Latest recommendations

| Id▲ | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
01 May 2024
Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of lifeCristóbal Uribe, Mariana F. Nery, Kattina Zavala, Gonzalo A. Mardones, Gonzalo Riadi & Juan C. Opazo https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.06.15.545160v8Positive selection acted upon cetacean ion channels during the aquatic transitionRecommended by Gavin Douglas based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
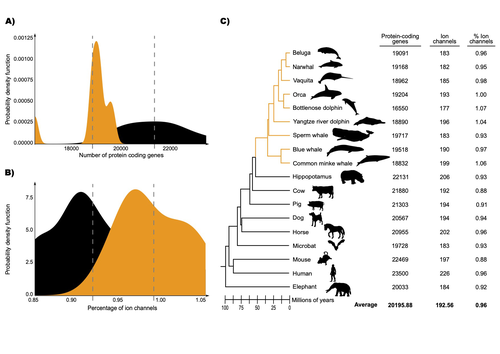
The transition of cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) from terrestrial to aquatic lifestyles is a striking example of natural selection driving major phenotypic changes (Figure 1). For instance, cetaceans have evolved the ability to withstand high pressure and to store oxygen for long periods, among other adaptations (Das et al. 2023). Many phenotypic changes, such as shifts in organ structure, have been well-characterized through fossils (Thewissen et al. 2009). Although such phenotypic transitions are now well understood, we have only a partial understanding of the underlying genetic mechanisms. Scanning for signatures of adaptation in genes related to phenotypes of interest is one approach to better understand these mechanisms. This was the focus of Uribe and colleagues’ (2024) work, who tested for such signatures across cetacean protein-coding genes.
Figure 1: The skeletons of Ambulocetus (an early whale; top) and Pakicetus (the earliest known cetacean, which lived about 50 million years ago; bottom). Copyright: J. G. M. Thewissen. Displayed here with permission from the copyright holder.
The authors were specifically interested in investigating the evolution of ion channels, as these proteins play fundamental roles in physiological processes. An important aspect of their work was to develop a bioinformatic pipeline to identify orthologous ion channel genes across a set of genomes. After applying their bioinformatic workflow to 18 mammalian species (including nine cetaceans), they conducted tests to find out whether these genes showed signatures of positive selection in the cetacean lineage. For many ion channel genes, elevated ratios of non-synonymous to synonymous substitution rates were detected (for at least a subset of sites, and not necessarily the entire coding region of the genes). The genes concerned were enriched for several functions, including heart and nervous system-related phenotypes. One top gene hit among the putatively selected genes was SCN5A, which encodes a sodium channel expressed in the heart. Interestingly, the authors noted a specific amino acid replacement, which is associated with sensitivity to the toxin tetrodotoxin in other lineages. This substitution appears to have occurred in the common ancestor of toothed whales, and then was reversed in the ancestor of bottlenose dolphins. The authors describe known bottlenose dolphin interactions with toxin-producing pufferfish that could result in high tetrodotoxin exposure, and thus perhaps higher selection for tetrodotoxin resistance. Although this observation is intriguing, the authors emphasize it requires experimental confirmation. The authors also recapitulated the previously described observation (Yim et al. 2014; Huelsmann et al. 2019) that cetaceans have fewer protein-coding genes compared to terrestrial mammals, on average. This signal has previously been hypothesized to partially reflect adaptive gene loss. For example, specific gene loss events likely decreased the risk of developing blood clots while diving (Huelsmann et al. 2019). Uribe and colleagues also considered overall gene turnover rate, which encompasses gene copy number variation across lineages, and found the cetacean gene turnover rate to be three times higher than that of terrestrial mammals. Finally, they found that cetaceans have a higher proportion of ion channel genes (relative to all protein-coding genes in a genome) compared to terrestrial mammals. Similar investigations of the relative non-synonymous to synonymous substitution rates across cetacean and terrestrial mammal orthologs have been conducted previously, but these have primarily focused on dolphins as the sole cetacean representative (McGowen et al. 2012; Nery et al. 2013; Sun et al. 2013). These projects have also been conducted across a large proportion of orthologous genes, rather than a subset with a particular function. Performing proteome-wide investigations can be valuable in that they summarize the genome-wide signal, but can suffer