugal based on reviews by Fanny Pouyet , David Castellano and 1 anonymous reviewerThe role of GC-biased gene conversion (gBGC) in molecular evolution has interested scientists for the last two decades since its discovery in 1999 (Eyre-Walker 1999; Galtier et al. 2001). gBGC is a process that is associated with meiotic recombination, and is characterized by a transmission distortion in favor of G and C over A and T alleles at GC/AT heterozygous sites that occur in the vicinity of recombination-inducing double-strand breaks (Duret and Galtier 2009; Mugal et al. 2015). This transmission distortion results in a fixation bias of G and C alleles, equivalent to directional selection for G and C (Nagylaki 1983). The fixation bias subsequently leads to a correlation between recombination rate and GC content across the genome, which has served as indirect evidence for the prevalence of gBGC in many organisms. The fixation bias also produces shifts in the allele frequency spectrum (AFS) towards higher frequencies of G and C alleles. These molecular signatures of gBGC provide a means to quantify the strength of gBGC and study its variation among species and across the genome. Following this idea, first Lartillot (2013) and Capra et al. (2013) developed phylogenetic methodology to quantify gBGC based on substitutions, and De Maio et al. (2013) combined information on polymorphism into a phylogenetic setting. Complementary to the phylogenetic methods, later Glemin et al. (2015) developed a method that draws information solely from polymorphism data and the shape of the AFS. Application of these methods to primates (Capra et al. 2013; De Maio et al. 2013; Glemin et al. 2015) and mammals (Lartillot 2013) supported the notion that variation in the strength of gBGC across the genome reflects the dynamics of the recombination landscape, while variation among species correlates with proxies of the effective population size. However, application of the polymorphism-based method by Glemin et al. (2015) to distantly related Metazoa did not confirm the correlation with effective population size (Galtier et al. 2018). Here, Galtier (2021) introduces a novel phylogenetic approach applicable to the study of closely related species. Specifically, Galtier introduces a statistical framework that enables the systematic study of variation in the strength of gBGC among species and among genes. In addition, Galtier assesses fine-scale variation of gBGC across the genome by means of spatial autocorrelation analysis. This puts Galtier in a position to study variation in the strength of gBGC at three different scales, i) among species, ii) among genes, and iii) within genes. Galtier applies his method to four families of mammals, Hominidae, Cercopithecidae, Bovidae, and Muridae and provides a thorough discussion of his findings and methodology. Galtier found that the strength of gBGC correlates with proxies of the effective population size (Ne), but that the slope of the relationship differs among the four families of mammals. Given the relationship between the population-scaled strength of gBGC B = 4Neb, this finding suggests that the conversion bias (b) could vary among mammalian species. Variation in b could either result from differences in the strength of the transmission distortion (Galtier et al. 2018) or evolutionary changes in the rate of recombination (Boman et al. 2021). Alternatively, Galtier suggests that also systematic variation in proxies of Ne could lead to similar observations. Finally, the present study reports intriguing inter-species differences between the extent of variation in the strength of gBGC among and within genes, which are interpreted in consideration of the recombination dynamics in mammals. References Boman J, Mugal CF, Backström N (2021) The Effects of GC-Biased Gene Conversion on Patterns of Genetic Diversity among and across Butterfly Genomes. Genome Biology and Evolution, 13. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evab064 Capra JA, Hubisz MJ, Kostka D, Pollard KS, Siepel A (2013) A Model-Based Analysis of GC-Biased Gene Conversion in the Human and Chimpanzee Genomes. PLOS Genetics, 9, e1003684. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003684 De Maio N, Schlötterer C, Kosiol C (2013) Linking Great Apes Genome Evolution across Time Scales Using Polymorphism-Aware Phylogenetic Models. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2249–2262. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst131 Duret L, Galtier N (2009) Biased Gene Conversion and the Evolution of Mammalian Genomic Landscapes. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics, 10, 285–311. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-082908-150001 Eyre-Walker A (1999) Evidence of Selection on Silent Site Base Composition in Mammals: Potential Implications for the Evolution of Isochores and Junk DNA. Genetics, 152, 675–683. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/152.2.675 Galtier N (2021) Fine-scale quantification of GC-biased gene conversion intensity in mammals. bioRxiv, 2021.05.05.442789, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.05.442789 Galtier N, Piganeau G, Mouchiroud D, Duret L (2001) GC-Content Evolution in Mammalian Genomes: The Biased Gene Conversion Hypothesis. Genetics, 159, 907–911. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/159.2.907 Galtier N, Roux C, Rousselle M, Romiguier J, Figuet E, Glémin S, Bierne N, Duret L (2018) Codon Usage Bias in Animals: Disentangling the Effects of Natural Selection, Effective Population Size, and GC-Biased Gene Conversion. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35, 1092–1103. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy015 Glémin S, Arndt PF, Messer PW, Petrov D, Galtier N, Duret L (2015) Quantification of GC-biased gene conversion in the human genome. Genome Research, 25, 1215–1228. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.185488.114 Lartillot N (2013) Phylogenetic Patterns of GC-Biased Gene Conversion in Placental Mammals and the Evolutionary Dynamics of Recombination Landscapes. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 489–502. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss239 Mugal CF, Weber CC, Ellegren H (2015) GC-biased gene conversion links the recombination landscape and demography to genomic base composition. BioEssays, 37, 1317–1326. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201500058 Nagylaki T (1983) Evolution of a finite population under gene conversion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 80, 6278–6281. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.80.20.6278 | Fine-scale quantification of GC-biased gene conversion intensity in mammals | Nicolas Galtier | <p style="text-align: justify;">GC-biased gene conversion (gBGC) is a molecular evolutionary force that favours GC over AT alleles irrespective of their fitness effect. Quantifying the variation in time and across genomes of its intensity is key t... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Population genomics, Vertebrates | Carina Farah Mugal | 2021-05-25 09:25:52 | View |











