Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture▲ | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
07 Sep 2023
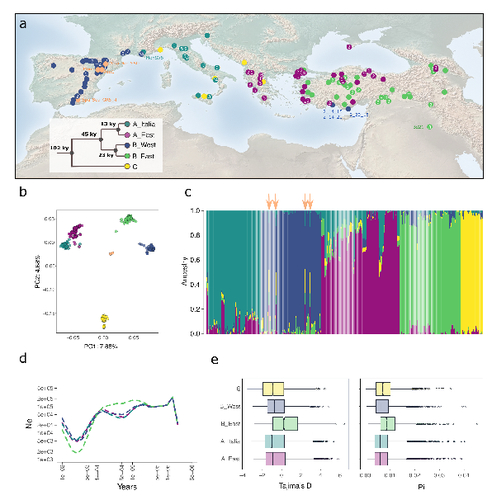
The demographic history of the wild crop relative Brachypodium distachyon is shaped by distinct past and present ecological nichesNikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.01.543285Natural variation and adaptation in Brachypodium distachyonRecommended by Josep Casacuberta based on reviews by Thibault Leroy and 1 anonymous reviewerIdentifying the genetic factors that allow plant adaptation is a major scientific question that is particularly relevant in the face of the climate change that we are already experiencing. To address this, it is essential to have genetic information on a high number of accessions (i.e., plants registered with unique accession numbers) growing under contrasting environmental conditions. There is already an important number of studies addressing these issues in the plant Arabidopsis thaliana, but there is a need to expand these analyses to species that play key roles in wild ecosystems and are close to very relevant crops, as is the case of grasses. The work of Minadakis, Roulin and co-workers (1) presents a Brachypodium distachyon panel of 332 fully sequences accessions that covers the whole species distribution across a wide range of bioclimatic conditions, which will be an invaluable tool to fill this gap. In addition, the authors use this data to start analyzing the population structure and demographic history of this plant, suggesting that the species experienced a shift of its distribution following the Last Glacial Maximum, which may have forced the species into new habitats. The authors also present a modeling of the niches occupied by B. distachyon together with an analysis of the genetic clades found in each of them, and start analyzing the different adaptive loci that may have allowed the species’ expansion into different bioclimatic areas. In addition to the importance of the resources made available by the authors for the scientific community, the analyses presented are well done and carefully discussed, and they highlight the potential of these new resources to investigate the genetic bases of plant adaptation. References 1. Nikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin. The demographic history of the wild crop relative Brachypodium distachyon is shaped by distinct past and present ecological niches. bioRxiv, 2023.06.01.543285, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.01.543285 | The demographic history of the wild crop relative *Brachypodium distachyon* is shaped by distinct past and present ecological niches | Nikolaos Minadakis, Hefin Williams, Robert Horvath, Danka Caković, Christoph Stritt, Michael Thieme, Yann Bourgeois, Anne C. Roulin | <p style="text-align: justify;">Closely related to economically important crops, the grass <em>Brachypodium distachyon</em> has been originally established as a pivotal species for grass genomics but more recently flourished as a model for develop... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Functional genomics, Plants, Population genomics | Josep Casacuberta | 2023-06-14 15:28:30 | View | |
23 Aug 2022

A novel lineage of the Capra genus discovered in the Taurus Mountains of Turkey using ancient genomicsKevin G. Daly, Benjamin S. Arbuckle, Conor Rossi, Valeria Mattiangeli, Phoebe A. Lawlor, Marjan Mashkour, Eberhard Sauer, Joséphine Lesur, Levent Atici, Cevdet Merih Erek, Daniel G. Bradley https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.08.487619Goat ancient DNA analysis unveils a new lineage that may have hybridized with domestic goatsRecommended by Laura Botigué based on reviews by Torsten Günther and 1 anonymous reviewerThe genomic analysis of ancient remains has revolutionized the study of the past over the last decade. On top of the discoveries related to human evolution, plant and animal archaeogenomics has been used to gain new insights into the domestication process and the dispersal of domestic forms. In this study, Daly and colleagues analyse the genomic data from seven goat specimens from the Epipalaeolithic recovered from the Direkli Cave in the Taurus Mountains in southern Turkey. They also generate new genomic data from Capra lineages across the phylogeny, contributing to the availability of genomic resources for this genus. Analysis of the ancient remains is compared to modern genomic variability and sheds light on the complexity of the Tur wild Capra lineages and their relationship with domestic goats and their wild ancestors. Authors find that during the Late Pleistocene in the Taurus Mountains wild goats from the Tur lineage, today restricted to the Caucasus region, were not rare and cohabited with Bezoar, the wild goats that are the ancestors of domestic goats. They identify the Direkli Cave specimens as a lineage separate from the A modified D statistic, Dex, is developed to examine the contribution of the ancient Tur lineage in domestic goats through time and space. Dex measures the relative degree of allele sharing, derived specifically in a selected genome or group of genomes, and may have some utility in genera with complex admixture histories or admixture from ghost lineages. Results confirm that Neolithic European goat had an excess of allele sharing with this ancient Tur lineage, something that is absent in contemporary goats eastwards or in modern goats. Interspecific gene flow is not uncommon among mammals, but the case of Capra has the additional motivation of understanding the origins of the domestic species. This work uncovers an ancient Tur lineage that is different from the modern ones and is additionally found in another geographic area. Furthermore, evidence shows that this ancient lineage exhibits substantial amounts of allele sharing with the wild