from a high multiple testing burden. More generally, investigating a more targeted question, such as the extent of positive selection acting on ion channels in this case, or on genes potentially linked to cetaceans’ increased brain sizes (McGowen et al. 2011) or hypoxia tolerance (Tian et al. 2016), can be easier to interpret, as opposed to summarizing broader signals. However, these smaller-scale studies can also experience a high multiple testing burden, especially as similar tests are conducted across numerous studies, which often is not accounted for (Ioannidis 2005). In addition, integrating signals across the entire genome will ultimately be needed given that many genetic changes undoubtedly underlie cetaceans’ phenotypic diversification. As highlighted by the fact that past genome-wide analyses have produced some differing biological interpretations (McGowen et al. 2012; Nery et al. 2013; Sun et al. 2013), this is not a trivial undertaking. Nonetheless, the work performed in this preprint, and in related research, is valuable for (at least) three reasons. First, although it is a challenging task, a better understanding of the genetic basis of cetacean phenotypes could have benefits for many aspects of cetacean biology, including conservation efforts. In addition, the remarkable phenotypic shifts in cetaceans make the question of what genetic mechanisms underlie these changes intrinsically interesting to a wide audience. Last, since the cetacean fossil record is especially well-documented (Thewissen et al. 2009), cetaceans represent an appealing system to validate and further develop statistical methods for inferring adaptation from genetic data. Uribe and colleagues’ (2024) analyses provide useful insights relevant to each of these points, and have generated intriguing hypotheses for further investigation.
Das, K., Sköld, H., Lorenz, A., Parmentier, E. 2023. Who are the marine mammals? In: “Marine Mammals: A Deep Dive into the World of Science”. Brennecke, D., Knickmeier, K., Pawliczka, I., Siebert, U., Wahlberg, M (editors). Springer, Cham. p. 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06836-2_1 Huelsmann, M., Hecker, N., Springer, M., S., Gatesy, J., Sharma, V., Hiller, M. 2019. Genes lost during the transition from land to water in cetaceans highlight genomic changes associated with aquatic adaptations. Science Advances. 5(9):eaaw6671. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw6671 Ioannidis, J., P., A. 2005. Why most published research findings are false. PLOS Medicine. 2(8):e124. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020124 McGowen MR, Montgomery SH, Clark C, Gatesy J. 2011. Phylogeny and adaptive evolution of the brain-development gene microcephalin (MCPH1) in cetaceans. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 11(1):98. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-98 McGowen MR, Grossman LI, Wildman DE. 2012. Dolphin genome provides evidence for adaptive evolution of nervous system genes and a molecular rate slowdown. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 279(1743):3643–3651. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.0869 Nery, M., F., González, D., J., Opazo, J., C. 2013. How to make a dolphin: molecular signature of positive selection in cetacean genome. PLOS ONE. 8(6):e65491. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065491 Sun, Y.-B., Zhou, W.-P., Liu, H.-Q., Irwin, D., M., Shen, Y.-Y., Zhang, Y.-P. 2013. Genome-wide scans for candidate genes involved in the aquatic adaptation of dolphins. Genome Biology and Evolution. 5(1):130–139. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evs123 Tian, R., Wang, Z., Niu, X., Zhou, K., Xu, S., Yang, G. 2016. Evolutionary genetics of hypoxia tolerance in cetaceans during diving. Genome Biology and Evolution. 8(3):827–839. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evw037 Thewissen, J., G., M., Cooper, L., N., George, J., C., Bajpai, S. 2009. From land to water: the origin of whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Evolution: Education and Outreach. 2(2):272–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12052-009-0135-2 Uribe, C., Nery, M., Zavala, K., Mardones, G., Riadi, G., Opazo, J. 2024. Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of life. bioRxiv, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.15.545160 Yim, H.-S., Cho, Y., S., Guang, X., Kang, S., G., Jeong, J.-Y., Cha, S.-S., Oh, H.-M., Lee, J.-H., Yang, E., C., Kwon, K., K., et al. 2014. Minke whale genome and aquatic adaptation in cetaceans. Nature Genetics. 46(1):88–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2835
