
WANG Sishuo
- Department of Microbiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
- Bacteria and archaea, Bioinformatics, Evolutionary genomics
- recommender
Recommendation: 1
Review: 1
Recommendation: 1

A Comprehensive Resource for Exploring Antiphage Defense: DefenseFinder Webservice, Wiki and Databases
DefenseFinder update advances prokaryotic antiviral system research
Recommended by Sishuo Wang based on reviews by Pierre Pontarotti , Pedro Leão and 1 anonymous reviewerProkaryotic antiviral systems, such as CRISPR-Cas and restriction-modification systems, provide defense against viruses through diverse mechanisms including intracellular signaling, chemical defense, and nucleotide depletion. However, bioinformatic tools and resources for identifying and cataloging these systems are still in development. The work by Tesson and colleagues (2024) presents a significant advancement in understanding the defense systems of prokaryotes. The authors have provided an update of their previously developed online service DefenseFinder, which helps to detect known antiviral systems in prokaryotes genomes (Tesson et al. 2022), plus three new databases: one serving as a wiki for defense systems, one housing experimentally determined and AlphaFold2-predicted structures, and a third one consisting of precomputed results from DefenseFinder. Users can analyze their own data through the user-friendly interface. This initiative will help promote a community-driven approach to sharing knowledge on antiphage systems, which is very useful given their complexity and diversity. The authors' commitment to maintaining an up-to-date platform and encouraging community contributions makes this resource accessible to both newcomers and experienced researchers in the rapidly growing field of defense system research. Experienced researchers will find that there are ways to contribute to the future expansion of these databases, while new users can easily access and use the platform. Overall, the updated DefenseFinder, as well as the other databases introduced in the manuscript, are well-suited for researchers (both dry- and wet-lab ones) interested in antiphage defense. I am hopeful that the efforts by the authors will collectively create valuable online resources for researchers in this field and will foster an environment of open science and accessible bioinformatics tools.
References
Tesson F, Hervé A, Mordret E, Touchon M, d’Humières C, Cury J, Bernheim A (2022) Systematic and quantitative view of the antiviral arsenal of prokaryotes. Nature Communications, 13, 2561. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30269-9
Tesson F, Planel R, Egorov A, Georjon H, Vaysset H, Brancotte B, Néron B, Mordret E, Atkinson G, Bernheim A, Cury J (2024) A comprehensive resource for exploring antiphage defense: DefenseFinder webservice, wiki and databases. bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.01.25.577194
Review: 1
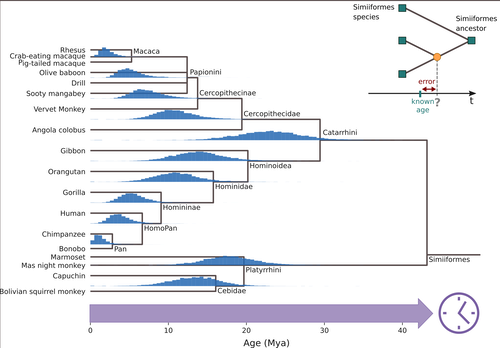
Factors influencing the accuracy and precision in dating single gene trees
Dating single gene trees in the age of phylogenomics
Recommended by Federico Hoffmann based on reviews by Sishuo Wang, David Duchêne and 1 anonymous reviewerDating evolutionary trees is a critical task that allows us to connect biological history to ecological and geological events, helping us explore connections between environmental change and genetic innovations. The central idea behind these techniques is to link changes at the sequence level to divergence times, under the general assumption that substitutions accumulate steadily over time. So, sequences that diverged earlier are expected to be more different than sequences that diverged more recently. For a number of biological and statistical reasons, the relationship between sequence divergence and time is not linear, so it is not always the case that more divergent sequences have accumulated more substitutions than less divergent ones. In the case of organismal-level divergences, a natural approach to mitigate these challenges is to incorporate as many genes as possible into the analyses. However, this route is not available when we are focusing our interest on a single gene or a gene family. Thus, exploring how different features of single gene trees impact the accuracy and precision of divergence time estimates is of interest. In this study, Louvel and Roest Crollius (2024), select a well-studied group of mammals, primates, extract single copy genes from their genomes, and explore how different factors such as alignment size, evolutionary rate variation and discordance between the gene and species trees impact divergence time estimates.
There are many strengths of this study. The central ones are the number of factors considered and the transparent discussion of the limitations. In this regard, the study is an elegant combination of empirical and simulated data. Some of the results match intuitive expectations. For example, the authors find that longer alignments are more informative than shorter ones, that differences in evolutionary rate among branches lead to loss in precision, and that slow-evolving genes perform worse. Intriguingly, they also find differences in performance among genes with different ontologies. The empirical data used in this study is limited to a single group, and generally considers genes that have apparently remained as single copies. Accordingly, the conclusions that can be drawn are somewhat limited, calling for future studies building on and expanding the concepts of the study by Louvel and colleagues. For example, including genes that have been lost or duplicated would be of interest because changes in gene complement are a prevalent source of variation at the genome level in mammals in general (Demuth et al. 2006), and particularly in primates (Hahn et al. 2007).
References
Demuth JP, De Bie T, Stajich JE, Cristianini N, Hahn MW (2006) The evolution of mammalian gene families. PLoS One, e85. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000085
Hahn MW, Demuth JP, Han SG (2007) Accelerated rate of gene gain and loss in primates. Genetics, 177,1941-1949. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.080077
Louvel, G and Roest Crollius, H (2024) Factors influencing the accuracy and precision in dating single gene trees. bioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.24.264671