
MASSART Sebastien
- Laboratory of integrated and urban Phytopathology, Liege University - Gembloux Agro-Bio Tech - TERRA, Gembloux, Belgium
- Bioinformatics, Metagenomics, Viruses and transposable elements
- recommender
Recommendation: 1
Reviews: 0
Recommendation: 1
T7 DNA polymerase treatment improves quantitative sequencing of both double-stranded and single-stranded DNA viruses
Improving the sequencing of single-stranded DNA viruses: Another brick for building Earth's complete virome encyclopedia
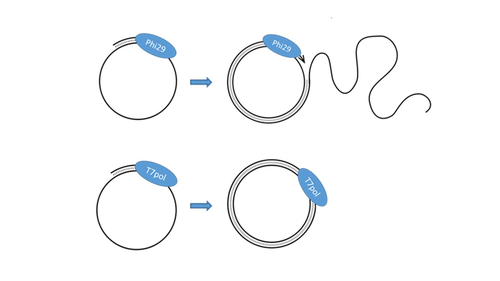
Recommended by Sebastien Massart based on reviews by Philippe Roumagnac and 3 anonymous reviewersThe wide adoption of high-throughput sequencing technologies has uncovered an astonishing diversity of viruses in most biosphere habitats. Among them, single-stranded DNA viruses are prevalent, infecting diverse hosts from all three domains of life (Malathi et al. 2014) with some species being highly pathogenic to animals or plants.
Sequencing of single-stranded DNA viruses requires a specific approach that usually leads to their over-representation compared to double-stranded DNA. The article from Billaud et al. (2024) addresses this challenge. It presents a novel and efficient method for converting single-stranded DNA to double-stranded DNA using T7 DNA polymerase before high-throughput virome sequencing. It compares this new method with the Phi29 polymerase method, demonstrating its advantages in the representation and accuracy of viral DNA content in well-defined synthetic phage mixtures and complex human virome samples from the stool. This T7 DNA polymerase treatment significantly improved the richness and abundance of the Microviridae fraction in their samples, suggesting a more comprehensive representation of viral diversity.
The article presents a compelling case for testing and adopting the T7 DNA polymerase methodology in preparing virome samples for shotgun sequencing. This novel approach, supported by comparative analysis with existing methodologies, represents a valuable contribution to metagenomics for characterizing virome diversity.
References
Billaud M, Theodorou I, Lamy-Besnier Q, Shah SA, Lecointe F, Sordi LD, Paepe MD, Petit M-A (2024) T7 DNA polymerase treatment improves quantitative sequencing of both double-stranded and single-stranded DNA viruses. bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.12.520144
Malathi VG, Renuka Devi P. (2019) ssDNA viruses: key players in global virome. Virus disease. 30: 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-019-00519-4