| Evolution of ion channels in cetaceans: A natural experiment in the tree of life | Cristóbal Uribe, Mariana F. Nery, Kattina Zavala, Gonzalo A. Mardones, Gonzalo Riadi & Juan C. Opazo | <p>Cetaceans could be seen as a natural experiment within the tree of life in which a mammalian lineage changed from terrestrial to aquatic habitats. This shift involved extensive phenotypic modifications, which represent an opportunity to explore... |  | Evolutionary genomics | Gavin Douglas | 2023-07-04 20:53:46 | View | |
20 Nov 2023
Building a Portuguese Coalition for Biodiversity GenomicsJoão Pedro Marques, Paulo Célio Alves, Isabel R. Amorim, Ricardo J. Lopes, Mónica Moura, Gene Meyers, Manuela Sim-Sim, Carla Sousa-Santos, Maria Judite Alves, Paulo AV Borges, Thomas Brown, Miguel Carneiro, Carlos Carrapato, Luís Ceríaco, Claudio Ciofi, Luís da Silva, Genevieve Diedericks, Maria Angela Diroma, Liliana Farelo, Giulio Formenti, Fátima Gil, Miguel Grilo, Alessio Ianucci, Henrique Leitão, Cristina Máguas, Ann Mc Cartney, Sofia Mendes, João Moreno, Marco Morselli, Alice Mouton, Chiar... https://doi.org/10.32942/X20W3QThe Portuguese genomics community teams up with iconic species to understand the destruction of biodiversityRecommended by Fernando Racimo based on reviews by Svein-Ole Mikalsen and 1 anonymous reviewerThis manuscript describes the ongoing work and plans of Biogenome Portugal: a new network of researchers in the Portuguese biodiversity genomics community. The aims of this network are to jointly train scientists in ecology and evolution, generate new knowledge and understanding of Portuguese biodiversity, and better engage with the public and with international researchers, so as to advance conservation efforts in the region. In collaboration across disciplines and institutions, they are also contributing to the European Reference Genome Atlas (ERGA): a massive scientific effort, seeking to eventually produce reference-quality genomes for all species in the European continent (Mc Cartney et al. 2023). The manuscript centers around six iconic and/or severely threatened species, whose range extends across parts of what is today considered Portuguese territory. Via the Portugal chapter of ERGA (ERGA-Portugal), the researchers will generate high-quality genome sequences from these species. The species are the Iberian hare, the Azores laurel, the Black wheatear, the Portuguese crowberry, the Cave ground beetle and the Iberian minnowcarp. In ignorance of human-made political borders, some of these species also occupy large parts of the rest of the Iberian peninsula, highlighting the importance of transnational collaboration in biodiversity efforts. The researchers extracted samples from members of each of these species, and are building reference genome sequences from them. In some cases, these sequences will also be co-analyzed with additional population genomic data from the same species or genetic data from cohabiting species. The researchers aim to answer a variety of ecological and evolutionary questions using this information, including how genetic diversity is being affected by the destruction of their habitat, and how they are being forced to adapt as a consequence of the climate emergency. The authors did a very good job in providing a justification for the choice of pilot species, a thorough methodological overview of current work, and well thought-out plans for future analyses once the genome sequences are available for study. The authors also describe plans for networking and training activities to foster a well-connected Portuguese biodiversity genomics community. Applying a genomic analysis lens is important for understanding the ever faster process of devastation of our natural world. Governments and corporations around the globe are destroying nature at ever larger scales (Diaz et al. 2019). They are also destabilizing the climatic conditions on which life has existed for thousands of years (Trisos et al. 2020). Thus, genetic diversity is decreasing faster than ever in human history, even when it comes to non-threatened species (Exposito-Alonso et al. 2022), and these decreases are disrupting ecological processes worldwide (Richardson et al. 2023). This, in turn, is threatening the conditions on which the stability of our societies rest (Gardner and Bullock 2021). The efforts of Biogenome Portal and ERGA-Portugal will go a long way in helping us understand in greater detail how this process is unfolding in Portuguese territories.