ancestor of the domestic goat, but also with the Neolithic Eurasian domestic goats, highlighting the complexity of the domestication process. This work has also important implications in understanding the effect of over-hunting and habitat disruption during the Anthropocene on the evolution of the Capra genus. The availability of more ancient specimens and better coverage of the modern genomic variability can help quantifying the lineages that went lost and identify the causes of their extinction. This work is limited by the current availability of whole genomes from modern Capra specimens, but pieces of evidence as well that an effort is needed to obtain more genomic data from ancient goats from different geographic ranges to determine to what extent these lineages contributed to goat domestication. References Daly KG, Arbuckle BS, Rossi C, Mattiangeli V, Lawlor PA, Mashkour M, Sauer E, Lesur J, Atici L, Cevdet CM and Bradley DG (2022) A novel lineage of the Capra genus discovered in the Taurus Mountains of Turkey using ancient genomics. bioRxiv, 2022.04.08.487619, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.08.487619 | A novel lineage of the Capra genus discovered in the Taurus Mountains of Turkey using ancient genomics | Kevin G. Daly, Benjamin S. Arbuckle, Conor Rossi, Valeria Mattiangeli, Phoebe A. Lawlor, Marjan Mashkour, Eberhard Sauer, Joséphine Lesur, Levent Atici, Cevdet Merih Erek, Daniel G. Bradley | <p>Direkli Cave, located in the Taurus Mountains of southern Turkey, was occupied by Late Epipaleolithic hunters-gatherers for the seasonal hunting and processing of game including large numbers of wild goats. We report genomic data from new and p... |  | Evolutionary genomics, Population genomics, Vertebrates | Laura Botigué | 2022-04-15 12:05:47 | View | |
11 Sep 2023
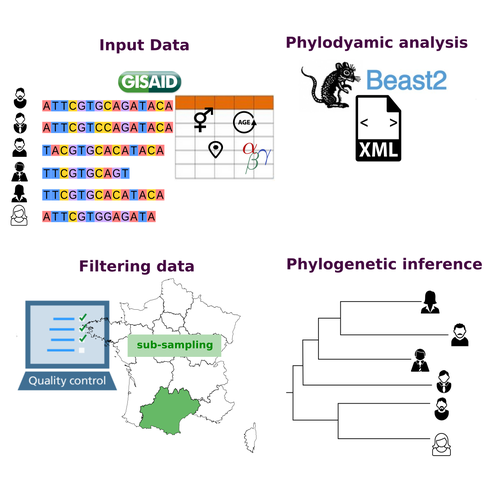
COVFlow: phylodynamics analyses of viruses from selected SARS-CoV-2 genome sequencesGonché Danesh, Corentin Boennec, Laura Verdurme, Mathilde Roussel, Sabine Trombert-Paolantoni, Benoit Visseaux, Stephanie Haim-Boukobza, Samuel Alizon https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.17.496544A pipeline to select SARS-CoV-2 sequences for reliable phylodynamic analysesRecommended by Emmanuelle Lerat based on reviews by Gabriel Wallau and Bastien BoussauPhylodynamic approaches enable viral genetic variation to be tracked over time, providing insight into pathogen phylogenetic relationships and epidemiological dynamics. These are important methods for monitoring viral spread, and identifying important parameters such as transmission rate, geographic origin and duration of infection [1]. This knowledge makes it possible to adjust public health measures in real-time and was important in the case of the COVID-19 pandemic [2]. However, these approaches can be complicated to use when combining a very large number of sequences. This was particularly true during the COVID-19 pandemic, when sequencing data representing millions of entire viral genomes was generated, with associated metadata enabling their precise identification. Danesh et al. [3] present a bioinformatics pipeline, CovFlow, for selecting relevant sequences according to user-defined criteria to produce files that can be used directly for phylodynamic analyses. The selection of sequences first involves a quality filter on the size of the sequences and the absence of unresolved bases before being able to make choices based on the associated metadata. Once the sequences are selected, they are aligned and a time-scaled phylogenetic tree is inferred. An output file in a format directly usable by BEAST 2 [4] is finally generated. To illustrate the use of the pipeline, Danesh et al. [3] present an analysis of the Delta variant in two regions of France. They observed a delay in the start of the epidemic depending on the region. In addition, they identified genetic variation linked to the start of the school year and the extension of vaccination, as well as the arrival of a new variant. This tool will be of major interest to researchers analysing SARS-CoV-2 sequencing data, and a number of future developments are planned by the authors. References [1] Baele G, Dellicour S, Suchard MA, Lemey P, Vrancken B. 2018. Recent advances in computational phylodynamics. Curr Opin Virol. 31:24-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2018.08.009 [2] Attwood SW, Hill SC, Aanensen DM, Connor TR, Pybus OG. 2022. Phylogenetic and phylodynamic approaches to understanding and combating the early SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Nat Rev Genet. 23:547-562. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-022-00483-8 [3] Danesh G, Boennec C, Verdurme L, Roussel M, Trombert-Paolantoni S, Visseaux B, Haim-Boukobza S, Alizon S. 2023. COVFlow: phylodynamics analyses of viruses from selected SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences. bioRxiv, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.17.496544 [4] Bouckaert R, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu C-H et al. 2014. BEAST 2: a software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput Biol 10: e1003537. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003537 | COVFlow: phylodynamics analyses of viruses from selected SARS-CoV-2 genome sequences | Gonché Danesh, Corentin Boennec, Laura Verdurme, Mathilde Roussel, Sabine Trombert-Paolantoni, Benoit Visseaux, Stephanie Haim-Boukobza, Samuel Alizon | <p style="text-align: justify;">Phylodynamic analyses generate important and timely data to optimise public health response to SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks and epidemics. However, their implementation is hampered by the massive amount of sequence data and... |  | Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics | Emmanuelle Lerat | 2022-12-12 09:04:01 | View |