References Díaz, Sandra, et al. "Pervasive human-driven decline of life on Earth points to the need for transformative change." Science 366.6471 (2019): eaax3100. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax3100 Exposito-Alonso, Moises, et al. "Genetic diversity loss in the Anthropocene." Science 377.6613 (2022): 1431-1435. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abn5642 Gardner, Charlie J., and James M. Bullock. "In the climate emergency, conservation must become survival ecology." Frontiers in Conservation Science 2 (2021): 659912. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcosc.2021.659912 Mc Cartney, Ann M., et al. "The European Reference Genome Atlas: piloting a decentralised approach to equitable biodiversity genomics." bioRxiv (2023): 2023-09, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.32942/X20W3Q Richardson, Katherine, et al. "Earth beyond six of nine planetary boundaries." Science Advances 9.37 (2023): eadh2458. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adh2458 Trisos, Christopher H., Cory Merow, and Alex L. Pigot. "The projected timing of abrupt ecological disruption from climate change." Nature 580.7804 (2020): 496-501. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2189-9 | Building a Portuguese Coalition for Biodiversity Genomics | João Pedro Marques, Paulo Célio Alves, Isabel R. Amorim, Ricardo J. Lopes, Mónica Moura, Gene Meyers, Manuela Sim-Sim, Carla Sousa-Santos, Maria Judite Alves, Paulo AV Borges, Thomas Brown, Miguel Carneiro, Carlos Carrapato, Luís Ceríaco, Claudio ... | <p style="text-align: justify;">The diverse physiography of the Portuguese land and marine territory, spanning from continental Europe to the Atlantic archipelagos, has made it an important repository of biodiversity throughout the Pleistocene gla... |  | ERGA, ERGA Pilot | Fernando Racimo | 2023-07-14 11:24:22 | View | |
06 Feb 2024

The need of decoding life for taking care of biodiversity and the sustainable use of nature in the Anthropocene - a Faroese perspectiveSvein-Ole Mikalsen, Jari í Hjøllum, Ian Salter, Anni Djurhuus, Sunnvør í Kongsstovu https://doi.org/10.32942/X21S4CWhy sequence everything? A raison d’être for the Genome Atlas of Faroese EcologyRecommended by Stephen Richards based on reviews by Tereza Manousaki and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Tereza Manousaki and 1 anonymous reviewer
When discussing the Earth BioGenome Project with scientists and potential funding agencies, one common question is: why sequence everything? Whether sequencing a subset would be more optimal is not an unreasonable question given what we know about the mathematics of importance and Pareto’s 80:20 principle, that 80% of the benefits can come from 20% of the effort. However, one must remember that this principle is an observation made in hindsight and selecting the most effective 20% of experiments is difficult. As an example, few saw great applied value in comparative genomic analysis of the archaea Haloferax mediterranei, but this enabled the discovery of CRISPR/Cas9 technology (1). When discussing whether or not to sequence all life on our planet, smaller countries such as the Faroe Islands are seldom mentioned.
1 Mojica, F. J., Díez-Villaseñor, C. S., García-Martínez, J. & Soria, E. Intervening sequences of regularly spaced prokaryotic repeats derive from foreign genetic elements. J Mol Evol 60, 174-182 (2005). 2 Mikalsen, S-O., Hjøllum, J. í., Salter, I., Djurhuus, A. & Kongsstovu, S. í. The need of decoding life for taking care of biodiversity and the sustainable use of nature in the Anthropocene – a Faroese perspective. EcoEvoRxiv (2024), ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.32942/X21S4C | The need of decoding life for taking care of biodiversity and the sustainable use of nature in the Anthropocene - a Faroese perspective | Svein-Ole Mikalsen, Jari í Hjøllum, Ian Salter, Anni Djurhuus, Sunnvør í Kongsstovu | <p>Biodiversity is under pressure, mainly due to human activities and climate change. At the international policy level, it is now recognised that genetic diversity is an important part of biodiversity. The availability of high-quality reference g... |  | ERGA, ERGA Pilot, Population genomics, Vertebrates | Stephen Richards | 2023-07-31 16:59:33 | View | |
24 Jan 2024

High quality genome assembly of the brown hare (Lepus europaeus) with chromosome-level scaffoldingCraig Michell, Joanna Collins, Pia K. Laine, Zsofia Fekete, Riikka Tapanainen, Jonathan M. D. Wood, Steffi Goffart, Jaakko L. O. Pohjoismaki https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.29.555262A high quality reference genome of the brown hareRecommended by Ed Hollox based on reviews by Merce Montoliu-Nerin and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Merce Montoliu-Nerin and 1 anonymous reviewer
The brown hare, or European hare, Lupus europaeus, is a widespread mammal whose natural range spans western Eurasia. At the northern limit of its range, it hybridises with the mountain hare (L. timidis), and humans have introduced it into other continents. It represents a particularly interesting mammal to study for its population genetics, extensive hybridisation zones, and as an invasive species. This study (Michell et al. 2024) has generated a high-quality assembly of a genome from a brown hare from Finland using long PacBio HiFi sequencing reads and Hi-C scaffolding. The contig N50 of this new genome is 43 Mb, and completeness, assessed using BUSCO, is 96.1%. The assembly comprises 23 autosomes, and an X chromosome and Y chromosome, with many chromosomes including telomeric repeats, indicating the high level of completeness of this assembly. While the genome of the mountain hare has previously been assembled, its assembly was based on a short-read shotgun assembly, with the rabbit as a reference genome. The new high-quality brown hare genome assembly allows a direct comparison with the rabbit genome assembly. For example, the assembly addresses the karyotype difference between the hare (n=24) and the rabbit (n=22). Chromosomes 12 and 17 of the hare are equivalent to chromosome 1 of the rabbit, and chromosomes 13 and 16 of the hare are equivalent to chromosome 2 of the rabbit. The new assembly also provides a hare Y-chromosome, as the previous mountain hare genome was from a female. This new genome assembly provides an important foundation for population genetics and evolutionary studies of lagomorphs. References Michell, C., Collins, J., Laine, P. K., Fekete, Z., Tapanainen, R., Wood, J. M. D., Goffart, S., Pohjoismäki, J. L. O. (2024). High quality genome assembly of the brown hare (Lepus europaeus) with chromosome-level scaffolding. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.29.555262 | High quality genome assembly of the brown hare (*Lepus europaeus*) with chromosome-level scaffolding | Craig Michell, Joanna Collins, Pia K. Laine, Zsofia Fekete, Riikka Tapanainen, Jonathan M. D. Wood, Steffi Goffart, Jaakko L. O. Pohjoismaki | <p style="text-align: justify;">We present here a high-quality genome assembly of the brown hare (Lepus europaeus Pallas), based on a fibroblast cell line of a male specimen from Liperi, Eastern Finland. This brown hare genome represents the first... |  | ERGA Pilot, Vertebrates | Ed Hollox | 2023-10-16 20:46:39 | View |











